Abstract
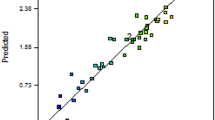
Due to its spore-forming ability, Bacillus coagulans has advantages over the other non-spore-forming probiotics. Among them, survival and stability during food processing and storage, resistance to acid pH, and digestive enzymes are important. However, there are few studies on the quality and amount of sporulation in B. coagulans. This study investigated the spore densities and formation efficiency of B. coagulans. The optimal medium formulation consisted of yeast extract (1.00 g L−1), potassium acetate (20.00 g L−1), and MnSO4 (0.01 g L−1 and 0.03 g L−1). After reaching the optimal medium, a response surface regression equation was established based on the results of central composite design (CCD) experimental designs to optimize time, temperature, and pH parameters. The predicted results thus obtained were in good agreement (R2 = 95.19%) with the results obtained by performing experiments. Multiple regression analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that pH is negative, and temperature and time dose are positive factors. The maximum spore cell densities by optimization plots have obtained 9.80 log at temperature 83.77 °C, pH 3.05, and time 111.19 h, considering that B. coagulans needs special environmental and cellular conditions to enter the sporulation stage. In this study, the composition of the culture medium and factors such as temperature, time, and pH were considered influencing factors in B. coagulans sporulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All generated or analyzed data as well as the utilized software and materials have been included in the published article. The generated results during the study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Charney, J., Fisher, W. P., & Hegarty, C. P. (1951). Manganese as an essential element for sporulation in the genus Bacillus. Journal of Bacteriology, 62(2), 145–148. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.62.2.145-148.1951
Ghosh, S., Ramirez-Peralta, A., Gaidamakova, E., Zhang, P., Li, Y. Q., Daly, M., & Setlow, P. (2011). Effects of Mn levels on resistance of Bacillus megaterium spores to heat, radiation and hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 111(3), 663–670.
Amaha, M., Ordal, Z. J., & Touba, A. (1956). Sporulation requirements of Bacillus coagulans var. thermoacidurans in complex media. Journal of Bacteriology, 72(1), 34–41. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.72.1.34-41.1956
Oomes, S. J. C., Brul, S. (2004). The effect of metal ions commonly present in food on gene expression of sporulating Bacillus subtilis cells in relation to spore wet heat resistance. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 5(3), 307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2004.03.006
Cazemier, A. E., Wagenaars, S. F. M., & Ter Steeg, P. F. (2001). Effect of sporulation and recovery medium on the heat resistance and amount of injury of spores from spoilage bacilli. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 90(5), 761–770. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01302.x
Costa, O. Y., Oguejiofor, C., Zühlke, D., Barreto, C. C., Wünsche, C., Riedel, K., & Kuramae, E. (2020). Impact of different trace elements on the growth and proteome of two strains of Granulicella, class “Acidobacteriia.” Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 1227.
Vasantha, N., & Freese, E. (1979). The role of manganese in growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of General Microbiology, 112(2), 329–336. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-112-2-329
Gbair, G. A., & Alshamsi, H. A. J. (2022). Facile green synthesis of CuO-ZnO nanocomposites from Argyreia nervosa leaves extract for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03408-x
Sinnelä, M. T., Park, Y. K., Lee, J. H., Jeong, K. C., Kim, Y.-W., Hwang, H.-J., & Mah, J.-H. (2019). Effects of calcium and manganese on sporulation of Bacillus species involved in food poisoning and spoilage. Foods, 84, 119.
Rekadwad, B. N., Gonzalez, J. M. & Khobragade, C. N. (2020). One plate-double nutrient endospore activation method. Bio-Protocol, e3474–e3474. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.3474
Acknowledgements
This study was a part of Seyedeh Habibeh Mirmajidi’s PhD dissertation proposed and approved in the Department of Medical Biotechnology, School of Advanced Medical Sciences and Technologies, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
Funding
This work was supported by the Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran (grant No. 22866).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seyedeh Habibeh Mirmajidi has performed the experimental analysis study. Seyedeh Habibeh Mirmajidi and Mohammad Hossein Morowvat have carried out the analysis and interpretation of the results. Cambyz Irajie, Mohammad Hossein Morowvat, and Seyedeh Habibeh Mirmajidi have designed the study concept and interpreted the data. Navid Nezafat, Younes Ghasemi, and Amir Savardashtaki read and revised the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran (IR.SUMS.REC.1401.153). This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mirmajidi, S.H., Irajie, C., Savardashtaki, A. et al. Optimization of Spore Production in Bacillus coagulans Using Response Surface Methodology Approach. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04934-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04934-2