Abstract
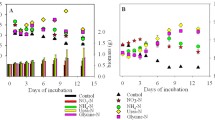
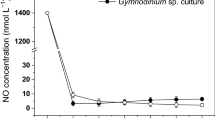
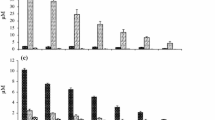
Effects of different nitrogen (N) compounds and concentrations on the growth of the three different phytoplankton taxa, Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyceae), Prorocentrum micans (Dinophyceae), and Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae), were investigated. The Monod equation was applied to examine effects of N concentrations on the growth of algal cells. Results showed that nitrate (NO3-N) and urea served as good N sources for the three phytoplankton taxa. S. costatum grew well on all of the seven N sources. C. marina can effectively use the two amino acids, glycine (Gly) and serine (Ser), however cannot utilize alanine (Ala), threonine (Thr), and asparaginic acid (Asp). P. micans cannot grow in five amino acid substrates. All of the three phytoplankton taxa grew well under different proportions of urea-N, and C. marina grew significantly better in medium with both NO3- and urea-N. The values of maximum growth rate (µmax) and half-saturation nutrient concentration (KS) for NO3-N were 0.71 divisions d−1 and 53.55 µmol L−1 for S. costatum, 0.67 divisions d−1 and 23.31 µmol L−1 for P. micans, and 0.23 divisions d−1 and 17.57 µmol L−1 for C. marina, respectively. The results suggested that S. costatum had a high N demand for growth, and was capable of using wide ranges of N compounds. The strategy of N utilization for S. costatum may make this species an advantage in N-enriched sea areas especially the dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) rich coastal waters, which might be the reason why S. costatum widely distributes in the cosmopolitan coastal and estuarine sea areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek, S. H., Shimode, S., Han, M. S., and Kikuchi, T., 2008. Growth of dinoflagellates, Ceratium furca and Ceratium fusus in Sagami Bay, Japan: The role of nutrients. Harmful Algae, 7: 729–739.
Berman, T., and Bronk, D. A., 2003. Dissolved organic nitrogen: A dynamic participant in aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 31: 273–305.
Burkholder, J. M., Glibert, P. M., and Skelton, H. M., 2008. Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. Harmful Algae, 8: 77–93.
Collos, Y., Gagne, C., Laabir, M., Vaquer, A., Cecchi, P., and Souchu, P., 2004. Nitrogenous nutrition of Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) in cultures and in Thau laggon, Southern France. Journal of Phycology, 40: 96–103.
Cucchiari, E., Guerrini, F., Penna, A., Totti, C., and Pistocchi, R., 2008. Effect of salinity, temperature, organic and inorganic nutrients on growth of cultured Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) from the northern Adriatic Sea. Harmful Algae, 7: 405–414.
Gilbert, P. M., 2017. Eutrophication, harmful algae and biodiversity-Challenging paradigms in a world of complex nutrient changes. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124: 591–606.
Glibert, P. M., and Burford, M. A., 2017. Globally changing nutrient loads and harmful algal blooms recent advances, new paradigms, and continuing challenges. Oceanography, 30: 58–69.
Glibert, P. M., Harrison, J., Heil, C., and Seitzinger, S., 2006. Escalating worldwide use of urea-A global change contributing to coastal eutrophication. Biogeochemistry, 77: 441–463.
Glibert, P. M., Wilkerson, F., Dugdale, R. C., Parker, A. E., Alexander, J. A., Blaser, S., and Murasko, S., 2014. Microbial communities from San Francisco Bay Delta respond differently to oxidized and reduced nitrogen substrates: Even under conditions that would otherwise suggest nitrogen sufficiency. Frontiers in Marine Science, 1: article 17.
Glibert, P. M., Wilkerson, F. P., Dugdale, R. C., Raven, J. A., Dupont, C. L., Leavitt, P. R., Parker, A. E., Burkholder, J. M., and Kana, T. M., 2016. Pluses and minuses of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation by phytoplankton and implications for productivity and community composition, with emphasis on nitrogen-enriched conditions. Limnology and Oceanography, 61: 165–197.
Gobler, C. J., Burson, A., Koch, F., Tang, Y., and Mulholland, M. R., 2012. The role of nitrogenous nutrients in the occurrence of harmful algal blooms caused by Cochlodinium polykrikoides in New York estuaries (USA). Harmful Algae, 17: 64–74.
Graneli, E., Weberg, M., and Salomon, P. S., 2008. Harmful algal blooms of allelopathic microalgal species: The role of eutrophication. Harmful Algae, 8: 94–102.
Guillard, R. R. L., 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Culture of Marine Invertebrates Animals. Smith, W. L., and Chanley, M. H., eds., Plenum Press, New York, 26–60.
Heisler, J., Glibert, P. M., Burkholder, J. M., Anderson, D. M., Cochlan, W., and Dennison, W. C., 2008. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae, 8: 3–13.
Herndon, J., and Cochlan, W. P., 2007. Nitrogen utilization by the raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo Growth and uptake kinetics in laboratory cultures. Harmful Algae, 6: 260–270.
Howard, M. D. A., Cochlan, W. P., Ladizinsky, N., and Kudela, R. M., 2007. Nitrogenous preference of toxigenic Pseudonitzschia australis (Bacillariophyceae) from field and laboratory experiments. Harmful Algae, 6: 206–217.
Hu, Z., Duan, S., Xu, N., and Mulholland, M. R., 2014. Growth and nitrogen uptake kinetics in cultured Prorocentrum donghaiense. PLoS One, 9: e94030.
Hu, Z., Xu, N., Duan, X., Li, A., and Zhang, C., 2010. Effects of urea on the growth of Phaeocystis globose, Scrippsiella trochoidea, Skeletonema costatum. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 30: 1265–1270 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Killberg-Thoreson, L., Mulholland, M. R., Heil, C. A., Sanderson, M. P., O’Neil, J. M., and Bronk, D. A., 2014. Nitrogen uptake kinetics in field populations and cultured strains of Karenia brevis. Harmful Algae, 38: 73–85.
Kudela, R. M., and Cochlan, W. P., 2000. Nitrogen and carbon uptake kinetics and influence of irradiance for a red tide bloom off southern California. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 21: 31–47.
Kwon, H. K., and Oh, S. J., 2014. The importance of dissolved organic nutrients on the interspecific competition between the harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides and the diatom Skeletonema sp. Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography, 19: 232–242 (in Korean with English abstract).
Lee, K. H., Jeong, H. J., Kim, H. J., and Lim, A. S., 2017. Nitrate uptake of the red tide dinoflagellate Prorocentrum micans measured using a nutrient repletion method: Effect of light intensity. Algae, 32 (2): 139–153.
Lewitus, A. J., Willis, B. M., Hayes, K. C., Burkholder, J. M., Glasgow, H. B., Glibert, P. M., and Burke, M. K., 1999. Mixotrophy and nitrogen uptake by Pfiesteria piscicida (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology, 35: 1430–1437.
Li, B., Ou, L., and Lu, S., 2009. Effects of different kinds of nitrogen on growth and nitrate reductase activity of Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae). Marine Environmental Science, 28 (3): 264–267 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, X., Yan, T., Yu, R., and Zhou, M. J., 2019. A review of Karenia mikimotoi: Bloom events, physiology, toxicity and toxic mechanism. Harmful Algae, 90: 101702.
Li, Z., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., Shi, X., and Zhang, C., 2017. Effect of urea on the growth of Skeletonema costatum and Karenia mikimotoi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37: 3193–3200 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lomas, M. W., and Glibert, P. M., 2000. Comparisons of nitrate uptake, storage, and reduction in marine diatoms and flagellates. Journal of Phycology, 36: 903–913.
Loureiro, S., Jauzein, C., Garcés, E., Collos, Y., Camp, J., and Vaqué, D., 2009. The significance of organic nutrients in the nutrition of Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima (Bacillariophyceae). Journal of Plankton Research, 31: 399–410.
Malone, T. C., 1980. Algal size. In: The Physiological Ecology of Phytoplankton. Morris, I., ed., Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 433–463.
Monod, J., 1949. The growth of bacterial cultures. Annual Review of Microbiology, 3: 371–394.
Moschonas, G., Gowen, R. J., Paterson, R. F., Mitchell, E., Stewart, B. M., McNeill, S., Glibert, P. M., Davidson, K., 2017. Nitrogen dynamics and phytoplankton community structure: The role of organic nutrients. Biogeochemistry, 134: 125–145.
Nagasoe, S., Shikata, T., Yamasaki, Y., Matsubara, T., Shimasaki, Y., Oshima, Y., and Honjo, T., 2010. Effects of nutrients on growth of the red-tide dinoflagellate Gyrodinium instriatum Freudenthal et Lee and a possible link to blooms of this species. Hydrobiologia, 651: 225–238.
Nishikawa, T., Tarutani, K., and Yamamoto, T., 2009. Nitrate and phosphate uptake kinetics of the harmful diatom Eucampia zodiacus Ehrenberg, a causative organism in the bleaching of aquacultured Porphyra thalli. Harmful Algae, 8: 513–517.
Nishikawa, T., Tarutani, K., and Yamamoto, T., 2010. Nitrate and phosphate uptake kinetics of the harmful diatom Coscinodiscus wailesii, a causative organism in the bleaching of aquacultured Porphyra thalli. Harmful Algae, 9: 563–567.
Oh, S., Park, J. S., and Yoon, Y. H., 2009. Growth kinetics on the nutrient of the harmful algae Chattonella marina and C. ovata (Raphidophyceae) isolated from the South Sea of Korea. Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 42: 674–682 (in Korean with English abstract).
Pustizzi, F., MacIntyre, H., Warner, M. E., and Hutchins, D. A., 2004. Interaction of nitrogen source and light intensity on the growth and photosynthesis of the brown tide alga Aureococcus anophagefferens. Harmful Algae, 3: 343–360.
Shilova, I. N., Mills, M. M., Robidart, J. C., Turk-Kubo, K. A., Bjorkman, K. M., and Kolber, Z., 2017. Differential effects of nitrate, ammonium, and urea as N sources for microbial communities in the North Pacific Ocean. Limnology and Oceanography, 62: 2550–2574.
Sipler, R. E., and Bronk, D. A., 2015. Chapter 4: Dynamics of dissolved organic nitrogen. In: Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter. 2nd edition. Carlson, D., ed., Academic Press, Boston, 127–232.
Sole, J., Garcia-Ladona, E., and Estrada, M., 2006. The role of selective predation in harmful algal blooms. Journal of Marine Systems, 62: 46–54.
Steidinger, K. A., Vargo, G. A., Tester, P. A., and Tomas, C. R., 1998. Bloom dynamics and physiology of Gymnodinium breve with emphasis on the Gulf of Mexico. In: Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms. Anderson, D. M., Cembella, A. D., and Hallegraeff, G. M., eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 133–153.
Tantanasarit, C., Englande, A. J., and Babel, S., 2013. Nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon uptake kinetics by marine diatom Chaetoceros calcitrans under high nutrient concentrations. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 446: 67–75.
Taylor, G. T., Gobler, C. J., and Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S. A., 2006. Speciation and concentrations of dissolved nitrogen as determinants of brown tide Aureococcus anophagefferens bloom initiation. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 312: 67–83.
Wang, Z. H., Guo, X., Ou, L. J., and Lin, L. C., 2017. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth of Levanderina fissa How it blooms in Pearl River Estuary. Journal of Ocean University of China, 16: 114–120.
Wang, Z. H., Zhao, J. G., Zhang, Y. J., and Cao, Y., 2009. Phytoplankton community structure and environmental parameters in aquaculture areas of Daya Bay, South China Sea. Journal of Environmental Science, 21: 1268–1275.
Yamaguchi, H., Sakamoto, S., and Yamaguchi, M., 2008. Nutrition and growth kinetics in nitrogen and phosphorus-limited cultures of the novel red tide flagellate Chattonella ovata (Raphidophyceae). Harmful Algae, 7: 26–32.
Yamamoto, T., Oh, S. J., and Kataoka, Y., 2004. Growth and uptake kinetics for nitrate, ammonium and phosphate by the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum isolated from Hiroshima Bay, Japan. Fisheries Science, 70: 108–115.
Zhang, C., and Zhou, J., 1997. Nutrient uptake kinetics and growth under nutrient limitation of Pseudonitzschia. Oceanologia et Limnology Sinica, 28: 599–603 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Y. H., Fu, F. X., Whereat, E., Coyne, K. J., and Hutchins, D. A., 2006. Bottom-up controls on a mixed-species HAB assemblage: A comparison of sympatric Chattonella subsalsa and Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) isolates from the Delaware Inland Bays, USA. Harmful Algae, 5: 310–320.
Zhou, Y. P., Zhang, Y. M., Li, F. F., Tan, L. J., and Wang, J. T., 2017. Nutrients structure changes impact the competition and succession between diatom and dinoflagellate in the East China Sea. Science of the Total Environment, 574: 499–508.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Science & Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China (No. 2018FY100200), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42076141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Wang, Z., Wang, C. et al. Effects of Nitrogen Sources and Concentrations on the Growth of Different Phytoplankton Taxa. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 721–728 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4564-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4564-z