Abstract
Background
Postauricular steroid administration has been popular for treating sudden sensorineural hearing loss. However, there are few reports on its use in patients with refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss (RSSNHL).
Aims
The objective of this study was to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of postauricular steroid injection as a salvage treatment for RSSNHL patients.
Methods
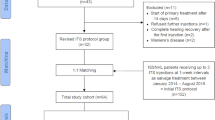
This retrospective study enrolled 63 RSSNHL patients between January 2016 and January 2019. Thirty-three patients of them who have been divided into the treatment group received postauricular methylprednisolone sodium succinate injection. The remaining 30 patients who formed the control group did not receive any steroid as a salvage therapy. Improvements in hearing were evaluated between pre-salvage therapy and 3 months follow-up after salvage therapy.
Results
The median hearing gain in PTA was 9.88 dB HL (quartile range 7.58, 18.65) in the treatment group and 0.90 dB HL (quartile range 0.00, 4.90) in the control group (P<0.01). According to the criteria of Furuhashi, the total percentage for effective prognosis was 48.48% (16/33) in the treatment group and 10.00% (3/30) in the control group (P<0.01). The time interval from onset to study entry was significantly and independently associated with the prognosis for RSSNHL patients (P< 0.01).
Conclusions
The present findings suggest that postauricular corticosteroid administration as a salvage treatment demonstrated better results than no treatment for RSSNHL patients. The time interval from onset to study entry was mainly the prognostic factor for RSSNHL patients. It is therefore considered that postauricular corticosteroid administration may be used as a salvage therapy for RSSNHL patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data and material are available.
References
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM et al (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngology-head and neck surgery: Official Journal of American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 146:S1–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812436449
Rauch SD (2004) Intratympanic steroids for sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 37:1061–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2004.04.004
Hunchaisri N, Chantapant S, Srinangyam N (2010) Intratympanic dexamethasone for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Med Assoc Thail = Chotmaihet thangphaet 93:1406–1414
Ahn JH, Han MW, Kim JH et al (2008) Therapeutic effectiveness over time of intratympanic dexamethasone as salvage treatment of sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol 128:128–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480701477602
Niedermeyer HP, Zahneisen G, Luppa P et al (2003) Cortisol levels in the human perilymph after intravenous administration of prednisolone. Audiol Neurootol 8:316–321. https://doi.org/10.1159/000073516
Li L, Ren J, Yin T, Lui W (2013) Intratympanic dexamethasone perfusion versus injection for treatment of refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology: Official Journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies (EUFOS): affiliated with the German Society for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 270:861–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2061-0
Erdur O, Kayhan FT, Cirik AA (2014) Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology: official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies (EUFOS): affiliated with the German Society for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 271:1431–1436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2594-x
Li X, Zhang XY, Wang QJ, Wang DY (2015) Efficacy of methylprednisolone sodium succinate for injection (postotic injection) on the auditory threshold and speech recognition rate of sudden deafness patients. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:14110–14114
Liu Y, Chen Q, Xu Y (2020) Research progress in refractory sudden hearing loss: steroid therapy. J Int Med Res 48:300060519889426. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519889426
Furuhashi A, Matsuda K, Asahi K, Nakashima T (2002) Sudden deafness: long-term follow-up and recurrence. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 27:458–463. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2273.2002.00612.x
Si Y, Jiang HL, Chen YB et al (2018) Round window niche drilling with intratympanic steroid is a salvage therapy of sudden hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol 23:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493086
Song J, Zhang L, Chen Y (2018) Analysis of the treatment effects of refractory sudden total frequency deafness with steroid from different topical administration routes. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery 32:1897–1899. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.24.012
Zou J (2015) Postaurical injection is a systemic delivery supported by symmetric distribution of Gd-DOTA in both the ipsilateral and contralateral ears. J Otol 10:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joto.2016.01.005
Li J, Yu L, Xia R et al (2013) Postauricular hypodermic injection to treat inner ear disorders: experimental feasibility study using magnetic resonance imaging and pharmacokinetic comparison. J Laryngol Otol 127:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215113000017
Wang Y, Han L, Diao T et al (2018) A comparison of systemic and local dexamethasone administration: from perilymph/cochlea concentration to cochlear distribution. Hear Res 370:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2018.09.002
Cros O, Knutsson H, Andersson M et al (2016) Determination of the mastoid surface area and volume based on micro-CT scanning of human temporal bones. Geometrical parameters depend on scanning resolutions. Hear Res 340:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2015.12.005
Yang XQ, Yu LS, Ma X (2007) Postaurical injection of compound betamethasone to treat the intractable low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Zhonghua er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. Chinese Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery 42:814–816
Zhang TY, Shang XL, Xie YX et al (2018) The effects of postauricular injection of methylprednisolone on medium-high frequency sudden hearing loss. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery 32:537–540. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.07.015
Zhu WY, Gao ZW, Qi H et al (2019) Analysis of prognostic factors in patients with refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery 33:532–536. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.06.014
Wang X, Liu XD, Zhao B et al (2018) Treatment of sudden deafness with type 2 diabetesmellitus by post-auricular subperiosteal injection of methylprednisolone. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery 32:1719–1722. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.22.009
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Jian-Bin Sun (Hearing Testing Centre, the First People’s Hospital of Huzhou, Zhejiang, China) for the technical assistance in auditory function testing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The medical records of patients were collated by Jue XU. The postauricular injection was performed by Gang Ren. The auditory function was measured by Longjiang Lan. Statistical analyses were performed by Bingliang Ma. Qi Zhang was responsible for designing the investigation and writing of the manuscript. All the authors reviewed and proved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent about participating in the study and publication of manuscript was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, G., Xu, J., Lan, L. et al. Postauricular injection of methylprednisolone sodium succinate as a salvage treatment for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ir J Med Sci 190, 1165–1172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02610-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02610-6