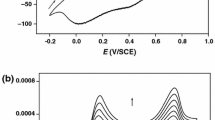
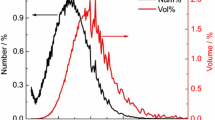
Abstract
In this study, caffeine-loaded MIL-100 (Fe), caffeine@MIL-100 (Fe), was used as a smart corrosion-inhibiting coating to protect 308L-16 stainless steel (308L-16 SS). For this purpose, a thin film of the smart anticorrosion caffeine@MIL-100 (Fe) coating was deposited on an 308L-16 SS surface using a decanoic acid self-assembled monolayer. A significant encapsulation efficiency for caffeine loading in the MIL-100 (Fe) metal organic framework was obtained as 17.8%. The experimental data indicated that the caffeine@MIL-100 (Fe) coating would release the caffeine very rapidly as the solution became acidified around the corrosion sites and formed a protective layer to prevent from penetrating solution into the substrate. The EIS results and the Tafel plots showed that the proposed smart coating has an excellent performance to protect 308L-16 SS from corrosion in saline media. Based on the results, decreasing the solution pH would cause the MIL-100 (Fe) framework to decompose and subsequently release caffeine at the 308L-16 SS surface.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gurrappa, I, Yashwanth, IVS, “The Importance of Corrosion and the Necessity of Applying Intelligent Coatings for Its Control.” In: Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control, pp 17–58. Elsevier Inc. (2015)
Xiang, T, Zheng, S, Zhang, M, et al. “Bioinspired Slippery Zinc Phosphate Coating for Sustainable Corrosion Protection.” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 6 10960–10968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02345 (2018)
Armelin, E, Alemán, C, Iribarren, JI, “Anticorrosion Performances of Epoxy Coatings Modified with Polyaniline: A Comparison Between the Emeraldine Base and Salt Forms.” Prog. Org. Coat., 65 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2008.10.001 (2009)
Ünal, HI, Zor, S, Erten, U, Gökergil, HM, “Effect of Ni-Co Alloy Coating on Corrosion Behavior of 0.8% C Steel.” Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 51 600–606. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205115040322 (2015)
Ding, R, Li, W, Wang, X, et al. “A Brief Review of Corrosion Protective Films and Coatings Based on Graphene and Graphene Oxide.” J. Alloys Compd., 764 1039–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.133 (2018)
Sheng, X, Ting, YP, Pehkonen, SO, “Evaluation of an Organic Corrosion Inhibitor on Abiotic Corrosion and Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Mild Steel.” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 46 7117–7125. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie070669f (2007)
Cui, J, Yang, Y, Li, X, et al. “Toward a Slow-Release Borate Inhibitor to Control Mild Steel Corrosion in Simulated Recirculating Water.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10 4183–4197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b15507 (2018)
Betova, I, Bojinov, M, Laitinen, T, et al. “The Transpassive Dissolution Mechanism of Highly Alloyed Stainless Steels I. Experimental Results and Modelling Procedure.” Corros. Sci., 44 2675–2697. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(02)00073-2 (2002)
Motalebi, A, Nasr-Esfahani, M, Ali, R, Pourriahi, M, “Improvement of Corrosion Performance of 316L Stainless Steel via PVTMS/Henna Thin Film.” Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 22 392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.10.006 (2012)
Lin, X, Peng, Q, Han, Y, et al. “Effect of Thermal Ageing and Dissolved Gas on Corrosion of 308L Stainless Steel Weld Metal in Simulated PWR Primary Water.” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 96 308–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.05.026 (2022)
Ma, C, Han, EH, Peng, Q, et al. “Effect of Polishing Process on Corrosion Behavior of 308L Stainless Steel in High Temperature Water.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 442 423–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.190 (2018)
Huang, GW, Xiao, HM, Fu, SY, “Electrical Switch for Smart pH Self-adjusting System Based on Silver Nanowire/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Film.” ACS Nano, 9 3234–3242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b00348 (2015)
Dai, M, Picot, OT, Verjans, JMN, et al. “Humidity-Responsive Bilayer Actuators Based on a Liquid-Crystalline Polymer Network.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 5 4945–4950. https://doi.org/10.1021/am400681z (2013)
Kameda, M, Tezuka, N, Hangai, T, et al. “Adsorptive Pressure-Sensitive Coatings on Porous Anodized Aluminium.” Meas. Sci. Technol., 15 489–500. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/15/3/001 (2004)
Cao, Z, Bian, Q, Chen, Y, et al. “Light-Responsive Janus-Particle-Based Coatings for Cell Capture and Release.” ACS Macro Lett., 6 1124–1128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.7b00714 (2017)
Wang, BL, Heng, L, Jiang, L, “Temperature-Responsive Anisotropic Slippery Surface for Smart Control of the Droplet Motion.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10 7442–7450. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b16818 (2018)
Volpi, E, Foiadelli, C, Trasatti, S, Koleva, DA, “Development of Smart Corrosion Inhibitors for Reinforced Concrete Structures Exposed to a Microbial Environment.” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 56 5778–5794. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b00127 (2017)
Fu, J, Chen, T, Wang, M, et al. “Acid and Alkaline Dual Stimuli-Responsive Mechanized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Smart Nanocontainers for Intelligent Anti-corrosion Coatings.” ACS Nano, 7 11397–11408. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4053233 (2013)
Claes, B, Boudewijns, T, Muchez, L, et al. “Smart Metal-Organic Framework Coatings: Triggered Antibiofilm Compound Release.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9 4440–4449. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14152 (2017)
Campagnol, N, Van Assche, TRC, Li, M, et al. “On the Electrochemical Deposition of Metal-Organic Frameworks.” J. Mater. Chem. A, 4 3914–3925. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta10782b (2016)
Li, H, Wang, K, Sun, Y, et al. “Recent Advances in Gas Storage and Separation Using Metal–Organic Frameworks.” Mater. Today, 21 108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2017.07.006 (2018)
Kadioglu, O, Keskin, S, “Efficient Separation of Helium from Methane Using MOF Membranes.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 191 192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.09.031 (2018)
Chen, X, Tong, R, Shi, Z, et al. “MOF Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Autophagy Inhibitor in Controlled Drug Delivery System for Antitumor.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10 2328–2337. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b16522 (2018)
Guo, Z, Xu, H, Su, S, et al. “A Robust Near Infrared Luminescent Ytterbium Metal-Organic Framework for Sensing of Small Molecules.” Chem. Commun., 47 5551–5553. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc10897b (2011)
Kang, YS, Lu, Y, Chen, K, et al. “Metal–Organic Frameworks with Catalytic Centers: From Synthesis to Catalytic Application.” Coord. Chem. Rev., 378 262–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.02.009 (2019)
Liu, W, Yan, Z, Zhang, Z, et al. “Bioactive and Anti-corrosive Bio-MOF-1 Coating on Magnesium Alloy for Bone Repair Application.” J. Alloys Compd., 788 705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.281 (2019)
Zhang, M, Ma, L, Wang, L, et al. “Insights into the Use of Metal-Organic Framework as High-Performance Anti-corrosion Coatings.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10 2259–2263. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b18713 (2018)
Zacher, D, Shekhah, O, Wöll, C, Fischer, RA, “Thin Films of Metal–Organic Frameworks.” Chem. Soc. Rev., 38 1418–1429. https://doi.org/10.1039/b805038b (2009)
Shustak, G, Domb, AJ, Mandler, D, “Preparation and Characterization of n-Alkanoic Acid Self-assembled Monolayers Adsorbed on 316L Stainless Steel.” Langmuir, 20 7499–7506. https://doi.org/10.1021/la036470z (2004)
Raman, A, Gawalt, ES, “Self-assembled Monolayers of Alkanoic Acids on the Native Oxide Surface of SS316L by Solution Deposition.” Langmuir, 23 2284–2288. https://doi.org/10.1021/la063089g (2007)
Li, W, Ren, B, Chen, Y, et al. “Excellent Efficacy of MOF Films for Bronze Artwork Conservation: The Key Role of HKUST-1 Film Nanocontainers in Selectively Positioning and Protecting Inhibitors.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10 37529–37534. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b13602 (2018)
Tian, H, Li, W, Liu, A, et al. “Controlled Delivery of Multi-substituted Triazole by Metal-Organic Framework for Efficient Inhibition of Mild Steel Corrosion in Neutral Chloride Solution.” Corros. Sci., 131 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2017.11.010 (2018)
Zhang, F, Shi, J, Jin, Y, et al. “Facile Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) Under HF-Free Conditions and Its Application in the Acetalization of Aldehydes with Diols.” Chem. Eng. J., 259 183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.119 (2015)
Guesh, K, Caiuby, CAD, Mayoral, Á, et al. “Sustainable Preparation of MIL-100(Fe) and Its Photocatalytic Behavior in the Degradation of Methyl Orange in Water.” Cryst. Growth Des., 17 1806–1813. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01776 (2017)
Strzempek, W, Menaszek, E, Gil, B, “Fe-MIL-100 as Drug Delivery System for Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Treatment and Diagnosis.” Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 280 264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.02.018 (2019)
Lee, JS, Jhung, SH, Yoon, JW, et al. “Adsorption of Methane on Porous Metal Carboxylates.” J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 15 674–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2009.09.043 (2009)
Mei, L, Wu, Y, Zhou, X, et al. “Adsorption Performance of MIL-100(Fe) for Separation of Olefin–Paraffin Mixtures.” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 70 74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.047 (2017)
Chen, X, Zhang, Y, Zhao, Y, et al. “Encapsulating Pt Nanoparticles through Transforming Fe3O4 into MIL-100(Fe) for Well-Defined Fe3O4@Pt@MIL-100(Fe) Core-Shell Heterostructures with Promoting Catalytic Activity.” Inorg. Chem., 58 12433–12440. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b02114 (2019)
Mileo, PGM, Ho Cho, K, Park, J, et al. “Unraveling the Water Adsorption Mechanism in the Mesoporous MIL-100(Fe) Metal-Organic Framework.” J. Phys. Chem. C, 123 23014–23025. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b06228 (2019)
De Souza, FS, Gonçalves, RS, Spinelli, A, “Assessment of Caffeine Adsorption Onto Mild Steel Surface as an Eco-friendly Corrosion Inhibitor.” J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 25 81–90. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20130270 (2014)
De Souza, FS, Giacomelli, C, Gonçalves, RS, Spinelli, A, “Adsorption Behavior of Caffeine as a Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper.” Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 32 2436–2444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.07.019 (2012)
Simon, MA, Anggraeni, E, Soetaredjo, FE, et al. “Hydrothermal Synthesize of HF-Free MIL-100 (Fe) for Isoniazid-Drug Delivery.” Sci. Rep., 9 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53436-3 (2019)
Duan, S, Li, J, Liu, X, et al. “HF-Free Synthesis of Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework NMIL-100 (Fe) as an Efficient Dye Adsorbent.” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 4 3368–3378. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00434 (2016)
De Taeye, J, Zeegers-Huyskens, T, “Infrared Spectrum of Caffeine and Its Hydrochloride Dihydrate.” Spectrosc. Lett., 19 299–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/00387018608069240 (1986)
Lv, H, Zhao, H, Cao, T, et al. “Efficient Degradation of High Concentration Azo-Dye Wastewater by Heterogeneous Fenton Process with Iron-Based Metal-Organic Framework.” J. Mol. Catal. A Chem., 400 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.02.007 (2015)
Lowell, S, Shields, JE, Thomas, MA, et al., Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density. Springer, Berlin. . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-2303-3 (2006)
Zheng, H, Zhang, Y, Liu, L, et al. “One-pot Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks with Encapsulated Target Molecules and Their Applications for Controlled Drug Delivery.” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 138 962–968. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b11720 (2016)
Cunha, D, Ben Yahia, M, Hall, S, et al. “Rationale of Drug Encapsulation and Release from Biocompatible Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks.” Chem. Mater., 25 2767–2776. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm400798p (2013)
Tukur, H, Yonghao, L, “A Review on the Behavior of 308L Cladding Material and Their Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants.” Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 15 1005–1021. https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.01.67 (2020)
Génin, JMR, Ruby, C, Géhin, A, Refait, P, “Synthesis of Green Rusts by Oxidation of Fe(OH)2, Their Products of Oxidation and Reduction of Ferric Oxyhydroxides; Eh-pH Pourbaix Diagrams.” Comptes Rendus - Geosci., 338 433–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2006.04.004 (2006)
Estrada-Villegas, GM, González-Pérez, G, Bucio, E, “Adsorption and Release of Caffeine from Smart PVDF Polyampholyte Membrane.” Iran Polym. J. (English Ed.), 28 639–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-019-00730-6 (2019)
Jadhav, SA, “Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) of Carboxylic Acids: An Overview.” Cent. Eur. J. Chem., 9 369–378. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-011-0024-8 (2011)
Biemmi, E, Scherb, C, Bein, T, “Oriented Growth of the Metal Organic Framework Cu3(BTC)2(H2O)3·xH2O Tunable with Functionalized Self-Assembled Monolayers.” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 129 8054–8055. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0701208 (2007)
Mohammadpour, Z, Zare, HR, “Structural Effect of Different Carbon Nanomaterials on the Corrosion Protection of Ni-W Alloy Coatings in Saline Media.” New J. Chem., 42 5425–5432. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj00030a (2018)
Mohammadpour, Z, Zare, HR, “The Effect of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets (GONSs) and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots (GOQDs) on Corrosion Resistance Enhancement of Ni–Fe Nanocomposite Coatings.” JOM, 72 4495–4504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04244-y (2020)
Zhou, Y, Ma, Y, Sun, Y, et al. “Robust Superhydrophobic Surface Based on Multiple Hybrid Coatings for Application in Corrosion Protection.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11 6512–6526. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b19663 (2019)
Daufin, G, Pagetti, J, Labbe, JP, Michel, F, “Pitting Initiation on Stainless Steels: Electrochemical and Micrographic Aspects.” Corrosion, 41 533–539. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3583024 (1985)
Suleiman, MI, Ragault, I, Newman, RC, “The Pitting of Stainless Steel Under a Rust Membrane at Very Low Potentials.” Corros. Sci., 36 479–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-938X(94)90038-8 (1994)
Pardo, A, Otero, E, Merino, MC, et al. “Influence of pH and Chloride Concentration on the Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Behavior of High-Alloy Stainless Steels.” Corrosion, 56 411–418. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3280545 (2000)
Mohammadpour, Z, Zare, HR, “A Comparative Study on the Effect of MWCNT as Reinforcement on the Corrosion Parameters of Different Ni–W/MWCNTS Nanocomposite Coatings in Various Corrosive Media.” Met. Mater. Int., 24 761–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0060-4 (2018)
Abreu, CM, Cristóbal, MJ, Losada, R, et al. “Long-Term Behaviour of AISI 304L Passive Layer in Chloride Containing Medium.” Electrochimica Acta, 51 1881–1890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.06.040 (2006)
da Trindade, LG, Gonçalves, RS, “Evidence of Caffeine Adsorption on a Low-Carbon Steel Surface in Ethanol.” Corros. Sci., 51 1578–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.03.038 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhavan-Bahabadi, Z., Zare, H.R. & Mohammadpour, Z. Use of caffeine-containing MIL-100 (Fe) metal organic framework as a high-performance smart anticorrosion coating to protect stainless steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. J Coat Technol Res 20, 883–898 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-022-00709-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-022-00709-8