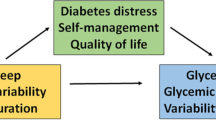
Abstract
Purpose of Review
To review the relationship between sleep and hypoglycemia, sleep characteristics, and their associations with glycemic control in persons with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The effects of sleep interventions and diabetes technology on sleep are summarized.
Recent Findings
Nocturnal hypoglycemia affects objective and subjective sleep quality and is related to behavioral, psychological, and physiological factors. Sleep disturbances are common, including inadequate sleep, impaired sleep efficiency, poor subjective satisfaction, irregular timing, increased daytime sleepiness, and sleep apnea. Some have a bidirectional relationship with glycemic control. Preliminary evidence supports sleep interventions (e.g., sleep extension and sleep coach) in improving sleep and glycemic control, while diabetes technology use could potentially improve sleep.
Summary
Hypoglycemia and sleep disturbances are common among persons with T1D. There is a need to develop sleep promotion programs and test their effects on sleep, glucose, and related outcomes (e.g., self-care, psychological health).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Martyn-Nemeth P, Duffecy J, Fritschi C, Quinn L. Challenges imposed by hypoglycemia in adults with type 1 diabetes. Clin Nurs Res. 2018:1054773818774702. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773818774702.
Nefs GM, Bazelmans E, Donga E, Tack CJ, de Galan BE. Sweet dreams or bitter nightmare: a narrative review of 25 years of research on the role of sleep in diabetes and the contributions of behavioural science. Diabet Med. 2020;37(3):418–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14211.
Monzon A, McDonough R, Meltzer LJ, Patton SR. Sleep and type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: proposed theoretical model and clinical implications. Pediatr Diabetes. 2019;20(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12797.
•• Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E. Interactions between sleep, circadian function, and glucose metabolism: Implications for risk and severity of diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1311(1):151–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12355. This paper provides an update on the current state of knowledge linking sleep disturbance, circadian dysfunction, and glucose metabolism by reviewing experimental, prospective, and interventional studies.
Tracy EL, Berg CA, Kent De Grey RG, Butner J, Litchman ML, Allen NA, et al. The role of self-regulation failures and self-care in the link between daily sleep quality and blood glucose among adults with type 1 diabetes. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2020;54(4):249–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/abm/kaz044.
Bendtson I, Gade J, Thomsen CE, Rosenfalck A, Wildschiødtz G. Sleep disturbances in IDDM patients with nocturnal hypoglycemia. Sleep. 1992;15(1):74–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/15.1.74.
Fulcher G, Singer J, Castaneda R, Fraige Filho F, Maffei L, Snyman J, et al. The psychosocial and financial impact of non-severe hypoglycemic events on people with diabetes: two international surveys. J Med Econ. 2014;17(10):751–61. https://doi.org/10.3111/13696998.2014.946992.
Matyka KA, Crawford C, Wiggs L, Dunger DB, Stores G. Alterations in sleep physiology in young children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: relationship to nocturnal hypoglycemia. J Pediatr. 2000;137(2):233–8. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2000.107186.
Porter PA, Byrne G, Stick S, Jones TW. Nocturnal hypoglycaemia and sleep disturbances in young teenagers with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch Dis Child. 1996;75(2):120–3. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.75.2.120.
Radan I, Rajer E, Ursic Bratina N, Neubauer D, Krzisnik C, Battelino T. Motor activity during asymptomatic nocturnal hypoglycemia in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2004;41(2):33–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-004-0141-3.
Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group. Impaired overnight counterregulatory hormone responses to spontaneous hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes. 2007;8(4):199–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00248.x.
Gill GV, Woodward A, Casson IF, Weston PJ. Cardiac arrhythmia and nocturnal hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes–the ‘dead in bed’ syndrome revisited. Diabetologia. 2009;52(1):42–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-008-1177-7.
Pillar G, Schuscheim G, Weiss R, Malhotra A, McCowen KC, Shlitner A, Peled N, Shedhadeh N. Interactions between hypoglycemia and sleep architecture in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 2003;142(2):163–8.
Wilson DM, Calhoun PM, Maahs DM, Chase HP, Messer L, Buckingham BA, et al. Factors associated with nocturnal hypoglycemia in at-risk adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015;17(6):385–91. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2014.0342.
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Goode K, Atkin SL. Relating mean blood glucose and glucose variability to the risk of multiple episodes of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007;50(12):2553–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0820-z.
Reddy R, El Youssef J, Winters-Stone K, Branigan D, Leitschuh J, Castle J, et al. The effect of exercise on sleep in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(2):443–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13065.
•• Jones TW, Porter P, Sherwin RS, Davis EA, O’Leary P, Frazer F, et al. Decreased epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia during sleep. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(23):1657–62. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199806043382303. This paper shows that sleep impairs counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes by using a case-control design.
Ly TT, Jones TW, Griffiths A, Dart J, Davis EA, Stick S, et al. Hypoglycemia does not change the threshold for arousal from sleep in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012;14(2):101–4. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2011.0144.
Schultes B, Jauch-Chara K, Gais S, Hallschmid M, Reiprich E, Kern W, et al. Defective awakening response to nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. PLoS Med. 2007;4(2): e69. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040069.
Banarer S, Cryer PE. Sleep-related hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in type 1 diabetes: reduced awakening from sleep during hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2003;52(5):1195–203. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.5.1195.
Hart HE, Redekop WK, Assink JH, Meyboom-de Jong B, Bilo HJ. Health-related quality of life in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26. doi:https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.4.1319.
Snogdal LS, Folkestad L, Elsborg R, Remvig LS, Beck-Nielsen H, Thorsteinsson B, et al. Detection of hypoglycemia associated EEG changes during sleep in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;98(1):91–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2012.04.014.
Nguyen LB, Nguyen AV, Ling SH, Nguyen HT. Analyzing EEG signals under insulin-induced hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes patients. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:1980–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2013.6609917.
Hansen GL, Foli-Andersen P, Fredheim S, Juhl C, Remvig LS, Rose MH, et al. Hypoglycemia-associated EEG changes in prepubertal children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2016;10(6):1222–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296816634357.
King P, Kong MF, Parkin H, Macdonald IA, Tattersall RB. Well-being, cerebral function, and physical fatigue after nocturnal hypoglycemia in IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(3):341–5. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.21.3.341.
Bergner EM, Williams R, Hamburger ER, Lyttle M, Davis AC, Malow B, et al. Sleep in teens with type 1 diabetes: perspectives from adolescents and their caregivers. Diabetes Educ. 2018;44(6):541–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145721718799086.
Brod M, Christensen T, Bushnell DM. Impact of nocturnal hypoglycemic events on diabetes management, sleep quality, and next-day function: results from a four-country survey. J Med Econ. 2012;15(1):77–86. https://doi.org/10.3111/13696998.2011.624144.
Martyn-Nemeth P, Phillips SA, Mihailescu D, Farabi SS, Park C, Lipton R, et al. Poor sleep quality is associated with nocturnal glycaemic variability and fear of hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(10):2373–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13765.
Martyn-Nemeth P, Schwarz Farabi S, Mihailescu D, Nemeth J, Quinn L. Fear of hypoglycemia in adults with type 1 diabetes: impact of therapeutic advances and strategies for prevention - a review. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(1):167–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.09.003.
Perfect MM, Elkins GR. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and hypnotic relaxation to treat sleep problems in an adolescent with diabetes. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66(11):1205–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.20732.
Liu J, Bispham J, Fan L, Poon JL, Hughes A, McAuliffe-Fogarty A, et al. Factors associated with fear of hypoglycaemia among the T1D Exchange Glu population in a cross-sectional online survey. BMJ Open. 2020;10(9): e038462. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038462.
Robinson RT, Harris ND, Ireland RH, Macdonald IA, Heller SR. Changes in cardiac repolarization during clinical episodes of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2004;47(2):312–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-003-1292-4.
Perfect MM. Sleep-related disorders in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: current insights. Nature and Science of Sleep. 2020;12:101–23. https://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s152555.
Griggs S, Redeker NS, Grey M. Sleep characteristics in young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;150:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.02.012.
Perez KM, Hamburger ER, Lyttle M, Williams R, Bergner E, Kahanda S, et al. Sleep in type 1 diabetes: Implications for glycemic control and diabetes management. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(2):5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-018-0974-8.
Reutrakul S, Thakkinstian A, Anothaisintawee T, Chontong S, Borel AL, Perfect MM, et al. Sleep characteristics in type 1 diabetes and associations with glycemic control: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2016;23:26–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2016.03.019.
•• Buysse DJ. Sleep health: can we define it? Does it matter? Sleep. 2014;37(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.3298. This paper proposes the definition (and measurement) of sleep health which includes five dimensions: sleep during, sleep continuity or efficiency, timing, alertness/sleepiness, and satisfcation/quality.
National Sleep Foundation. How much sleep do you really need? 2020. https://www.thensf.org/how-many-hours-of-sleep-do-you-really-need/. Accessed Feb 22 2021.
Gilsanz P, Lacy ME, Beeri MS, Karter AJ, Eng CW, Whitmer RA. Sleep quality and cognitive function in type 1diabetes: findings from the Study of Longevity in Diabetes (SOLID). Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2020;34(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/wad.0000000000000351.
• Macaulay GC, Galland BC, Boucher SE, Wiltshire EJ, Haszard JJ, Campbell AJ et al. Impact of type 1 diabetes mellitus, glucose levels, and glycemic control on sleep in children and adolescents: a case-control study. Sleep. 2020;43(2). https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsz226. This paper shows that short- and long-term suboptimal glycemic control (HbA1c≥7.5%) in children with type 1 diabetes is associated with sleep alterations including sleep duration.
Rechenberg K, Griggs S, Jeon S, Redeker N, Yaggi HK, Grey M. Sleep and glycemia in youth with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr Health Care. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedhc.2019.12.002.
Frye SS, Perfect MM, Silva GE. Diabetes management mediates the association between sleep duration and glycemic control in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Sleep Med. 2019;60:132–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2019.01.043.
Monzon AD, Marker AM, Noser AE, Clements MA, Patton SR. Associations between objective sleep behaviors and blood glucose variability in young children with type 1 diabetes. Ann Behav Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/abm/kaaa040.
Salah NY, Abido AY, Rashed HR. Relationship of glycaemic derangement using continuous glucose monitoring system with sleep pattern among children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3407.
Feeley CA, Sereika SM, Chasens ER, Siminerio L, Charron-Prochownik D, Muzumdar RH et al. Sleep in parental caregivers and children with type 1 diabetes. The Journal of School Nursing. 2019:1059840519865942. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059840519865942.
Suteau V, Saulnier PJ, Wargny M, Gonder-Frederick L, Gand E, Chaillous L, et al. Association between sleep disturbances, fear of hypoglycemia and psychological well-being in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus, data from cross-sectional VARDIA study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;160: 107988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107988.
Rusu A, Ciobanu D, Bala C, Cerghizan A, Roman G. Social jetlag, sleep-related parameters, and glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes: results of a cross-sectional study. J Diabetes. 2019;11(5):394–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12867.
Mattos A, Campos YS, Fiorini VO, Sab Y, Tavares BL, Velarde LGC, et al. Relationship between sleep disturbances, lipid profile and insulin sensitivity in type 1 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study. Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2020;64(4):412–7. https://doi.org/10.20945/2359-3997000000228.
Hamburger ER, Goethals ER, Choudhary A, Jaser SS. Sleep and depressive symptoms in adolescents with type 1 diabetes not meeting glycemic targets. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;169: 108442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108442.
Dijk DJ, von Schantz M. Timing and consolidation of human sleep, wakefulness, and performance by a symphony of oscillators. J Biol Rhythms. 2005;20(4):279–90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748730405278292.
Fritz J, Phillips AJK, Hunt LC, Imam A, Reid KJ, Perreira KM et al. Cross-sectional and prospective associations between sleep regularity and metabolic health in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Sleep. 2021;44(4). https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsaa218.
Wong PM, Hasler BP, Kamarck TW, Muldoon MF, Manuck SB. Social Jetlag, Chronotype, and cardiometabolic risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(12):4612–20. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-2923.
Taillard J, Sagaspe P, Philip P, Bioulac S. Sleep timing, chronotype and social jetlag: Impact on cognitive abilities and psychiatric disorders. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2021:114438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114438.
Wittmann M, Dinich J, Merrow M, Roenneberg T. Social jetlag: misalignment of biological and social time. Chronobiol Int. 2006;23(1–2):497–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420520500545979.
Roenneberg T, Allebrandt KV, Merrow M, Vetter C. Social jetlag and obesity. Curr Biol. 2012;22(10):939–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.038.
Larcher S, Gauchez AS, Lablanche S, Pépin JL, Benhamou PY, Borel AL. Impact of sleep behavior on glycemic control in type 1 diabetes: the role of social jetlag. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;175(5):411–9. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-16-0188.
Saylor J, Ji X, Calamaro CJ, Davey A. Does sleep duration, napping, and social jetlag predict hemoglobin A1c among college students with type 1 diabetes mellitus? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;148:102–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.01.007.
Patel NJ, Savin KL, Kahanda SN, Malow BA, Williams LA, Lochbihler G, et al. Sleep habits in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: variability in sleep duration linked with glycemic control. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12689.
von Schnurbein J, Boettcher C, Brandt S, Karges B, Dunstheimer D, Galler A, et al. Sleep and glycemic control in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018;19(1):143–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12538.
Barone MT, Wey D, Schorr F, Franco DR, Carra MK, Lorenzi FG, et al. Sleep and glycemic control in type 1 diabetes. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2015;59(1):71–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/2359-3997000000013.
Papandreou C, Bulló M, Díaz-López A, Martínez-González MA, Corella D, Castañer O, et al. High sleep variability predicts a blunted weight loss response and short sleep duration a reduced decrease in waist circumference in the PREDIMED-Plus Trial. Int J Obes. 2020;44(2):330–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-019-0401-5.
Chontong S, Saetung S, Reutrakul S. Higher sleep variability is associated with poorer glycaemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Sleep Res. 2016;25(4):438–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12393.
Denic-Roberts H, Costacou T, Orchard TJ. Subjective sleep disturbances and glycemic control in adults with long-standing type 1 diabetes: the Pittsburgh’s Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;119:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2016.06.013.
Feupe SF, Frias PF, Mednick SC, McDevitt EA, Heintzman ND. Nocturnal continuous glucose and sleep stage data in adults with type 1 diabetes in real-world conditions. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013;7(5):1337–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/193229681300700525.
Janovsky CC, Rolim LC, de Sá JR, Poyares D, Tufik S, Silva AB, et al. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy contributes to sleep apnea in young and lean type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:119. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00119.
Sinisterra M, Hamburger S, Tully C, Hamburger E, Jaser S, Streisand R. Young children with type 1 diabetes: sleep, health-related quality of life, and continuous glucose monitor use. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(8):639–42. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2019.0437.
Happe S, Treptau N, Ziegler R, Harms E. Restless legs syndrome and sleep problems in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type 1. Neuropediatrics. 2005;36(2):98–103. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-837685.
Adler A, Gavan MY, Tauman R, Phillip M, Shalitin S. Do children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes have increased prevalence of sleep disorders? Pediatr Diabetes. 2017;18(6):450–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12419.
Manin G, Pons A, Baltzinger P, Moreau F, Iamandi C, Wilhelm JM, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea in people with type 1 diabetes: prevalence and association with micro- and macrovascular complications. Diabet Med. 2015;32(1):90–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12582.
Schober AK, Neurath MF, Harsch IA. Prevalence of sleep apnoea in diabetic patients. Clin Respir J. 2011;5(3):165–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-699X.2010.00216.x.
Borel AL, Benhamou PY, Baguet JP, Halimi S, Levy P, Mallion JM, et al. High prevalence of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome in a type 1 diabetic adult population: a pilot study. Diabet Med. 2010;27(11):1328–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03096.x.
Perfect MM, Patel PG, Scott RE, Wheeler MD, Patel C, Griffin K, et al. Sleep, glucose, and daytime functioning in youth with type 1 diabetes. Sleep. 2012;35(1):81–8. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1590.
Meyer L, Massuyeau M, Canel C, Bahougne T, Assemi P, Perrin AE, et al. Association of sleep apnoea syndrome and autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2019;45(2):206–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2017.10.011.
Villa MP, Multari G, Montesano M, Pagani J, Cervoni M, Midulla F, et al. Sleep apnoea in children with diabetes mellitus: effect of glycaemic control. Diabetologia. 2000;43(6):696–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250051365.
Elrokhsi SH, Bluez GP, Chin CN, Wheeler MD, Silva GE, Perfect MM. Differences in sleep architecture according to body mass index in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020;21(1):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12918.
Donga E, M. vD, van Dijk JG, Biermasz NR, Lammers GJ, van KK et al. Partial sleep restriction decreases insulin sensitivity in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(7):1573–7. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-2317.
Lee SW, Ng KY, Chin WK. The impact of sleep amount and sleep quality on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. 2017;31:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2016.02.001.
Jauch-Chara K, Schmid SM, Hallschmid M, Born J, Schultes B. Altered neuroendocrine sleep architecture in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(6):1183–8. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-1986.
Kostkova M, Durdik P, Ciljakova M, Vojtkova J, Sujanska A, Pozorciakova K, et al. Short-term metabolic control and sleep in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2018;32(6):580–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.03.010.
Farabi SS, Quinn L, Phillips S, Mihailescu D, Park C, Ali M, et al. Endothelial dysfunction is related to glycemic variability and quality and duration of sleep in adults with type 1 diabetes. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2018;33(4):E21–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/jcn.0000000000000485.
Griggs S, Redeker NS, Jeon S, Grey M. Daily variations in sleep and glucose in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020;21(8):1493–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13117.
Jaser SS, Foster NC, Nelson BA, Kittelsrud JM, DiMeglio LA, Quinn M, et al. Sleep in children with type 1 diabetes and their parents in the T1D Exchange. Sleep Med. 2017;39:108–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2017.07.005.
Rusu A, Bala C, Ciobanu D, Cerghizan A, Roman G. Sleep quality and sleep duration, but not circadian parameters are associated with decreased insulin sensitivity in type 1 diabetes. Chronobiol Int. 2019;36(8):1148–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420528.2019.1615501.
McDonough RJ, Clements MA, DeLurgio SA, Patton SR. Sleep duration and its impact on adherence in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2017;18(4):262–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12381.
Young J, Waclawski E, Young JA, Spencer J. Control of type 1 diabetes mellitus and shift work. Occup Med (Lond). 2013;63(1):70–2. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqs176.
Abdelmaksoud AA, Salah NY, Ali ZM, Rashed HR, Abido AY. Disturbed sleep quality and architecture in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: relation to glycemic control, vascular complications and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021:108774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108774.
•• Spiegel K, Leproult R, Van Cauter E. Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. Lancet. 1999;354(9188):1435–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)01376-8. This paper shows that sleep debt has a harmful impact on carbohydrate metabolism and endocrine function, similar to those seen in normal ageing.
Broussard JL, Ehrmann DA, Van Cauter E, Tasali E, Brady MJ. Impaired insulin signaling in human adipocytes after experimental sleep restriction: a randomized, crossover study. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(8):549–57. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-157-8-201210160-00005.
Farabi SS, Carley DW, Quinn L. Glucose variations and activity are strongly coupled in sleep and wake in young adults with type 1 diabetes. Biol Res Nurs. 2017;19(3):249–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099800416685177.
Jauch-Chara K, Schultes B. Sleep and the response to hypoglycaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;24(5):801–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2010.07.006.
Tracy EL, Berg CA, Baucom KJW, Turner SL, Kelly CS, Van Vleet M, et al. Daily sleep quality and daily stressors in couples coping with type 1 diabetes. Health Psychol. 2019;38(1):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000690.
Perfect MM, Beebe D, Levine-Donnerstein D, Frye SS, Bluez GP, Quan SF. The development of a clinically relevant sleep modification protocol for youth with type 1 diabetes. Clin Pract Pediatr Psychol. 2016;4(2):227–40. https://doi.org/10.1037/cpp0000145.
Perfect M, Frye S, Bluez GP. The effects of a sleep extension intervention on glucose control in youth with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2018;67(Supplement 1):849-P. https://doi.org/10.2337/db18-849-P.
Tumakaka GYS, Agustini N, Nurhaeni N, Rustina Y. The effect of sleep hygiene education on sleep quality in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a preliminary study. Comprehensive Child and Adolescent Nursing. 2019;42(sup1):189–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/24694193.2019.1578440.
• Jaser SS, Hamburger ER, Bergner EM, Williams R, Slaughter JC, Simmons JH, et al. Sleep coach intervention for teens with type 1 diabetes: randomized pilot study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020;21(3):473–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12991. The pilot randomized trial shows that sleep coach intervention is a feasible and acceptable program to improve sleep in teens with type 1 diabetes.
Jaser SS, Bergner EM, Hamburger ER, Bhatia S, Lyttle M, Bell GE, et al. Pilot trial of a sleep-promoting intervention for children with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr Psychol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsaa105.
Buckingham B, Block J, Burdick J, Kalajian A, Kollman C, Choy M, et al. Response to nocturnal alarms using a real-time glucose sensor. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2005;7(3):440–7. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2005.7.440.
Al Hayek AA, Al Dawish MA. Assessing diabetes distress and sleep quality in young adults with type 1 diabetes using FreeStyle Libre: a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Therapy: Research, Treatment and Education of Diabetes and Related Disorders. 2020;11(7):1551–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-020-00849-3.
Polonsky WH, Fortmann AL. Impact of real-time CGM data sharing on quality of life in the caregivers of adults and children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020:1932296820978423. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296820978423.
Messer LH, Campbell K, Pyle L, Forlenza GP. Basal-IQ technology in the real world: Satisfaction and reduction of diabetes burden in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine. 2020:e14381. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14381.
Cobry EC, Jaser SS. Brief Literature Review: The potential of diabetes technology to improve sleep in youth with type 1 diabetes and their parents: an unanticipated benefit of hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery systems. Diabetes Spectrum. 2019;32(3):284–7. https://doi.org/10.2337/ds18-0098.
Sharifi A, De Bock MI, Jayawardene D, Loh MM, Horsburgh JC, Berthold CL, et al. Glycemia, treatment satisfaction, cognition, and sleep quality in adults and adolescents with type 1 diabetes when using a closed-loop system overnight versus sensor-augmented pump with low-glucose suspend function: a randomized crossover study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016;18(12):772–83. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2016.0288.
Bisio A, Brown SA, McFadden R, Pajewski M, Yu PL, DeBoer MD et al. Sleep and diabetes-specific psycho-behavioral outcomes of a new automated insulin delivery system in young children with type 1 diabetes and their parents. Pediatric Diabetes. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13164.
Bisio A, Gonder-Frederick L, McFadden R, Cherñavvsky D, Voelmle M, Pajewski M et al. The impact of a recently approved automated insulin delivery system on glycemic, sleep, and psychosocial outcomes in older adults with type 1 diabetes: a pilot study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021:1932296820986879. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296820986879.
Cobry EC, Hamburger E, Jaser SS. Impact of the hybrid closed-loop system on sleep and quality of life in youth with type 1 diabetes and their parents. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(11):794–800. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2020.0057.
Malone SK, Peleckis AJ, Grunin L, Yu G, Jang S, Weimer J, et al. Characterizing glycemic control and sleep in adults with long-standing type 1 diabetes and hypoglycemia unawareness initiating hybrid closed loop insulin delivery. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:6611064. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6611064.
Hale L, Troxel W, Buysse DJ. Sleep health: an opportunity for public health to address health equity. Annu Rev Public Health. 2020;41:81–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040119-094412.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Kevin Grandfiled from the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing (Department of Biobehavioral Nursing Science) for his editorial assistance.
Funding
Bingqian Zhu was supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission “Young Eastern Scholar” (China). The funding sources have no roles in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
S.R. received speaker fee from Becton Dickinson, outside the submitted work. All other authors declared no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Other Forms of Diabetes and Its Complications
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, B., Abu Irsheed, G.M., Martyn-Nemeth, P. et al. Type 1 Diabetes, Sleep, and Hypoglycemia. Curr Diab Rep 21, 55 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01424-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01424-1