Abstract
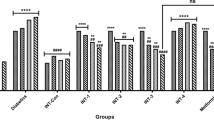
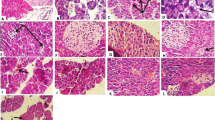
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common metabolic disorder which arises due to the improper carbohydrate metabolism, decreased secretion/activity of insulin, and genetic abnormalities, which result in the increased blood glucose level generally known as hyperglycemia. Diabetes holds an increased global prevalence in each year and is responsible for increased morbidity and mortality rates. Hence, the current investigation focusses to assess the antidiabetic potential of sinigrin on diabetic animal model through the suppression of inflammation. Diabetes was initiated to the animals via administering streptozotocin (STZ) and supplemented with the sinigrin at 25- and 50-mg/kg dose via oral route. The diabetic rats demonstrated the elevated glucose, food and water intake, kidney and liver weights, and reduced bodyweight and depleted insulin status. The sinigrin treatment remarkably improved and modulated these changes in diabetic animals. Additionally, the sinigrin supplementation also modulated the changes in glucose-6-phosphatase; fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase; AST; ALT; creatinine; and inflammatory mediators in the STZ-provoked diabetic animals. The levels of hexokinase, protein, and antioxidants also improved by the sinigrin treatment. The histological investigations of pancreas also witnessed the therapeutic actions of sinigrin, which is supported by the findings of biochemical examinations. Therefore, it was clear that the sinigrin supplementation displayed remarkable antidiabetic effect on STZ-initiated diabetic animals via modulating inflammation and other biochemical changes, which recommends that sinigrin could be a talented candidate for diabetes management in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Tran, N., Pham, B., & Le, L. (2020). Bioactive compounds in anti-diabetic plants: From herbal medicine to modern drug discovery. Biology (Basel)., 9(9), 252.
Luc, K., Schramm-Luc, A., Guzik, T. J., & Mikolajczyk, T. P. (2019). Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 70(6), 809–824.
Charlton, A., Garzarella, J., Jandeleit-Dahm, K. A. M., & Jha, J. C. (2021). Oxidative stress and inflammation in renal and cardiovascular complications of diabetes. Biology (Basel)., 10(1), 18.
Jamali-Raeufy, N., Baluchnejadmojarad, T., Roghani, M., Keimasi, S., & Goudarzi, M. (2019). Isorhamnetic exerts neuroprotective effects in STZ-induced diabetic rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 102, 101709.
Tsalamandris, S., Antonopoulos, A. S., Oikonomou, E., Papamikroulis, G. A., Vogiatzi, G., Papaioannou, S., Deftereos, S., & Tousoulis, D. (2019). The role of inflammation in diabetes: Current concepts and future perspectives. European Cardiology, 14(1), 50–59.
Furman, B. L., Candasamy, M., Bhattamisra, S. K., & Veettil, S. K. (2020). Reduction of blood glucose by plant extracts and their use in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: Discrepancies in effectiveness between animal and human studies. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 247, 112264.
Nomura, T., Shinoda, S., Yamori, T., Sawaki, S., Nagata, I., Ryoyama, K., & Fuke, Y. (2005). Selective sensitivity to wasabi-derived 6-(methylsulfinyl)hexyl isothiocyanate of human breast cancer and melanoma cell lines studied in vitro. Cancer Detection and Prevention, 29, 155–160.
Mazumder, A., Dwivedi, A., & du Plessis, J. (2016). Sinigrin and its therapeutic benefits. Molecules, 21, 416.
Trinder, P. (1969). Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 22, 158–161.
Bürgi, W., Briner, M., Franken, N., & Kessler, A. C. (1988). One-step sandwich enzyme immunoassay for insulin using monoclonal antibodies. Clinical Biochemistry, 21, 311–314.
Nayak, S. S., & Pattabiraman, T. N. (1981). A new colorimetric method for the estimation of glycosylated hemoglobin. Clinica Chimica Acta, 109, 267–274.
Reitman, S., & Frankel, S. (1957). A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 28, 56–63.
Gancedo, J. M., & Gancedo, C. (1971). Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting and non fermenting yeasts. Archiv für Mikrobiologie, 76, 132–138.
Kind, P. R., & King, E. J. (1954). Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolysed phenol with amino-antipyrine. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 7, 322–326.
Koide, H., & Oda, T. (1959). Pathological occurrence of glucose-6-phosphatase in serum in liver diseases. Clinica Chimica Acta, 4, 554–561.
Brandstrup, N., Kirk, J. E., & Bruni, C. (1957). The hexokinase and phosphoglucoisomerase activities of aortic and pulmonary artery tissue in individuals of various ages. Journal of Gerontology, 12, 166–171.
Ohkawa, H., Ohishi, N., & Yagi, K. (1979). Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Analytical Biochemistry, 95, 351–358.
Jiang, Z. Y., Hunt, J. V., & Wolff, S. P. (1992). Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxide in low density lipoprotein. Analytical Biochemistry, 202, 384–389.
Sinha, A. K. (1972). Colorimetric assay of catalase. Analytical Biochemistry, 47, 389–394.
Kakkar, P., Das, B., & Viswanathan, P. N. (1984). A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics, 21, 130–132.
Rotruck, J. T., Pope, A. L., Ganther, H. E., Swanson, A. B., Hafeman, D. G., & Hoekstra, W. G. (1973). Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science, 179, 588–590.
Beutler, E., & Kelly, B. M. (1963). The effect of sodium nitrite on red cell GSH. Experientia, 19, 96–97.
Prabhakar, U., Eirikis, E., & Davis, H. M. (2002). Simultaneous quantification of proinflammatory cytokines in human plasma using the LabMAP assay. Journal of Immunological Methods, 260(1–2), 207–218.
Florence, N. T., Benoit, M. Z., Jonas, K., Alexandra, T., Désiré, D. D., Pierre, K., & Théophile, D. (2014). Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of Annona muricata (Annonaceae), aqueous extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 151, 784–790.
Abbas, Q., Hassan, M., Raza, H., Kim, S. J., Chung, K. W., Kim, G. H., & Seo, S. Y. (2017). In vitro, in vivo and in silico anti-hyperglycemic inhibition by sinigrin. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 10, 372–9.
Bamagous, G. A., Al Ghamdi, S. S., Ibrahim, I. A., Mahfoz, A. M., Afify, M. A., Alsugoor, M. H., Shammah, A. A., Arulselvan, P., & Rengarajan, T. (2018). Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of ethyl acetate extract fraction of Moringa oleifera leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetes rats via inhibition of inflammatory mediators. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 8, 320–327.
Wasana, K. G. P., Attanayake, A. P., Jayatilaka, K. A. P. W., & Weerarathna, T. P. (2021). Antidiabetic activity of widely used medicinal plants in the Sri Lankan traditional healthcare system: New insight to medicinal flora in Sri Lanka. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2021, 6644004.
El-Marasy, S. A., Zaki, E. R., Abdallah, H. M., & Arbid, M. S. (2017). Therapeutic effects of aqueous, methanol and ethanol extracts of Egyptian Artemisia herba-alba in STZ-induced diabetic neuropathy in rats. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 7, 180–187.
Wei, Q., Zhan, Y., Chen, B., Xie, B., Fang, T., Ravishankar, S., & Jiang, Y. (2020). Assessment of antioxidant and antidiabetic properties of Agaricus blazi Murill extracts. Food Science & Nutrition, 8(1), 332–339.
Chis, I. C., Ungureanu, M. I., Marton, A., Simedrea, R., Muresan, A., Postescu, I. D., & Decea, N. (2009). Antioxidant effects of a grape seed extract in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research, 6, 200–204.
Ippoushi, K., Takeuchi, A., & Azuma, K. (2010). Sinigrin suppresses nitric oxide production in rats administered intraperitoneally with lipopolysaccharide. Food Chemistry, 120, 1119–1121.
Ghanbari, E., Nejati, V., & Khazaei, M. (2016). Improvement in serum biochemical alterations and oxidative stress of liver and pancreas following use of royal jelly in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cell Journal, 18, 362–370.
Karan, S. K., Mondal, A., Mishra, S. K., Pal, D., & Rout, K. K. (2013). Antidiabetic effect of Streblus asper in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmaceutical Biology, 51, 369–375.
Scheller, J., Chalaris, A., Schmidt-Arras, D., & Rose-John, S. (2011). The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1813, 878–888.
Abo-Salem, O. M. (2014). Kaempferol attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathic pain in mice: Possible anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms. Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 7, 424–430.
Rossi, S., D’Amico, M., Capuano, A., Romano, M., Petronella, P., & Di Filippo, C. (2006). Hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetes leads to persistent inflammation and tissue damage following uveitis due to reduced levels of ciliary body heme oxygenase-1. Mediators of Inflammation, 2006, 60285.
Lee, H. W., Lee, C. G., Rhee, D. K., Um, S. H., & Pyo, S. (2017). Sinigrin inhibits production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB/MAPK pathways or NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. International Immunopharmacology, 45, 163–173.
Lee, H., Lee, C., Kim, J., & Pyo, S. (2014). The inhibitory effect of sinigrin on the production of inflammatory mediators induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7 macrophages (1056.5). The FASEB J., 28, 1056–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors consented to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors consented for the publication of their work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, S. Antidiabetic Potential of Sinigrin Against Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes via Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 4279–4291 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03739-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03739-x