Abstract
Garden berries and grapes constitute an integral part of a healthy and functional diet. Reduction of post-harvest losses can maximize the shelf life of berry fruits, increasing their market value and promoting consumption. Among current storage techniques, the use of edible films is an emerging strategy for packaging and protecting the surface of small fruits. They provide the necessary barrier for berries against adverse external biotic or abiotic factors while supporting the necessary physiological processes such as moisture and gas exchange. Carbohydrate polymers are an important component of edible films. The desired mechanical strength as well as barrier properties are achieved by combining carbohydrate polymers with other bio-based compounds, such as lipids, proteins, and functional additives. Unlike plant polysaccharides, the studies and use of microbial extracellular polysaccharides (EPSs) remain scarce, especially for films and coatings of garden berries and grapes. This review summarizes the available data for currently used (xanthan, pullulan, gellan, dextran, bacterial cellulose) and prospective microbial EPSs (levan, curdlan, kefiran, bacterial alginate). Directions in future research to achieve more widespread, cost-effective, environmentally friendly production and applications of edible microbial EPS films are discussed.

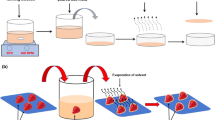
Adapted from Barcelos et al. (2019)
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the first author on reasonable request and/or are freely accessible via the Internet.
References
Abdallah, M. R., Mohamed, M. A., Mohamed, H., & Emara, T. M. (2018). Application of alginate and gelatin-based edible coating materials as alternatives to traditional coating for improving the quality of pastirma. Food Science and Biotechnology., 27, 1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0393-2
Aguirre-Joya, J., De Leon-Zapata, M. A., Alvarez-Perez, O. B., Torres-León, C., Nieto-Oropeza, D. E., Ventura-Sobrevila, J. M., et al. (2018). Basic and applied concepts of edible packaging for foods. In: A.M.Grumezesku & A.M.Holban (Eds.), Food packaging and preservation (pp. 1–61). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811516-9.00001-4
Ahmad, M., Nirmal, N. P., & Chuprom, J. (2015). Blend film based on fish gelatine/curdlan for packaging applications: spectral, microstructural and thermal characteristics. RSC Advances, 5(120), 99044–99057. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA20925K
Ahmad, N. H., Mustafa, S., & Che Man, Y. B. (2014). Microbial polysaccharides and their modification approaches: a review. International Journal of Food Properties, 18(2), 332–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2012.693561
Angelina, & Vijayendra, S. V. N. (2015). Microbial biopolymers: the exopolysaccharides. In: V. Kalia (Ed.), Microbial factories (pp. 113–125). New Delhi: Springer.
Alizadeh-Sani, M., Ehsani, A., Moghaddas, K. E., & Khezerlou, A. (2019). Microbial gums: introducing a novel functional component of edible coatings and packaging. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(17), 6853–6866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09966-x
Arancon, R. A. D., Lin, C. S. K., Chan, K. M., Kwan, T. H., & Luque, R. (2013). Advances on waste valorization: new horizons for a more sustainable society. Energy Science & Engineering, 1(2), 53–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.9
Avramescu, S. M., Butean, C., Popa, C. V., Ortan, A., Moraru, I., & Temocico, G. (2020). Edible and functionalized films/coatings—performances and perspectives. Coatings, 10(7), 687. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2012.693561
Azeredo, M. C., Barud, H., Farinas, C. S., Vasconcellos, V. M., & Claro, A. M. (2019). Bacterial cellulose as a raw material for food and food packaging applications. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 3, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00007
Baicu, A. A., & Popa, M. E. (2018). Trends in prolonging the post-harwest life of strawberries – a review. Food Technology, 42(1), 9–16.
Banks, N. H., Dadzie, B. K., & Cleland, D. J. (1993). Reducing gas exchange of fruits with surface coatings. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 3(3), 269–284.
Barcelos, M. C. S., Vespermann, K. A. C., Pelissari, F. M. & Molina, G. (2019). Current status of biotechnological production and applications of microbial exopolysaccharides. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 60(9), 1475– 1495. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1575791
Barone, J. R., & Medynets, M. (2007). Thermally processed levan polymers. Carbohydrate Polymers, 69(3), 554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.01.017
Baraiya, N. S., Ramana, R. T. V., & Thakkar, V. R. (2016). composite coating as a carrier of antioxidants improves the postharvest shelf life and quality of table grapes (Vitis vinifera l. var. Thompson seedless). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 18(1), 93–107.
Becker, A. (2015). Challenges and perspectives in combinatorial assembly of novel exopolysaccharide biosynthesis pathways. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 687. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00687
Bostan, M. S., Mutlu, E. C., Kazak, H., Keskin, S., Öner, E. T., & Eroglu, M. S. (2014). Comprehensive characterization of chitosan/PEO/levan ternary blend films. Carbohydrate Polymers, 102, 993–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.096
Cazon, P., Velazquez, G., Ramirez, J. A., & Vazquez, M. (2017). Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocolloids, 68, 136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.09.009
Chen, X., Gao, H., & Ploehn, H. J. (2014). Montmorillonite-levan nanocomposites with improved thermal and mechanical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 101, 565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.073
Combie, J., & Öner, E. T. (2018). From healing wounds to resorbable electronics, levan can fill bioadhesive roles in scores of markets. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 14, 011001. https://doi.org/10.1088/11748-319
Crater, J. S., & Lievense, J. C. (2018). Scale-up of industrial microbial processes. FEMS microbiology letters, 365(13), fny138. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny138
Davidović, S., Miljković, M., Tomić, M., Gordić, M., Nešić, A., & Dimitrijević, S. (2018). Response surface methodology for optimisation of edible coatings based on dextran from Leuconostoc mesenteroides T3. Carbohydrate Polymers, 184, 207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.061
De Souza, E. L., Lundgren, G. A., Oliveira, K. Á. R., Berger, L. R. R., & Magnani, M. (2019). An analysis of the published literature on the effects of edible coatings formed by polysaccharides and essential oils on postharvest microbial control and overall quality of fruit. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 18(6), 1947–1967. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12498
Devi, G. K., & Alamu, A. (2013). Production of biopolymer levan by Bacillus subtilis using non-ionic surfactants. Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 3(4), 149–154.
Dhaka, R., & Upadhyay, A. (2018). Edible films and coatings: a brief overview. The Pharma Innovation, 7(7), 331–333.
Diab, T., Biliaderis, C. G., Gerasopoulos, D., & Sfakiotakis, E. (2001). Physicochemical properties and application of pullulan edible films and coatings in fruit preservation. The Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 81(10), 988–1000. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.883
El-Badawy, H. E. M., Baiea, M. H. M., Eman, A. A., & El-Moneim, A. (2012). Efficacy of propolis and wax coatings in improving fruit quality of ‘Washington’ navel orange under cold storage. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 8(5), 420–428.
El-Ramady, H. R., Domokos-Szabolcsy, E., Abdalla, N. A., Taha, H. S. & Fári, M. (2015). Postharvest management of fruits and vegetables storage, In: E. Lichtfouse (Eds.), Sustainable Agriculture Reviews Volume 15 (pp. 65–152). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09132-7_2
Eroglu, E., Torun, M., Dincer, C., & Topuz, A. (2014). Influence of pullulan-based edible coating on some quality properties of strawberry during cold storage. Packaging Technology and Science, 27(10), 831–838. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2077
Fereydoon, M., & Ebnesajjad, S. (2013). Development of high barrier films for food packaging. In S. Ebnesajjad (Ed.), Plastic films in food packaging (pp. 671–692). Elsevier.
Gahlawat, G., & Srivastava, A. K. (2017). Model-based nutrient feeding strategies for the increased production of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Alcaligenes latus. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 183(2), 530–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2482-8
Ghasemlou, M., Khodaiyan, F., Oromiehie, A., & Yarmand, M. S. (2011). Development and characterisation of a new biodegradable edible film made from kefiran, an exopolysaccharide obtained from kefir grains. Food Chemistry, 127(4), 1496–1502.
Galgano, F., Condelli, N., Favati, F., Di Bianco V., Perretti G., & Caruso M. C. (2015). Biodegradable packaging and edible coating for fresh-cut fruits and vegetables. Italian Journal of Food Science, 27, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.14674/1120-1770%2Fijfs.v27i1.70
Galus, S., Arik, K., Emine, A., Gniewosz, M., & Krasniewska, K. (2020). Novel materials in the preparation of edible films and coatings—A review. Coatings, 10(7), 674–688. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10070674
Gaston, A., Osorio, S., Denoyes, B., & Rothan, C. (2020). Applying the Solanaceae strategies to strawberry crop improvement. Trends in Plant Science, 25(2), 130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2019.10.003
Giampieri, F., Tulipanim S., Alvarez-Suarez, J. M., Quiles, J. L., Mezzetti, B., & Battino, M. (2012). The strawberry: Composition, nutritional quality, and impact on human health. Nutrition, 28(1), 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2011.08.009
Gil-Giraldo, E. Y., Duque-Cifuentes, A. L., & Quintero-Castaño, V. D. (2018). Obtaining minimally processed strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa) products and their physicochemical, microbiological, and sensory characterization by using edible coatings. Dyna, 85, 183–191.
Golly, M. K., Ma, H., Sarpong, F., Dotse, B. P.,Oteng-Darko, P., & Dong,Y. (2019). Shelf-life extension of grape (Pinot noir) by xanthan gum enriched with ascorbic and citric acid during cold temperature storage. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 56(11), 4867–4878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03956-7
González Sandoval, D. C., Luna Sosa, B., Martínez-Ávila, G. C. G., Rodríguez Fuentes, H., Avendaño Abarca, V. H., & Rojas, R. (2019). Formulation and characterization of edible films based on organic mucilage from Mexican Opuntia ficus-indica. Coatings, 9(8), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080506
Guerreiro, A. C. (2015). Innovative edible coatings to improve storage of small fruits and fresh cut. Ph D Thesis, Universidade do Algarve. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/84111522.pdf
Hagenmaier, R. D. (2005). A comparison of ethane, ethylene and CO2 peel permeance for fruit with different coatings. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 37(6), 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.02.012
Hannum, S. M. (2004). Potential impact of strawberries on human health: A review of the science. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 44(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690490263756
Hassan, B., Chatha, S. A. S., Hussain, A. I., Zia, K. M., & Akhtar, N. (2018). Recent advances on polysaccharides, lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 109, 1095–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.097
Hing, Y., Li, W., Wang, Q., Li, X., Xu, Q., Guo, X., Bi, X., et al. (2019). Antimicrobial nanoparticles incorporated in edible coatings and films for the preservation of fruits and vegetables. Molecules, 24(9), 1695–1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091695
Huber, A. E., Kaplan, D. L., & Viney, C. (1994). Liquid crystallinity of levan/water/starch solutions. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2(4), 195–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02067445
Janjarasskul, T., & Krochta, J. M. (2010). Edible packaging materials. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 1(1), 415–448. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100836
Jindal, N., & Khattar, S. (2018). Microbial polysaccharides in food industry In: A.M.Grumezesku & A.M.Holban (Eds.) Biopolymers for Food Design (pp. 95–123). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811449-0.00004-9415448
Kahramanoğlu, İ, Okatan, V., & Wan, C. (2020). Biochemical composition of propolis and its efficacy in maintaining postharvest storability of fresh fruits and vegetables. Journal of Food Quality, 2020, e8869624.
Kambourova, M., Oner, E.T., & Poli, A. (2015). Exopolysaccharides from prokaryotic microorganisms – promising sources for white biotechnology, In: A.Pandey, R. Höfer. Ch. Larroche,M. Taherzadeh & M. Nampoothiri (Eds.), Industrial biorefineries & white biotechnology (pp. 523–554). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2012.693561
Kolesovs, S., & Semjonovs, P. (2020). Production of bacterial cellulose from whey - current state and prospects. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104(18):7723–7730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10803-9
Krasniewska, K., Galus, S., & Gniewosz, M. (2020). Biopolymers-based materials containing silver nanoparticles as active packaging for food applications—a review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 698.
Kumar, A. S., Mody, K., & Jha, B. (2007). Bacterial exopolysaccharides – a perception. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 47(2), 103–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200610203
Kumar, P., & Sethi, S. (2018). Edible coating for fresh fruit: A review. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7(5), 2619–2626. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.303
Kumar, N., & Neeraj (2019). Polysaccharide-based component and their relevance in edible film/coating: A review. Nutrition & Food Science, 49(5), 793–823. https://doi.org/10.1108/nfs-10-2018-0294
Kwon, K. Y., Lee, J. S., Ko, G. J., Sunwoo, S. H., Lee, S., Jo, Y. J., et al. (2018). Biosafe, eco-friendly levan polysaccharide toward transient electronics. Small, 32, e1801332. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201801332.
Lacroix, M. L., & Tien, C. L. (2005). Edible films and coatings from nonstarch polysaccharides. In: H. Jung (Ed.) Innovations in Food Packaging (pp. 338–361). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012311632-1/50052-8
Lakshmi Bhavani, A., & Nisha, J. (2010). Dextran—the polysaccharide with versatile uses. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences, 1(4), 569–573.
Leite, B. S. F., Borges, C. D., Carvalho, P. G. B., & Botrel, N. (2015). Revestimento comestível à base de goma xantana, compostos lipofílicos e/ou cloreto de cálcio na conservação de morangos. Revista Brasileira De Fruticultura, 37(4), 1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-2945-228/14
Li, L., Sun, J., Gao, H., Shen, Y., Li, Ch., Yi, P., He, X., et al. (2017). Effects of polysaccharide-based edible coatings on quality and antioxidant enzyme system of strawberry during cold storage. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2017(3), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9746174
Liston, A., Cronn, R., & Ashman, T. L. (2014). Fragaria: A genus with deep historical roots and ripe for evolutionary and ecological insights. American Journal of Botany, 101(10), 1686–99. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400140
Lule, V. K., Singh, R., Pophaly, S. D., Poonam, S. K., & Tomar, S. K. (2016). Production and structural characterisation of dextran from an indigenous strain of Leuconostoc mesenteroides BA08 in whey. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 69(4), 520–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12271
Luzi, F., Torre, L., Kenny, J., & Puglia, D. (2019). Bio - and fossil-based polymeric blends and nanocomposites for packaging: structure–property relationship. Materials, 12(3), 471–520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030471
Mantovan, J., Bersaneti, G. T., Faria-Tischer, P. C., Celligoi, M. A., & Mali, S. (2018). Use of microbial levan in edible films based on cassava starch. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 18, 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FPSL.2018.08.003
Marangoni Junior, L., Vieira, R. P., & Anjos, C. A. R. (2020). Kefiran-based films: fundamental concepts, formulation strategies and properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 246, 116609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116609.
Maringgal, B., Hashim, N., Mohamed Amin Tawakkal, I. S., & Muda Mohamed, M. T. (2020). Recent advance in edible coating and its effect on fresh/fresh-cut fruits quality. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 96, 253–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.12.024
Mohamed, S. A. A., El-Sakhawy, M., & El-Sakhawy, M. A. Monem. (2020). Polysaccharides, protein and lipid - based natural edible films in food packaging: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 238, 116178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116178
Mohite, B. V., Koli, S. H., Narkhede, C. P., Patil, S. N., & Patil, S. V. (2017). Prospective of microbial exopolysaccharide for heavy metal exclusion. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 183(3), 582–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2591-4
Mohsin, A., Zaman, W. Q., Guo, M., Ahmed, W., Khan, I. M., Niazi S., et al. (2020). Xanthan-Curdlan nexus for synthesizing edible food packaging films. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 162, 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.008
Moncayo-Martínez, D. (2013). Desarrollo de un recubrimiento comestible a partir de un biopolímero para prolongar la vida útil de frutas frescas. Tesis de maestría, Universidad Nacional de Colombia. http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/44864/1/24336979.2013.pdf.
Müller, K., Scheuerer, Z., Florian, V., Skutschik, T., & Sängerlaub, S. (2017). Comparison of test methods for oxygen permeability: Optical method versus carrier gas method. Polymer Testing, 63, 126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.08.006
Nair, M. S., Tomar, M., Punia, S., Kukula-Koch, W., & Kumar M.(2020). Enhancing the functionality of chitosan - and alginate-based active edible coatings/films for the preservation of fruits and vegetables: A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 164, 304–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.083
Nešić, A., Cabrera-Barjas, G., Dimitrijević-Branković, S., Davidović, S., Radovanović, N., & Delattre, C. (2019). Prospect of polysaccharide-based materials as advanced food packaging. Molecules, 25(1), 135–170. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010135
Nielsen, J., & Keasling, J. D. (2016). Engineering cellular metabolism. Cell, 164(6), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.004
Niu, B., Shao, P., Chen, H., & Sun, P. (2019). Structural and physiochemical characterization of novel hydrophobic packaging films based on pullulan derivatives for fruits preservation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 208, 276–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.070
Nwodo, U., Green, E., & Okoh, A. (2012). Bacterial exopolysaccharides: functionality and prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(11), 14002–14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114002
Olivas, G. I., & Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V. (2005). Edible coatings for fresh-cut fruits. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 45(7–8), 657–670. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690490911837
Olivas, G. I., Dávila-Aviña, J., Salas-Salazar, N. A., & Molina, F. J. (2008). Use of edible coatings to preserve the quality of fruits and vegetables during storage. Stewart Postharvest Review, 4(3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.2212/spr.2008.3.6
Onilude, A. A., Olaoye, O., Fadahunsi, I. F., Owoseni, A., Garuba, E. O., & Atoyebi, T. (2013). Effects of cultural conditions on dextran production by Leuconostoc spp. International Food Research Journal, 20(4), 1645–1651.
Palou, L., Valencia-Chamorro, S. A., & Pérez-Gago, M. B. (2015). Antifungal edible coatings for fresh citrus fruit: A review. Coatings, 5, 962–986.
Panahirad, S., Dadpour, M., Peighambardoust, S. H., Soltanzadeh, M., Gullón, B., Alirezalu, K., & Lorenzo, J. M. (2021). Applications of carboxymethyl cellulose – and pectin-based active edible coatings in preservation of fruits and vegetables: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 110, 663–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.025
Park, H. J. (1999). Development of advanced edible coatings for fruits. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 10(8), 254–260.
Pascall, M. A., & Lin, S. J. (2013). The application of edible polymeric films and coatings in the food industry. Journal of Food Processing and Technology, 4, e116. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7110.1000e116
Piermaria, J., Bosch, A., Pinotti, A., Yantorno, O., Garcia, M. A., & Abraham, A. G. (2011). Kefiran films plasticized with sugars and polyols: Water vapor barrier and mechanical properties in relation to their microstructure analyzed by ATR/FT-IR spectroscopy. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 1261–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.11.024
Pina-Barrera, A. M., Alvarez-Romanm R., Baez-Gonzalez, J. G., Amaya-Guerra, C. A., Rivas-Morales, C., et al. (2019). Application of a multisystem coating based on polymeric nanocapsules containing essential oil of Thymus Vulgaris L. to increase the shelf life of table grapes (Vitis Vinifera L.). IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 18(4), 549–557. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2019.2941931
Pobiega, K., Igielska, M., Walodarczyk, P., & Gniewosz, M. (2020). The use of pullulan coatings with propolis extract to extend the shelf life of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) fruit. Journal of Food Processing and Technology, 56(2),1013–1020. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7110.1000e116
Quezada Gallo, J., Gramin, A., Pattyn, C., Díaz Amaro, M. R., Debeaufort, F., & Voilley, A. (2005). Biopolymers used as edible coating to limit water transfer, colour degradation and aroma compound 2-pentanone lost in Mexican fruits. Acta Horticulturae, 682, 1709–1716. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2005.682.228
Radev, R., & Pashova, S. (2020). Application of edible films and coatings for fresh fruit and vegetables. Acces La Success, 21(177), 108–112.
Ramesh, H. P., & Tharanathan, R. N. (2003). Carbohydrates – the renewable raw materials of high biotechnological value. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 23(2), 149–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/713609312
Ramos, Ó. L., Reinas, I., Silva, S. I., Catalão, J., Cerqueira, M., Pereira, R. N., et al. (2013). Effect of whey protein purity and glycerol content upon physical properties of edible films manufactured therefrom. Food Hydrocollids, 30(1), 110–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.05.001
Ribeiro, A. M., Estevinho, B. N., & Rocha, F. (2020). Preparation and incorporation of functional ingredients in edible films and coatings. Food and Bioprocess Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02528-4
Roca, C., Alves, V. D., Freitas, F., & Reis, M. A. (2015). Exopolysaccharides enriched in rare sugars: bacterial sources, production, and applications. Frontiers in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00288
Sadh, P. K., Duhan, S., & Duhan, J. (2018). Agro-industrial wastes and their utilization using solid state fermentation: A review. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0187-z
Saklani, P., Siddnath Das, S. K., & Singh, S. M. (2019). A review of edible packaging for foods. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8(7), 2885–2895. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.807.359
Saleem, M. S., Ejaz, S., Anjum, M. A., Nawaz, A., Naz, S., Hussain, S., Ali, S. & Canan, I. (2020). Postharvest application of gum arabic edible coating delays ripening and maintains quality of persimmon fruits during storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 44(8), e14583. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14583
Salehi, F. (2020). Edible coating of fruits and vegetables using natural gums: A review. International Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538362.2020.1746730
Shao, P., Niu, B., Chen, H., & Sun, P.(2018). Fabrication and characterization of tea polyphenols loaded pullulan-CMC electrospun nanofiber for fruit preservation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 107(Pt B), 1908–1914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.054
Shit, S. C., & Shah, P. M. (2014). Edible polymers: Challenges and opportunities. Journal of Polymers, 2014(427259), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/427259
Semjonovs, P., Shakirova, L., Broks, R., Kistkins, S., & Zikmanis, P. (2017). Influence of environmental factors on extracellular fructan and oligosaccharide production by Gluconobacter nephelii. Research Journal of Microbiology, 12, 33–41. https://doi.org/10.3923/jm.2017.33.41
Sengupta, D., Datta, S., & Biswas, D. (2018). Towards a better production of bacterial exopolysaccharides by controlling genetic as well as physico-chemical parameters. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(4), 1587–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8745-7
Senturk Parreidt, T., Schott, M., Schmid, M., & Müller, K. (2018a). Effect of presence and concentration of plasticizers, vegetable oils, and surfactants on the properties of sodium-alginate-based edible coatings. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030742
Senturk Parreidt, T., Müller, K., & Schmid, M. (2018b). Alginate-based edible films and coatings for food packaging applications. Foods, 7(10), 170–208. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7100170
Shahbazi, Y., Shavisi, N., & Karami, N. (2020). Development of edible bioactive coating based on mucilages for increasing the shelf life of strawberries. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00638-3
Sharma, P., Shehin, V. P., Kaur, N., & Vyas ,P. (2019). Application of edible coatings on fresh and minimally processed vegetables: a review. International Journal of Vegetable Science, 25(3), 295–314. https://doi.org/10.1108/NFS-08-2018-0246
Siracusa, V, Rocculi, P., Romani, S., & Dalla Rosa, M. (2008). Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 19(12), 634–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2008.07.003
Skrovankova, S., Sumczynski, D., Mlcek, J., Jurikova, T., & Sochor, J. (2015). Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in different types of berries. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(10), 24673–24706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024673
Souza, B. W. S., Cerqueira, M. A., Teixeira, J. A., & Vicente, A. A. (2010). The use of electric fields for edible coatings and films development and production: A review. Food Engineering Reviews, 2(4), 244–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-010-9029-x
Stroescu, M., Isopencu, G., Busuioc, C., & Stoica-Guzun, A. (2018). Antimicrobial food pads containing bacterial cellulose and polysaccharides. In: Md. I. H. Mondal (Ed.) Cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels, polymers and polymeric composites: A reference series (pp. 1 – 36). Springer International Publishing AG. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76573-0_3-1
Tabasum, S., Noreen, A., Maqsood, M. F., Umar, H., Akram N, Nazli, Z. -i. -H., et al. (2018). A review on versatile applications of blends and composites of pullulan with natural and synthetic polymers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 120(Pt A), 603–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.154
Tahir, H. E., Xiaobo, Z., Mahunu, G. K., Arslan, M., Abdalhai, M., & Zhihua, L. (2019). Recent developments in gum edible coating applications for fruits and vegetables preservation: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 224, 115141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115141
Tan, K. X., Chamundeswari, V. N., & Loo, S. C. J. (2020). Prospects of kefiran as a food-derived biopolymer for agri-food and biomedical applications. RSC Advances, 10(42), 25339–25351. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA02810J
Tiwari, O. N., Sasmal, S., Kataria, A. K., & Devi, I. (2020). Application of microbial extracellular carbohydrate polymeric substances in food and allied industries. 3 Biotech, 10(5), 221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02200-w
Tomadoni, B., Moreira, M. R., Pereda, M., & Ponce, A. G. (2018). Gellan-based coatings incorporated with natural antimicrobials in fresh-cut strawberries: Microbiological and sensory evaluation through refrigerated storage. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 97, 384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.07.029
Tomulescu, C., Stoica, R., Sevcenco, C., Casarica, A., Moscovici, M., & Vamanu, A. (2016). Levan-a mini review. Scientific Bulletin. Series F. Biotechnologies, 20, 309–317.
Totad, M. G., Sharma, R. R., & Verma, M. A. (2019). Effect of edible coatings on ‘Misty’ blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) fruits stored at low temperature. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 41, 183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2973-z
Treviño-Garza, M. Z., García, S., del Socorro Flores-González, M., & Arévalo-Niño, K. (2015). Edible active coatings based on pectin, pullulan, and chitosan increase quality and shelf life of strawberries (Fragaria ananassa). Journal of Food Science, 80(8), M1823–M1830. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12938
Tsang, Y. F., Kumar, V., Samadar, P., Yang, Y., Lee, J., Ok, Y. S., et al. (2019). Production of bioplastic through food waste valorization. Environment International, 127, 625–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.076
Urtuvia, V., Maturana, N., Acevedo, F., Peña, C., & Díaz-Barrera, A. (2017). Bacterial alginate production: an overview of its biosynthesis and potential industrial production. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2363-x
Wang, K., Du, L., Zhang, C., Lu, Z., Lu, F., & Zhao, H. (2019). Preparation of chitosan/curdlan/carboxymethyl cellulose blended film and its characterization. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 56(12), 5396–5404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04010-2
Whitfield, C., Wear, S. S., & Sande, C. (2020). Assembly of bacterial capsular polysaccharides and exopolysaccharides. Annual Review of Microbiology, 74, 521–543. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-011420-075607
Widyaningrum, D., & Meindrawan, B. (2020). The application of microbial extracellular polymeric substances in food industry. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 426, 012181.
Zambrano-Zaragoza, M. L., Quintanar-Guerrero, D., Del Real, A., & González –Reza, R. M., Cornejo-Villegas, M. A. & Gutiérrez-Cortez, E. . (2020). Effect of nano-edible coating based on beeswax solid lipid nanoparticles on strawberry’s preservation. Coatings, 10(3), 253–264. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030253
Zhang, Y., Zhou, L., Zhang, C., Show, P. L., Du, A., Fu, J., & Ashokkumar, V. (2020). Preparation and characterization of curdlan/polyvinyl alcohol/ thyme essential oil blending film and its application to chilled meat preservation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 247, 116670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116670
Zhang, Z., Vriesekoop, F., Yuan, Q., & Liang, H. (2014). Effects of nisin on the antimicrobial activity of d-limonene and its nanoemulsion. Food Chemistry, 150, 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.160
Zhu, J., Wang, Q., Han, L., Zhang, C., Wang, Y., Tu, K., et al. (2021). Effects of caprolactam content on curdlan-based food packaging film and detection by infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 245, 118942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118942
Zikmanis, P., Kolesovs, S., & Semjonovs, P. (2020a). Production of biodegradable microbial polymers from whey. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 7, 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00326-6
Zikmanis, P., Brants, K., Kolesovs, S., & Semjonovs, P. (2020b). Extracellular polysaccharides produced by bacteria of the Leuconostoc genus. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 36, 161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02937-9
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Support Service of the Republic of Latvia (grant number 19–00-A01612-000004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zikmanis, P., Juhņeviča-Radenkova, K., Radenkovs, V. et al. Microbial Polymers in Edible Films and Coatings of Garden Berry and Grape: Current and Prospective Use. Food Bioprocess Technol 14, 1432–1445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02666-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02666-3