Abstract
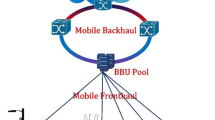
Building low-latency and high-capacity optical networks is vital for new high-speed cellular technologies. Coherent wavelength division multiplexing passive optical networks (WDM-PONs) are expected to play a key role in these applications. In this article, an overview of PON technologies for the 5th generation (5G) transport systems has been given. Moreover, a modified scheme based on coherent WDM-PON has been investigated using a dual polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) transceiver. The aim of the scheme is to build a 1 600 Gbit/s network that will be used in the construction of the transport architecture of 5G and beyond cellular networks either in mobile front haul (MFH) or mobile back haul (MBH). The results indicate that the proposed scheme offers a promising solution for future 5G transport systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ericsson, Ericsson Mobility Report, EAB-19:003442 Uen, Revision A, 2019.
Jun Shane Wey and Junwen Zhang, IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 37, 2830 (2019).
Curtis Knittle, Proc. OFC, Th11.6 (2016).
Naoki Suzuki, Journal of Lightwave Technology 36, 1485 (2018).
Chi-Wai Chow and Chien-Hung Yeh, IEEE Photon. J. 5, 7900407 (2013).
Chien-Hung Yeh, Opt. Exp. 16, 18857 (2008).
Tien-Thang Pham, Xianbin Yu, Timothy Gibbon, Lars Dittmann and Idelfonso Monroy, IEEE Photon. J. 3, 13 (2011).
Lap Chan, Chun-kit Chan, D. T. K. Tong, Fanglu Tong and Lian-Kuan Chen, Electron. Lett. 38, 43 (2002).
Gee-Kung Chang, IEEE/OSA J. Opt. Comm. Net. 1, C35 (2009).
Wen-Yi Lin, Ching-Hung Chang, Peng-Chun Peng, Hai-Han Lu and Ching-Hsiu Huang, Opt. Exp. 18, 10.301 (2010).
Chi-Wai Chow, Opt. Exp. 16, 12096 (2008).
Peter Vetter, Proc. of ECOC 2012, Tu.3.G (2012).
Fady I. El-Nahal and Norbert Hanik, IET Optoelectronics 14, 53 (2020).
Xiang Liu and Frank Effenberger, Journal of Optical Communication Networks 8, B70 (2016).
Recommendation ITU-T G.989.2, 2019.
Daisuke Umeda and Dekun Liu, IEEE 802.3ca Meeting, umeda_3ca_1b_0318, 2018.
Junwen Zhang, Jun Shan Wey and Xingang Huang, IEEE 802.3ca meeting, 2017.
Vincent Houtsma and Doutje van Veen, Journal of Lightwave Technol. 36, 122 (2018).
Junwen Zhang, Jun Shan Wey, Jianjun Yu, Zhijuan Tu, Bo Yang, Wei Yang, Yong Guo, Xingang Huang and Zhuang Ma, Optical Fiber Communications Conference, M1B.4 (2018).
Minghui Tao, Lei Zhou, Huaiyu Zeng, Shengping Li and Xiang Liu, Optical Fiber Communications Conference, 2017.
Saki Hatta, Nobuyuki Tanaka and Takeshi Sakamoto, IEICE Communications Express, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1587/comex.2016XBL0143, 2016.
Saki Hatta, Nobuyuki Tanaka and Takeshi Sakamoto, Optical Fiber Communications Conference, M3I.2 (2017).
Jun Li, Weiqiang Sun, Hongyang Yang and Weisheng Hu, Journal of Optical Communication Networks 6, 943 (2014).
Yang Bo, ZTE Technology Magazine 19, 30 (2017).
Xu Zhou and Ning Deng, European Conference on Optical Communication, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ECOC.2015.7341998, 2015.
Kazuaki Honda, Hirotaka Nakamura, Kazutaka Hara, Kyosuke Sone, Goji Nakagawa, Yoshio Hirose, Takeshi Hoshida, Jun Terada and Akihiro Otaka, Optical Fiber Communications Conference, 2018.
Vicent Sales, Josep Segarra, Víctor Polo, J. Camilo Velásquez and Josep Prat, Journal of Optical Comm. and Netw. 8, 582 (2016).
Harald Rohde, J. Lightwave Technol. 32, 2041 (2014).
Ali Shahpari, J. Lightwave Technol. 35, 1050 (2017).
Jesper Bevensee Jensen, J. Lightwave Technol. 32, 1423 (2014).
Bernhard Schrenk and Fotini Karinou, Proc. of OFC 2018, Paper Th1A.4 (2018).
Hisao Nakashima, Optical Fiber Communication Conf., Los Angeles, CA, USA, W1G.5 (2017).
Kazuro Kikuchi, J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 157 (2016).
David S. Millar, Toshiaki Koike-Akino, Sercan Ö. Arık, Keisuke Kojima, Kieran Parsons, Tsuyoshi Yoshida and Takashi Sugihara, Opt. Express 22, 8798 (2014).
Fady I. El-Nahal, Optoelectronics Letters 14, 372 (2018).
Fady I. El-Nahal, Photonics Letters of Poland 10, 57 (2018).
Olga Vassilieva, Inwoong Kim and Tadashi Ikeuchi, J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 50 (2019).
Govind Agrawal, Nonlinear Fiber Optics, Fifth Edition, Rochester, New York, 2013.
Marco Secondini, Erik Agrell, Enrico Forestieri, Domenico Marsella and Menelaos Ralli Camara, J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 2270 (2019).
Stefano Straullu, Proc. Eur. Conf. Opt. Commun., Cannes, France, P7.10 (2014).
Robert Maher, David S. Millar, Seb J. Savory and Benn C. Thomsen, IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 30, 3924 (2012).
Ryo Koma, Masamichi Fujiwara, Jun-ichi Kani, Ken-Ichi Suzuki and Akihiro Otaka, Proc. 2016 Opt. Fiber Commun. Conf. Exhib., Anaheim, CA, M3C.6 (2016).
Waseem Shbair and Fady I. El-Nahal, the 7th IEEE PICECE 2019, DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/PICECE.2019.8747183, 2019.
Huan Chen, Tao Yang, Liqian Wang, Xue Chen and Yueying Zhan, Optics Communications 434, 218 (2019).
Optiwave, OptiSystem Software Tool to Simulate Optical Networks, Optiwave Systems Inc, Ottawa, Canada, https://optiwave.com/, 2020.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shbair, W.W., El-Nahal, F.I. Coherent passive optical network for 5G and beyond transport. Optoelectron. Lett. 17, 546–551 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-021-0178-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-021-0178-3