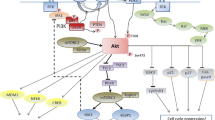
Abstract
Purpose of Review
The outcome of patients with lymphoid malignancies has markedly improved in recent years which is likely due to a combination of advances in supportive care, and therapeutic options. In this article, we will provide an overview over the role PI3-kinase signalling, one of the most important dysregulated pathways in cancer, and its successful inhibition in lymphoma.
Recent Findings
PI3-kinase inhibitors have shown remarkable activity in an increasing subset of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The first drug to be approved was idelalisib for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma and CLL/SLL as monotherapy, or in combination with rituximab, respectively. After an initial setback related to increased toxicity including deaths observed in several upfront studies, there has been a resurgence in interest in this pathway following the promising efficacy of second-generation PI3K inhibitors including in patients with T cell lymphomas.
Summary
PI3K inhibition continues to be an invaluable tool in the therapy of patients with lymphoid malignancies if managed cautiously. Preclinical models are helpful in predicting possible side effects and identifying new lymphoma subtypes that may be susceptible to this class of agents. The future will likely involve rationally designed combinatorial approaches to deepen the response rate and prevent the emergence of resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet. 2017;390(10091):298–310.
Tan D, Horning SJ, Hoppe RT, Levy R, Rosenberg SA, Sigal BM, et al. Improvements in observed and relative survival in follicular grade 1-2 lymphoma during 4 decades: the Stanford University experience. Blood. 2013;122(6):981–7.
Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124–30.
Younes A, Ansell S, Fowler N, Wilson W, de Vos S, Seymour J, et al. The landscape of new drugs in lymphoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14(6):335–46.
Kuppers R. Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(4):251–62.
Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Mermel CH, Robinson JT, Garraway LA, Golub TR, et al. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature. 2014;505(7484):495–501.
Okkenhaug K, Vanhaesebroeck B. PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(4):317–30.
Young RM, Staudt LM. Targeting pathological B cell receptor signalling in lymphoid malignancies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(3):229–43.
Bi L, Okabe I, Bernard DJ, Wynshaw-Boris A, Nussbaum RL. Proliferative defect and embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for a deletion in the p110alpha subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(16):10963–8.
Bi L, Okabe I, Bernard DJ, Nussbaum RL. Early embryonic lethality in mice deficient in the p110beta catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Mamm Genome. 2002;13(3):169–72.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Ali K, Bilancio A, Geering B, Foukas LC. Signalling by PI3K isoforms: insights from gene-targeted mice. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30(4):194–204.
Clayton E, Bardi G, Bell SE, Chantry D, Downes CP, Gray A, et al. A crucial role for the p110delta subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in B cell development and activation. J Exp Med. 2002;196(6):753–63.
Okkenhaug K, Bilancio A, Farjot G, Priddle H, Sancho S, Peskett E, et al. Impaired B and T cell antigen receptor signaling in p110delta PI 3-kinase mutant mice. Science. 2002;297(5583):1031–4.
Hirsch E, Katanaev VL, Garlanda C, Azzolino O, Pirola L, Silengo L, et al. Central role for G protein-coupled phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in inflammation. Science. 2000;287(5455):1049–53.
Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Jones RG, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Stanford WL, Bolon B, et al. Function of PI3Kgamma in thymocyte development, T cell activation, and neutrophil migration. Science. 2000;287(5455):1040–6.
Reif K, Okkenhaug K, Sasaki T, Penninger JM, Vanhaesebroeck B, Cyster JG. Cutting edge: differential roles for phosphoinositide 3-kinases, p110 gamma and p110 delta, in lymphocyte chemotaxis and homing. J Immunol. 2004;173(4):2236–40.
Kaneda MM, Messer KS, Ralainirina N, Li HY, Leem CJ, Gorjestani S, et al. PI3K gamma is a molecular switch that controls immune suppression (vol 539, pg 437, 2016). Nature. 2017;542(7639):124.
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB, et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;463(7277):88–92.
Lannutti BJ, Meadows SA, Herman SE, Kashishian A, Steiner B, Johnson AJ, et al. CAL-101, a p110delta selective phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of B-cell malignancies, inhibits PI3K signaling and cellular viability. Blood. 2011;117(2):591–4.
Srinivasan L, Sasaki Y, Calado DP, Zhang B, Paik JH, DePinho RA, et al. PI3 kinase signals BCR-dependent mature B cell survival. Cell. 2009;139(3):573–86.
Hoellenriegel J, Meadows SA, Sivina M, Wierda WG, Kantarjian H, Keating MJ, et al. The phosphoinositide 3′-kinase delta inhibitor, CAL-101, inhibits B-cell receptor signaling and chemokine networks in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118(13):3603–12.
Burger JA, Tsukada N, Burger M, Zvaifler NJ, Dell’Aquila M, Kipps TJ. Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood. 2000;96(8):2655–63.
Ali K, Soond DR, Pineiro R, Hagemann T, Pearce W, Lim EL, et al. Inactivation of PI(3)K p110delta breaks regulatory T-cell-mediated immune tolerance to cancer. Nature. 2014;510(7505):407–11.
Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S, Wagner-Johnston ND, Schuster SJ, Jurczak WJ, et al. PI3Kdelta inhibition by idelalisib in patients with relapsed indolent lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(11):1008–18.
Furman RR, Sharman JP, Coutre SE, Cheson BD, Pagel JM, Hillmen P, et al. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(11):997–1007.
Coutre SE, Barrientos JC, Brown JR, de Vos S, Furman RR, Keating MJ, et al. Management of adverse events associated with idelalisib treatment: expert panel opinion. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(10):2779–86.
Cheah CY, Nastoupil LJ, Neelapu SS, Forbes SG, Oki Y, Fowler NH. Lenalidomide, idelalisib, and rituximab are unacceptably toxic in patients with relapsed/refractory indolent lymphoma. Blood. 2015;125(21):3357–9.
Smith SM, Pitcher BN, Jung SH, Bartlett NL, Wagner-Johnston N, Park SI, et al. Safety and tolerability of idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab in relapsed and refractory lymphoma: the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology A051201 and A051202 phase 1 trials. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4(4):e176–e82.
Barr PM, Saylors GB, Spurgeon SE, Cheson BD, Greenwald DR, O’Brien SM, et al. Phase 2 study of idelalisib and entospletinib: pneumonitis limits combination therapy in relapsed refractory CLL and NHL. Blood. 2016;127(20):2411–5.
Cheah CY, Fowler NH. Idelalisib in the management of lymphoma. Blood. 2016;128(3):331–6.
Cuneo A, Barosi G, Danesi R, Fagiuoli S, Ghia P, Marzano A, et al. Management of adverse events associated with idelalisib treatment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and follicular lymphoma: a multidisciplinary position paper. Hematol Oncol. 2019;37(1):3–14.
Liu N, Rowley BR, Bull CO, Schneider C, Haegebarth A, Schatz CA, et al. BAY 80-6946 is a highly selective intravenous PI3K inhibitor with potent p110alpha and p110delta activities in tumor cell lines and xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(11):2319–30.
Patnaik A, Appleman LJ, Tolcher AW, Papadopoulos KP, Beeram M, Rasco DW, et al. First-in-human phase I study of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946), an intravenous pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(10):1928–40.
• Dreyling M, Morschhauser F, Bouabdallah K, Bron D, Cunningham D, Assouline SE, et al. Phase II study of copanlisib, a PI3K inhibitor, in relapsed or refractory, indolent or aggressive lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(9):2169–78 The results of this phase II study were the basis for the approval of copanlisib for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma.
Dreyling M, Santoro A, Mollica L, Leppa S, Follows GA, Lenz G, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety from the copanlisib CHRONOS-1 study in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;132.
Flinn IW, O’Brien S, Kahl B, Patel M, Oki Y, Foss FF, et al. Duvelisib, a novel oral dual inhibitor of PI3K-delta,gamma, is clinically active in advanced hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2018;131(8):877–887.
• Flinn IW, Miller CB, Ardeshna KM, Tetreault S, Assouline SE, Mayer J, et al. DYNAMO: a phase II study of duvelisib (IPI-145) in patients with refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(11):912–22 The results of this study were the basis for the approval of duvelisib for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma.
• Flinn IW, Hillmen P, Montillo M, Nagy Z, Illes A, Etienne G, et al. The phase 3 DUO trial: duvelisib vs ofatumumab in relapsed and refractory CLL/SLL. Blood. 2018;132(23):2446–55 The results of this study were the basis for the approval of duvelisib for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL.
Deng CC, Lipstein MR, Scotto L, Serrano XOJ, Mangone MA, Li SR, et al. Silencing c-Myc translation as a therapeutic strategy through targeting PI3K delta and CK1 epsilon in hematological malignancies. Blood. 2017;129(1):88–99.
Bryja V, Schulte G, Rawal N, Grahn A, Arenas E. Wnt-5a induces Dishevelled phosphorylation and dopaminergic differentiation via a CK1-dependent mechanism. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(4):586–95.
Sato A, Kayama H, Shojima K, Matsumoto S, Koyama H, Minami Y, et al. The Wnt5a-Ror2 axis promotes the signaling circuit between interleukin-12 and interferon-gamma in colitis. Sci Rep-Uk. 2015;5.
Burris HA, Flinn IW, Patel MR, Fenske TS, Deng CC, Brander DM, et al. Umbralisib, a novel PI3K delta and casein kinase-1 epsilon inhibitor, in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and lymphoma: an open-label, phase 1, dose-escalation, first-in-human study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(4):486–96.
Nastoupil LJ, Lunning MA, Vose JM, Schreeder MT, Siddiqi T, Flowers CR, et al. Tolerability and activity of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a phase 1 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6(2):E100–E9.
Davids MS, Kim HT, Nicotra A, Savell A, Francoeur K, Hellman JM, et al. Umbralisib in combination with ibrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or mantle cell lymphoma: a multicentre phase 1-1b study. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6(1):e38–47.
Soumerai JD, Pagel JM, Jagadeesh D, Salman HS, Kenkre VP, Asch AS, et al. Initial results of a dose escalation study of a selective and structurally differentiated PI3K delta inhibitor, ME-401, in relapsed/refractory (R/R) follicular lymphoma (FL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15).
Zelenetz AD, Soumerai JD, Jagadeesh D, Reddy N, Stathis A, Asch AS, et al. Preliminary safety and efficacy results with an intermittent schedule of the PI3k delta inhibitor ME-401 alone or in combination with rituximab for B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2018;132.
Younes A, Salles G, Martinelli G, Bociek RG, Barrigon DC, Barca EG, et al. Pan-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition with buparlisib in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica. 2017;102(12):2104–12.
Bendell JC, Rodon J, Burris HA, de Jonge M, Verweij J, Birle D, et al. Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(3):282–90.
Nanni P, Nicoletti G, Palladini A, Croci S, Murgo A, Ianzano ML, et al. Multiorgan metastasis of human HER-2+ breast cancer in Rag2-/-;Il2rg-/- mice and treatment with PI3K inhibitor. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39626.
Di Leo A, Johnston S, Lee KS, Ciruelos E, Lonning PE, Janni W, et al. Buparlisib plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer progressing on or after mTOR inhibition (BELLE-3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(1):87–100.
Baselga J, Im SA, Iwata H, Cortes J, De Laurentiis M, Jiang Z, et al. Buparlisib plus fulvestrant versus placebo plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (BELLE-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(7):904–16.
Phillips TJ, Forero-Torres A, Sher T, Diefenbach CS, Johnston P, Talpaz M, et al. Phase 1 study of the PI3K delta inhibitor INCB040093 +/- JAK1 inhibitor itacitinib in relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;132(3):293–306.
Younes A, Berdeja JG, Patel MR, Flinn I, Gerecitano JF, Neelapu SS, et al. Safety, tolerability, and preliminary activity of CUDC-907, a first-in-class, oral, dual inhibitor of HDAC and PI3K, in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma or multiple myeloma: an open-label, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(5):622–31.
Moskowitz AJ, Lunning MA, Horwitz SM. How I treat the peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2014;123(17):2636–44.
Horwitz SM, Koch R, Porcu P, Oki Y, Moskowitz A, Perez M, Myskowski P, Officer A, Jaffe JD, Morrow SN, Allen K, Douglas M, Stern H, Sweeney J, Kelly P, Kelly V, Aster JC, Weaver D, Foss FM, Weinstock DM Activity of the PI3K-delta,gamma inhibitor duvelisib in a phase 1 trial and preclinical models of T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;131(8):888–898.
Horwitz SM, Moskowitz AJ, Jacobsen ED, Mehta-Shah N, Khodadoust MS, Fisher DC, et al. The combination of duvelisib, a PI3K-δ,γ inhibitor, and romidepsin is highly active in relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma with low rates of transaminitis: results of parallel multicenter, phase 1 combination studies with expansion cohorts. Blood. 2018;132(Suppl 1):683.
Dreyling M, Santoro A, Mollica L, Leppa S, Follows GA, Lenz G, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition by copanlisib in relapsed or refractory indolent lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(35):3898–905.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Gottfried von Keudell has received consulting honoraria from Genentech, Pharmacyclics, and Bayer.
Alison J. Moskowitz has received research support from Seattle Genetics, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Incyte. In addition, she has received honorarium from Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Miragen Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, ADC Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Cell Medica, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Erytech Pharma.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on B-cell NHL, T-cell NHL, and Hodgkin Lymphoma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Keudell, G., Moskowitz, A.J. The Role of PI3K Inhibition in Lymphoid Malignancies. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 14, 405–413 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-019-00540-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-019-00540-w