Abstract
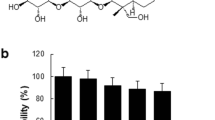
Hibiscus syriacus (H. syriacus), which belongs to Malvaceae, is a perennial herb widely distributed in East Asia. In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects and its potential molecular mechanisms of leaves extracted with 70% ethanol of H. syriacus (HS-L) at the mRNA and protein level when RAW264.7 macrophages were stimulated by LPS. HS-L dose dependently (0, 25, 50, 100 μg/mL) reduced NO production by inhibiting iNOS, COX-2, and IL-β expression in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. HS-L decreased the LPS-stimulated degradation and phosphorylation of IkB-a. Moreover, treatment with HS-L suppressed LPS-induced DNA binding of NF-kB and nuclear translocation of p65. Furthermore, HS-L suppressed the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38. HS-L was analyzed to contain compounds such as 2-pentadecanone, methyl palmitate, and ethyl palmitate in GC/MS analysis. These results suggested that HS-L could utilize anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways and that HS-L could be used as a natural anti-inflammatory agent.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 June 2020
In the original publication of the article, the name of third author was published incorrectly as “Som Da Kim”. The correct name is “Da Som Kim”.
References
Ahn SK, Goo YM, Ko KH, Lee SJ, Moon YH, Lee SS, Kim JW, Lee SS (2014) Study on the evaluation of nutritional values and antioxidant activities for herbal medicine by-products. J Agriculture Life Sci 48:101–110
Choi DH, Cho UM, Hwang HS (2018) Anti-inflammation effect of rebaudioside A by inhibition of the MAPK and NF-κB signal pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage. J Appl Biol Chem 61:205–211
El-Demerdash E (2011) Anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of methyl palmitate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254:238–244
Hsu RJ, Hsu YC, Chen SP, Fu CL, Yu JC, Chang FW, Chen YH, Liu JM, Ho JY, Yu CP (2015) The triterpenoids of Hibiscus syriacus induce apoptosis and inhibit cell migration in breast cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:65–74
Jang AR (2012) A study on cosmetic physiological and skin cell activity of Hibiscus syriacus extracts. M. S Thesis. Hannam University Daejeon Kor.
Kaminska B (2005) MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochem Biophys Acta 1754:253–262
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochem Biophys Acta 1802:396–405
Kim HN, Park SB, Park GH, Eo HJ, Song JH, Kwon HY, Jeong JB (2018) Anti-inflammatory effect of the root extracts from Hibiscus syriacus in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Korean J Plant Res 31:211–217
Kim HK (2014) Role of ERK/MAPK signalling pathway in anti-inflammatory effects of Ecklonia cava in activated human mast cell line-1 cells. Asian Pacific J Tropical Med 7:703–708
Kim JB, Han AR, Park EY, Kim JY, Cho W, Lee J, Seo EK, Lee KT (2007) Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2 and cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-k B inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biol Pharm Bull 30:2345–2351
Kim KH, Ko KI, Kang EJ, Yang EK, Park SN (2004) A research trend of natural product on well-being industry. J Soc Cosmet Sci Korea 30:239–343
Kim MJ, Kim KBWR, Park SH, Choi JS, Ahn DH (2017) Anti-inflammatory effect of Chondria crassicaulis ethanol extract on MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Korean Soc Biotechnol Bioeng J 32:352–360
Lee ST, Jeong YR, Ha MH, Kim SH, Byun MW, Jo SK (2000) Induction of nitric oxide and TNF-α by herbal plant extracts in mouse macrophages. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 29:342–348
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Trans Targeted Therapy 2:e17023
Lu J, Fang K, Wan S, Xiong L, Zhang C, Liu Z, Guan X, Zheng R, Wang G, Zheng J, Wang F (2018) Anti-inflammatory effect of columbianetin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mediators Inflamm 2018:1–8
Morrison DK, Davis RJ (2003) Regulation of MAP kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:91–118
Park SB, Song HM, Kim HN, Park GH, Son HJ, Um Y, Park JA, Jeong JB (2018) Anti-inflammatory effect of biji (soybean curd residue) on LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Korean J Plant Res 31:117–123
Raduan SZ, Abdul Aziz MWH, Roslida AH, Zakaria ZA, Zuraini A, Hakim MN (2013) Anti- inflammatory effects of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. and Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. alba ethanol extracts. Int J Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Sci 5:754–762
Saeed NM, El-Demerdash E, Abdel-Rahman HM, Algandaby MM, Al-Abbasi FA, Abdel-Naim AB (2012) Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 264:84–93
Siyumbwa SN, Ekeuku SO, Amini F, Emerald NM, Sharma D, Okechukwu PN (2019) Wound healing and antibacterial activities of 2-Pentadecanone in streptozotocin-induced Type 2 diabetic rats. Phcog mag 15:71–77
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107:7–11
Whitmarsh AJ (2006) The J.I.P. family of MAPK scaffold proteins. Biochem Soc Trans 34:828–832
Woo HS, Lee SM, Heo JD, Lee MS, Kim YS, Kim DW (2018) Anti-inflammatory activity of extracts of Hovenia dulcis on lipopolysaccharides-stimulated RAW264.7 cells Korean. J Plant Res 31:466–477
Youn HS (2012) The anti-inflammatory effects of phytochemicals by the modulation of innate immunity. J Exp Biomed Sci 18:181–192
Zhang C, Li C, Jia X, Wang K, Tu Y, Wang R, Liu K, Lu T, He C (2019) In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of polyphyllin VII through downregulating MAPK and NF-B pathways. Molecules 24:1–17
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from National Institute of Forest Science in 2020 (project number: FG0403-2018-01-2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eo, H.J., Kwon, H.Y., Da Kim, S. et al. GC/MS analysis and anti-inflammatory effect of leaf extracts from Hibiscus syriacus through inhibition of NF-κB and MAPKs signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Plant Biotechnol Rep 14, 539–546 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-020-00628-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-020-00628-3