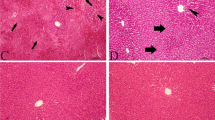
Abstract
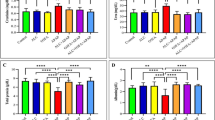
Acetaminophen (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol, APAP, or paracetamol) is one of the drugs that may be damaging to the kidneys and liver when used in excess. In this context, it is vital to treat these side effects on the liver and kidneys with various antioxidants. Diseases have been treated using herbal and mineral remedies since ancient times. The mineral boron, found in rocks and water, is a crucial ingredient with multiple positive biological effects. The primary objective of this research is to determine whether or not boron has a protective effect against the toxicity generated by APAP in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were pretreated orally with boron-source sodium pentaborate (B50 and B100 mg/kg) for 6 days by gastric gavage in order to counteract the toxicity caused by a single dose of APAP (1g/kg). APAP increased lipid peroxidation as well as serum BUN, creatinine concentrations, and serum activities of AST, ALP, and ALT by consuming GSH in liver and kidney tissues. In addition, the activity of antioxidative enzymes, including SOD, CAT, and GPx, was diminished. Inflammatory indicators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-33 were elevated in conjunction with APAP toxicity. In kidney and liver tissues, APAP dramatically increased the activity of caspase-3 and triggered apoptosis. Sodium pentaborate therapy on a short-term basis reduced biochemical levels despite these effects of APAP. This study showed that boron protects rats from the harmful effects of APAP by acting as an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic agent.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukai M, Bischoff K, Ramaiah SK (2012) Liver toxicity. Vet Toxicol Basic Clin Princ:246–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385926-6.00017-X
Perazella MA (2009) Renal vulnerability to drug toxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1275–1283
Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Eldutar E et al (2017) Chrysin protects rat kidney from paracetamol-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy: Amulti-biomarker approach. Sci Pharm 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010004
Pizzorno J (2015) The kidney dysfunction epidemic, part 1: causes. Integr Med: A Clin J 14:8
Ozkaya O, Genc G, Bek K, Sullu Y (2010) A case of acetaminophen (paracetamol) causing renal failure without liver damage in a child and review of literature. Ren Fail 32:1125–1127. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2010.509830
Wallace JL (2004) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: NO to the rescue. Br J Pharmacol 143:1–2
Kato H, Fujigaki Y, Inoue R et al (2014) Therapeutic dose of acetaminophen as a possible risk factor for acute kidney injury: learning from two healthy young adult cases. Intern Med 53:1531–1534. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.53.1502
Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A et al (2006) Paracetamol: new vistas of an old drug. CNS Drug Rev 12:250–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1527-3458.2006.00250.X
James LP, Mayeux PR, Hinson JA (2003) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J Drug Met and Disp 31:1499–1506. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.31.12.1499
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, Ramachandran A, Bajt ML (2012) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and repair: the role of sterile inflammation and innate immunity. Liver Int 32:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1478-3231.2011.02501.X
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ (2014) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev 94:909–950
Devirian TA, Volpe SL (2003) The physiological effects of dietary boron. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690390826491
Hakki SS, Bozkurt BS, Hakki EE (2010) Boron regulates mineralized tissue-associated proteins in osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1). J Trace Elem Med Biol 24:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.03.003
Armstrong TA, Spears JW, Lloyd KE (2001) Inflammatory response, growth, and thyroid hormone concentrations are affected by long-term boron supplementation in gilts. J Anim Sci 79:1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.2527/2001.7961549x
Nielsen FH (2002) Does boron have an essential function similar to an omega-3 fatty acid function? In: Anke M, Muller R, Schafer U, Stoeppler M (eds) Macro and trace elements. Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany, October 18-19-2002. Leipzig, Germany:Schubert-Verlag. 1238–1250. https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=139342. Accessed 30 Feb 2023
Jin E, Ren M, Liu W et al (2017) Effect of boron on thymic cytokine expression, hormone secretion, antioxidant functions, cell proliferation, and apoptosis potential via the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 65:11280–11291. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04069
Comba B, Oto G, Mis L et al (2016) 3-Metilkolatren uygulanan sıçanlarda boraksın inflamasyon, hematolojik parametreler ve total oksidan-antioksidan durumlar üzerine etkileri. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 22:539–544. https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2016.15001
Hunt CD, Herbel JL, Idso JP (1994) Dietary boron modifies the effects of vitamin D3 nutrition on indices of energy substrate utilization and mineral metabolism in the chick. J Bone Miner Res 9:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/JBMR.5650090206
Cao J, Jiang L, Zhang X et al (2008) Boric acid inhibits LPS-induced TNF-α formation through a thiol-dependent mechanism in THP-1 cells. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2008.03.005
Pizzorno L (2015) Nothing boring about boron. Integr Med: A Clin J 14:35
Nielsen FH, Stoecker BJ (2009) Boron and fish oil have different beneficial effects on strength and trabecular microarchitecture of bone. J Trace Elem Med Biol 23:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JTEMB.2009.03.003
Uysal T, Ustdal A, Sonmez MF, Ozturk F (2009) Stimulation of bone formation by dietary boron in an orthopedically expanded suture in rabbits. meridian.allenpress.com. 79. https://doi.org/10.2319/Original
Demirci S, Doğan A, Aydın S et al (2016) Boron promotes streptozotocin-induced diabetic wound healing: roles in cell proliferation and migration, growth factor expression, and inflammation. Mol Cell Biochem 417:119–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2719-9
Samman S, Naghii MR, Lyons Wall PM, Verus AP (1998) The nutritional and metabolic effects of boron in humans and animals. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783140
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH et al (2014) Protective effects of boron on cyclophosphamide induced lipid peroxidation and genotoxicity in rats. Chemosphere 108:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.038
Nielsen FH (2018) Boron in aging and longevity. Trace Elem Min Health longev:163–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03742-0_6
Hunt CD (2003) Dietary boron: an overview of the evidence for its role in immune function. J Trace Elem Exp Med 16(4):291–306
Doğan A, Demirci S, Apdik H et al (2017) A new hope for obesity management: boron inhibits adipogenesis in progenitor cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Metabolism 69:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.021
Turkez H, Geyikoglu F (2010) Boric acid: a potential chemoprotective agent against aflatoxin b 1 toxicity in human blood. Cytotechnology 62:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-010-9272-2
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Cigerci IH et al (2010) The effects of dietary boric acid and borax supplementation on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant activity, and DNA damage in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 24:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.01.003
De Seta F, Schmidt M, Vu B et al (2009) Antifungal mechanisms supporting boric acid therapy of Candida vaginitis. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkn486
Türkez H, Geyikoǧlu F, Tatar A et al (2007) Effects of some boron compounds on peripheral human blood. Z Naturforsch - Sec C J Biosci 62:889–896. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2007-11-1218
Başaran N, Duydu Y, Bacanlı M et al (2020) Evaluation of oxidative stress and immune parameters of boron exposed males and females. Food Chem Toxicol 142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111488
Aba PE, Ozioko IE, Udem ND, Udem SC (2014) Some biochemical and haematological changes in rats pretreated with aqueous stem bark extract of Lophira lanceolata and intoxicated with paracetamol (acetaminophen). J Complement Integr Med 11:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2014-0007
Ucar F, Taslipinar MY, Alp BF et al (2013) The effects of N-acetylcysteine and ozone therapy on oxidative stress and inflammation in acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity model. Ren Fail 35:640–647. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2013.780530
Ullah H, Khan A, Bibi T et al (2022) Comprehensive in vivo and in silico approaches to explore the hepatoprotective activity of poncirin against paracetamol toxicity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 395:195–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00210-021-02192-1/FIGURES/15
Ince S, Keles H, Erdogan M et al (2012) Protective effect of boric acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Drug Chem Toxicol 35:285–292. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2011.607825
Pfeiffer CC, Hallman LF, Gersh I (1945) Boric acid ointment: a study of possible intoxication in the treatment of burns. J Am Med Assoc 128:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1945.02860210022006
Weir RJ, Fisher RS (1972) Toxicologic studies on borax and boric acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 23:351–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008X(72)90037-3
Murray FJ (1998) A comparative review of the pharmacokinetics of boric acid in rodents and humans. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:331–341
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Rahman MM, Hafez MM, Omran FM (2007) Role of nitric oxide and reduced glutathione in the protective effects of aminoguanidine, gadolinium chloride and oleanolic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology 234:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.02.014
Prescott LF (2000) Paracetamol, alcohol and the liver. Br J Clin Pharmacol 49:291–301
Mccrae JC, Mccrae JC, Morrison EE et al (2018) Long-term adverse effects of paracetamol–a review. Wiley Online Library 84:2218–2230. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13656
Sundari K, Karthik D, Ilavenil S et al (2013) Hepatoprotective and proteomic mechanism of Sphaeranthus indicus in paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in wistar rats. Food Biosci 1:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2013.03.004
Ko JW, Shin JY, Kim JW et al (2017) Protective effects of diallyl disulfide against acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity: a possible role of CYP2E1 and NF-κB. Food Chem Toxicol 102:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.02.021
Motawi TK, Ahmed SA, El-Boghdady NA et al (2020) Impact of betanin against paracetamol and diclofenac induced hepato-renal damage in rats. Biomarkers 25:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2019.1697365
Mazer M, Perrone J (2008) Acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity: pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. J Med Toxicol 4:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160941
Yildirim S, Celikezen FC, Oto G et al (2018) An investigation of protective effects of litium borate on blood and histopathological parameters in acute cadmium-induced rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 182:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1089-9
Cekmen M, Ilbey YO, Ozbek E et al (2009) Curcumin prevents oxidative renal damage induced by acetaminophen in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1480–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.03.034
Hazman Ö, Bozkurt MF, Fidan AF et al (2018) The effect of boric acid and borax on oxidative stress, inflammation, ER stress and apoptosis in cisplatin toxication and nephrotoxicity developing as a result of toxication. Inflammation 41:1032–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0756-0
Acaroz U, Ince S, Arslan-Acaroz D et al (2018) The ameliorative effects of boron against acrylamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and metabolic changes in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 118:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.029
Ahmed MB, Khater MR (2001) Evaluation of the protective potential of Ambrosia maritima extract on acetaminophen-induced liver damage. J Ethnopharmacol 75:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00400-1
Abirami A, Nagarani G, Siddhuraju P (2015) Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts from Citrus hystrix and C. maxima against paracetamol induced liver injury in rats. Food Sci Hum Wellness 4:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FSHW.2015.02.002
Alam J, Mujahid M, Jahan Y, Bagga P, Rahman MA (2017) Hepatoprotective potential of ethanolic extract of Aquilaria agallocha leaves against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. J Tradit Complement Med 7:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JTCME.2015.12.006
Kumar G, Banu GS, Pappa PV et al (2004) Hepatoprotective activity of Trianthema portulacastrum L. against paracetamol and thioacetamide intoxication in albino rats. J Ethnopharmacol 92:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2003.12.009
Amin KA, Hashem KS, Alshehri FS et al (2017) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective efficiency of selenium nanoparticles against acetaminophen-induced hepatic damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 175:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0748-6
Agha FE, Youness ER, Selim MMH, Ahmed HH (2014) Nephroprotective potential of selenium and taurine against mercuric chloride induced nephropathy in rats. Ren Fail 36:704–716. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2014.890012
Apaydin Yildirim B, Kordali S, Terim Kapakin KA et al (2017) Effect of Helichrysum plicatum DC. subsp. plicatum ethanol extract on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 18:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500291
Campos R, Garrido A, Guerra R, Valenzuela A (1989) Silybin dihemisuccinate protects against glutathione depletion and lipid peroxidation induced by acetaminophen on rat liver. Planta Med 55:417–419. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-962055
Girish C, Koner BC, Jayanthi S et al (2009) Hepatoprotective activity of picroliv, curcumin and ellagic acid compared to silymarin on paracetamol induced liver toxicity in mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 23:735–745. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00722.x
Masson MJ, Collins LA, Carpenter LD et al (2010) Pathologic role of stressed-induced glucocorticoids in drug-induced liver injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.126
El-Maddawy ZK, El-Sayed YS (2018) Comparative analysis of the protective effects of curcumin and N-acetyl cysteine against paracetamol-induced hepatic, renal, and testicular toxicity in Wistar rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3468–3479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0750-3
Salem GA, Shaban A, Diab HA et al (2018) Phoenix dactylifera protects against oxidative stress and hepatic injury induced by paracetamol intoxication in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 104:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2018.05.049
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH et al (2020) Boron, a trace mineral, alleviates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 195:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12011-019-01875-4
Coban FK, Ince S, Kucukkurt I et al (2015) Boron attenuates malathion-induced oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:391–399. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2014.974109
Kucukkurt I, Ince S, Demirel HH et al (2015) The effects of boron on arsenic-induced lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in male and female rats. Wiley Online Library 29:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21729
Mohora M, Boghianu L, Muscurel C, et al. Effects of boric acid on redox status in the rat liver. rjb.ro
Tracey KJ, Cerami A (1994) Tumor necrosis factor: a pleiotropic cytokine and therapeutic target. Annu Rev Med 45:491–503. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.MED.45.1.491
Bae Y, Lee S, Kim SH (2011) Chrysin suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: involvement of calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.04.008
Adams JM, Cory S (2001) Life-or-death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 26:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01740-0
Strasser A, O’Connor L, Dixit VM (2000) Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 69:217–245. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.BIOCHEM.69.1.217
Eldutar E, Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Caglayan C (2017) Restorative effects of Chrysin pretreatment on oxidant–antioxidant status, inflammatory cytokine production, and apoptotic and autophagic markers in acute paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: An experimental and biochemical study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:e21960. https://doi.org/10.1002/JBT.21960
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Faruk Durukan and Kale Natural Corp. for the supply of sodium pentaborate.
Funding
This study received financial support from Ataturk University-The Coordination Unit of Scientific Research Projects, Türkiye (within the project’s scope, numbered TDK-2018-6715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aktas Senocak, E., Utlu, N., Kurt, S. et al. Sodium Pentaborate Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatorenal Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress, Lipid Peroxidation, Apoptosis, and Inflammatory Cytokines in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 1164–1173 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03755-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03755-4