Abstract
Polycomb group protein Bmi1 is essential for hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal and terminal differentiation. However, its target genes in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells are largely unknown. We performed gene expression profiling assays and found that genes of the Wnt signaling pathway are significantly elevated in Bmi1 null hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Bmi1 is associated with several genes of the Wnt signaling pathway in hematopoietic cells. Further, we found that Bmi1 represses Wnt gene expression in HSPCs. Importantly, loss of β-catenin, which reduces Wnt activation, partially rescues the HSC self-renewal and differentiation defects seen in the Bmi1 null mice. Thus, we have identified Bmi1 as a novel regulator of Wnt signaling pathway in HSPCs. Given that Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in hematopoiesis, our studies suggest that modulating Wnt signaling may hold potential for enhancing HSC self-renewal, thereby improving the outcomes of HSC transplantation.
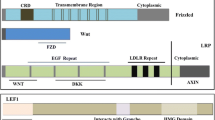
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondo, M., Wagers, A. J., Manz, M. G., Prohaska, S. S., Scherer, D. C., Beilhack, G. F., Shizuru, J. A., & Weissman, I. L. (2003). Biology of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Progenitors: Implications for Clinical Application. Annual Review of Immunology, 21, 759–806.
Attar, E. C., & Scadden, D. T. (2004). Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell growth. Leukemia, 18, 1760–1768.
Akala, O. O., & Clarke, M. F. (2006). Hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 16, 496–501.
Zon, L. I. (2008). Intrinsic and extrinsic control of haematopoietic stem-cell self-renewal. Nature, 453, 306–313.
Walasek, M. A., van Os, R., & de Haan, G. (2012). Hematopoietic stem cell expansion: Challenges and opportunities. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1266, 138–150.
Valk-Lingbeek, M. E., Bruggeman, S. W., & van Lohuizen, M. (2004). Stem cells and cancer; the polycomb connection. Cell, 118, 409–418.
Sparmann, A., & van Lohuizen, M. (2006). Polycomb silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 6, 846–856.
Schuettengruber, B., Chourrout, D., Vervoort, M., Leblanc, B., & Cavalli, G. (2007). Genome Regulation by Polycomb and Trithorax Proteins. Cell, 128, 735–745.
Pietersen, A. M., & van Lohuizen, M. (2008). Stem cell regulation by polycomb repressors: Postponing commitment. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 20, 201–207.
Bracken, A. P., & Helin, K. (2009). Polycomb Group Proteins: Navigators of Lineage Pathways Led Astray in Cancer. Nature Review of Cancer, 9, 773–784.
Simon, J. A., & Kingston, R. E. (2009). Mechanisms of Polycomb Gene Silencing: Knowns and Unknowns. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 10, 697–708.
Sauvageau, M., & Sauvageau, G. (2010). Polycomb Group Proteins: Multi-Faceted Regulators of Somatic Stem Cells and Cancer. Cell Stem Cell, 7, 299–313.
Konuma, T., Oguro, H., & Iwama, A. (2010). Role of the polycomb group proteins in hematopoietic stem cells. Development, Growth & Differentiation, 52, 505–516.
Park, I. K., Qian, D., Kiel, M., Becker, M. W., Pihalja, M., Weissman, I. L., Morrison, S. J., & Clarke, M. F. (2003). Bmi-1 is required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells. Nature, 423, 302–305.
Lessard, J., & Sauvageau, G. (2003). Bmi-1 determines the proliferative capacity of normal and leukaemic stem cells. Nature, 423, 255–260.
Liu, Y., Liu, F., Yu, H., Zhao, X., Sahsida, G., Deblasio, A., Chen, Z., Lin, H.K., Di Giandomenico, S., Elf, S.E., Yang, Y.Y., Miyata, Y., Huang, G., Menendez, S., Mellinghoff, I., Pandolfi, P.P., Hedvat, C.V. and Nimer, S.D. (2012). Akt Phosphorylates the Transcriptional Repressor Bmi1 to Block Its Association with Tumor Suppressing Ink4a-Arf locus. Science Signaling, 5, ra77.
Oguro, H., Yuan, J., Ichikawa, H., Ikawa, T., Yamazaki, S., Kawamoto, H., Nakauchi, H., & Iwama, A. (2010). Poised lineage specification in multipotential hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by the polycomb protein Bmi1. Cell Stem Cell, 6, 279–286.
Gao, R., Chen, S., Kobayashi, M., Yu, H., Young, S. K., Soltis, A., Zhang, Y., Wan, Y., Vemula, S., Fraenkel, E., Cantor, A., Xu, Y., Yoder, M. C., Wek, R., Ellis, S., Kapur, R., Zhu, X., & Liu, Y. (2015). Bmi1 promotes erythroid development through regulating ribosome biogenesis. Stem Cells, 33, 925–938.
Kobayashi, M., Lin, Y., Mishra, A., Shelly, C., Gao, R., Reeh, C. W., Wang, P. Z., Xi, R., Liu, Y., Wenzel, P., Ghosn, E., Liu, Y., & Yoshimoto, M. (2020). Bmi1 Maintains the Self-Renewal Property of Innate-like B Lymphocytes. The Journal of Immunology, 204, 3262–3272.
Jacobs, J. J., Kieboom, K., Marino, S., DePinho, R. A., & van Lohuizen, M. (1999). The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through the ink4a locus. Nature, 397, 164–168.
Bracken, A. P., Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D., Dietrich, N., Pasini, D., Gargiulo, G., Beekman, C., Theilgaard-Mönch, K., Minucci, S., Porse, B. T., Marine, J. C., Hansen, K. H., & Helin, K. (2007). The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes & Development, 21, 525–530.
Oguro, H., Iwama, A., Morita, Y., Kamijo, T., van Lohuizen, M., & Nakauchi, H. (2006). Differential impact of Ink4a and Arf on hematopoietic stem cells and their bone marrow microenvironment in Bmi1-deficient mice. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 203, 2247–2253.
Reya, T., & Clevers, H. (2005). Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature, 434(7035), 843–850.
Staal, F. J., & Sen, J. M. (2008). The canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis. European Journal of Immunology, 38, 1788–1794.
Staal, F. J., Chhatta, A., & Mikkers, H. (2016). Caught in a Wnt storm: Complexities of Wnt signaling in hematopoiesis. Experimental Hematology, 44, 451–457.
Luis, T. C., Naber, B. A., Roozen, P. P., Brugman, M. H., de Haas, E. F., Ghazvini, M., Fibbe, W. E., van Dongen, J. J., Fodde, R., & Staal, F. J. (2011). Canonical wnt signaling regulates hematopoiesis in a dosage-dependent fashion. Cell Stem Cell, 9, 345–356.
Reya, T., Duncan, A. W., Ailles, L., Domen, J., Scherer, D. C., Willert, K., Hintz, L., Nusse, R., & Weissman, I. L. (2003). A role for Wnt signalling in self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature, 423, 409–414.
Duncan, A. W., Rattis, F. M., DiMascio, L. N., Congdon, K. L., Pazianos, G., Zhao, C., Yoon, K., Cook, J. M., Willert, K., Gaiano, N., & Reya, T. (2005). Integration of Notch and Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Nature Immunology, 6, 314–322.
Qian, Z., Chen, L., Fernald, A. A., Williams, B. O., & Le Beau, M. M. (2008). A critical role for Apc in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell survival. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 205, 2163–2175.
Wang, J., Fernald, A. A., Anastasi, J., Le Beau, M. M., & Qian, Z. (2010). Haploinsufficiency of Apc leads to ineffective hematopoiesis. Blood, 115, 3481–3488.
Liu, Y., Elf, S. E., Miyata, Y., Sashida, G., Liu, Y. H., Huang, G., Di Giandomenico, S., Lee, J. M., Deblasio, A., Menendez, S., Antipin, J., Reva, B., Koff, A., & Nimer, S. D. (2009). p53 Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Quiescence. Cell Stem Cell, 4, 37–48.
Chen, S., Wang, Q., Yu, H., Capitano, M. L., Vemula, S., Nabinger, S. C., Gao, R., Yao, C., Kobayashi, M., Geng, Z., Fahey, A., Henley, D., Liu, S. Z., Barajas, S., Cai, W., Wolf, E. R., Ramdas, B., Cai, Z., Gao, H., … Liu, Y. (2019). Mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis through modulating epigenetic pathway. Nature Communications, 10, 5649.
Yu, M., Mazor, T., Huang, H., Huang, H. T., Kathrein, K. L., Woo, A. J., Chouinard, C. R., Labadorf, A., Akie, T. E., Moran, T. B., Xie, H., Zacharek, S., Taniuchi, I., Roeder, R. G., Kim, C. F., Zon, L. I., Fraenkel, E., & Cantor, A. B. (2012). Direct recruitment of polycomb repressive complex 1 to chromatin by core binding transcription factors. Molecular Cell, 45, 330–343.
Yu, J., Liu, D., Sun, X., Yang, K., Yao, J., Cheng, C., Wang, C., & Zheng, J. (2019). CDX2 inhibits the proliferation and tumor formation of colon cancer cells by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via transactivation of GSK-3beta and Axin2 expression. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 26.
Jeannet, G., Scheller, M., Scarpellino, L., Duboux, S., Gardiol, N., Back, J., Kuttler, F., Malanchi, I., Birchmeier, W., Leutz, A., Huelsken, J., & Held, W. (2008). Long-term, multilineage hematopoiesis occurs in the combined absence of beta-catenin and gamma-catenin. Blood, 111, 142–149.
Scheller, M., Huelsken, J., Rosenbauer, F., Taketo, M. M., Birchmeier, W., Tenen, D. G., & Leutz, A. (2006). Hematopoietic stem cell and multilineage defects generated by constitutive beta-catenin activation. Nature Immunology, 7, 1037–1047.
Luis, T. C., Weerkamp, F., Naber, B. A., Baert, M. R., de Haas, E. F., Nikolic, T., Heuvelmans, S., De Krijger, R. R., van Dongen, J. J., & Staal, F. J. (2009). Wnt3a deficiency irreversibly impairs hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and leads to defects in progenitor cell differentiation. Blood, 113, 546–554.
Luis, T. C., Naber, B. A., Fibbe, W. E., van Dongen, J. J., & Staal, F. J. (2010). Wnt3a nonredundantly controls hematopoietic stem cell function and its deficiency results in complete absence of canonical Wnt signaling. Blood, 116, 496–497.
Kabiri, Z., Numata, A., Kawasaki, A., Tenen, D. G., & Virshup, D. M. (2015). Wnts are dispensable for differentiation and self-renewal of adult murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood, 126, 1086–1094.
Cho, J. H., Dimri, M., & Dimri, D. P. (2013). A positive feedback loop regulates the expression of polycomb group protein BMI1 via WNT signaling pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 3406–3418.
Yu, F., Zhou, C., Zeng, H., Liu, Y., & Li, S. (2018). BMI1 activates WNT signaling in colon cancer by negatively regulating the WNT antagonist IDAX. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 496, 468–474.
Yu, T., Chen, X., Zhang, W., Colon, D., Shi, J., Napier, D., Rychahou, P., Lu, W., Lee, E. Y., Weiss, H. L., Evers, B. M., & Liu, C. (2012). Regulation of the potential marker for intestinal cells, Bmi1, by β-catenin and the zinc finger protein KLF4: Implications for colon cancer. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 3760–3768.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by R01 HL150624, R56 DK119524, R56 AG052501, DoD W81XWH-18-1-0265 and DoD W81XWH-19-1-0575 awards to YL. This work was supported in part by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Translational Research Program award 6581-20 and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award to YL. The authors would like to acknowledge the Flow Cytometry Core and In vivo Therapeutic Core Laboratories, which were sponsored, in part, by the NIDDK Cooperative Center of Excellence in Hematology (CCEH) grant U54 DK106846. This work was supported, in part, by a Project Development Team within the ICTSI NIH/NCRR Grant Number UL1TR001108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Y., R.G., S.C., R.X., and Y.L. Designed the research. H.Y., R.G., S.C., X.L., Q.W., W.C., S.V., A.C.F., D.H., M.K., and S.Z.L. Performed the research; H.Y., R.G., S.C., Q.W., and Y.L. Analyzed the data and performed the statistical analysis. Z.Q., R.K., H.E.B., and Z.G. Provided reagents and constructive advice to the study. S.C., R.X., and Y.L. Wrote the manuscript. All authors read, commented on, and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict Interest
The authors declared that no conflict interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Gao, R., Chen, S. et al. Bmi1 Regulates Wnt Signaling in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 17, 2304–2313 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10253-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10253-4