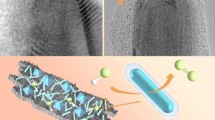
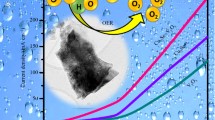
Abstract
Non-precious electro catalysts with high-efficiency, cheapness and stablility are of great significance to replace noble metal electro catalysts in the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER). In this work, triangular Cu@CuO nanorods on Cu nanosheets were fabricated by a novel in-situ oxidation approach using Cu nanosheets as self-template and conductive nano-substrate in an aqueous solution of NaOH/H2O2, and then by low-temperature phosphorization treatments. The experimental results show that the phosphating temperature has a significant effect on the morphology, composition and number of active sites of Cu@Cu3P nanorods. The Cu@Cu3P-280 electrode exhibits a good HER catalytic activity of achieving a current density of 10 mA/cm2 at 252 mV in acid electrolyte. After catalysis for 14 h, the current density can still reach 72% of the initial value. Moreover, the Cu@Cu3P-280 electrode also shows an excellent OER catalytic activity in basic electrolyte, reaching a current density of 10 mA/cm2 at the overpotential value of 200 mV. After catalysis for 12 h, the current density remained more than 93% of the initial value. This work provides a theoretical basis for the directional design and preparation of sustainable, low-cost, bifunctional electrocatalytic materials.
摘要
开发能够取代贵金属的高效、廉价、稳定的非贵金属催化剂,对于推动电催化水裂解析氢、析氧技术的发展具有重要意义。本文以铜纳米片为模板和导电基底,H2O2为氧源,NaOH 为pH 调节剂,通过原位氧化的方法在Cu 纳米片表面构筑三角柱状结构的Cu@CuO, 再对Cu@CuO 进行低温磷化,获得三角纳米柱状Cu@Cu3P。实验结果表明,磷化温度在调节Cu@Cu3P 纳米柱阵列的形貌、组成及活性位点数量方面具有显著效果。当磷化温度为280 ℃时,可获得形貌均一、活性高的纳米三角柱状阵列结构材料(Cu@Cu3P-280)。Cu@Cu3P-280 电极在0.5 mol/L H2SO4 电解质中表现出良好的析氢催化活性,在电流密度为10 mA/cm2时,其过电位为252 mV,催化14 h 后,电流密度仍可达初始值的72%。Cu@Cu3P-280 电极在1 mol/L KOH 电解质中也展现出优异的催化析氧活性,当电流密度为10 mA/cm2时,其过电位仅为200 mV,催化12 h 后,电流密度保持初始值的93%。此研究为可持续、低价、双功能电催化材料的定向设计与制备提供理论基础。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Mao-sen, FU Wen-ying, DU Lei, et al. Surface engineering by doping manganese into cobalt phosphide towards highly efficient bifunctional HER and OER electrocatalysis [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 515: 146059. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146059.
YAN Hai-jing, XIE Ying, WU Ai-ping, et al. Anionmodulated HER and OER activities of 3D Ni-V-based interstitial compound heterojunctions for high-efficiency and stable overall water splitting [J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2019, 31(23): e1901174. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201901174.
ALOBAID A, WANG Chun-sheng, ADOMAITIS R A. Mechanism and kinetics of HER and OER on NiFe LDH films in an alkaline electrolyte [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(15): J3395–J3404. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0481815jes.
ENSAFI A A, JAFARI-ASL M, NABIYAN A, et al. Ni3S2/ball-milled silicon flour as a bi-functional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions [J]. Energy, 2016, 116: 392–401. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.09.128.
JIANG Hao, GU Jin-xing, ZHENG Xu-sheng, et al. Defect-rich and ultrathin N doped carbon nanosheets as advanced trifunctional metal-free electrocatalysts for the ORR, OER and HER [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(1): 322–333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EE03276A.
SILVA V D, DA SILVA F E F, DE MEDEIROS E S, et al. Catalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions (HER/OER) in cells [M]//Heterogeneous Catalysis. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2022: 457 - 470. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-85612-6.00016-4.
CHENG Jin-bin, ZHANG Hua-min, MA Hai-peng, et al. Study of carbon-supported IrO2 and RuO2 for use in the hydrogen evolution reaction in a solid polymer electrolyte electrolyzer [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(5): 1855–1861. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.081.
CHEREVKO S, GEIGER S, KASIAN O, et al. Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir, and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: A comparative study on activity and stability [J]. Catalysis Today, 2016, 262: 170–180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.08.014.
WANG Ya-rong, WANG Zhang-jun, JIN Chao, et al. Enhanced overall water electrolysis on a bifunctional perovskite oxide through interfacial engineering [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 318: 120–129. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.06.073.
HAO Shao-yun, WANG Ya-hui, ZHENG Guo-kui, et al. Tuning electronic correlations of ultra-small IrO2 nanoparticles with La and Pt for enhanced oxygen evolution performance and long-durable stability in acidic media [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 266: 118643. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118643.
SUNG M, KIM J. Oxygen evolution reaction on Pt sphere and Ir-modified Pt sphere electrodes with porous structures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(4): 2130–2138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.167.
DIAO Fang-yuan, HUANG Wei, CTISTIS G, et al. Bifunctional and self-supported NiFeP-layer-coated NiP rods for electrochemical water splitting in alkaline solution [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(20): 23702–23713. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c03089.
LUO Shan-shan, WANG Ran, HEI Peng, et al. Self-assembled Ni2P nanosheet-implanted reduced graphene oxide composite as highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 612: 125992. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125992.
SU Zhe, LU Ying-jiong, SRINIVAS K, et al. Carbon nanotubes-interconnected heterostructural FeP/Ni2P nanospindles as efficient and stable electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 883: 160926. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160926.
YANG Fang, CHEN Xin, LI Zhe, et al. Ultrathin FeP nanosheets as an efficient catalyst for electrocatalytic water oxidation: Promoted intermediates adsorption by surface defects [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(4): 3577–3585. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c00080.
XIONG De-hua, WANG Xiao-guang, LI Wei, et al. Facile synthesis of iron phosphide nanorods for efficient and durable electrochemical oxygen evolution [J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(56): 8711–8714. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04151E.
WANG Ke-wei, TAN Jin-shan, LU Ze-jia, et al. Nanoscale engineering MoP/Fe2P/RGO toward efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(30): 13939–13945. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.012.
JIAO Yan-qing, YAN Hai-jing, WANG Rui-hong, et al. Porous plate-like MoP assembly as an efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(44): 49596–49606. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c13533.
ZHOU Ze-qi, MAHMOOD N, ZHANG Yong-chao, et al. CoP nanoparticles embedded in P and N co-doped carbon as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2017, 26(6): 1223–1230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2017.07.021.
ZHUANG Ming-hao, OU Xue-wu, DOU Yu-bing, et al. Polymer-embedded fabrication of Co2P nanoparticles encapsulated in N, P-doped graphene for hydrogen generation [J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(7): 4691–4698. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02203.
JIN Zhao-yu, LI Pan-pan, XIAO Dan. Metallic Co2P ultrathin nanowires distinguished from CoP as robust electrocatalysts for overall water-splitting [J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(6): 1459–1464. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC02462E.
KIM B K, KIM S K, CHO S K, et al. Enhanced catalytic activity of electrodeposited Ni-Cu-P toward oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 237: 409–415. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.082.
LIU Zi-xuan, WANG Xiao-long, HU Ai-ping, et al. 3D Sedoped NiCoP nanoarrays on carbon cloth for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(8): 2345–2359. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4774-y.
MONDAL I, MAHATA A, KIM H, et al. A combined experimental and theoretical approach revealing a direct mechanism for bifunctional water splitting on doped copper phosphide [J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(34): 17769–17779. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr03414b.
PI Ming-yu, ZHANG Ding-ke, WANG Shu-xia, et al. Enhancing electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution of WP2 three-dimensional nanowire arrays via Mo doping [J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 213: 315–318. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.11.058.
NKABINDE S S, MWONGA P V, MPELANE S, et al. Phase-dependent electrocatalytic activity of colloidally synthesized WP and α-WP2 electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(34): 15594–15606. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ00927C.
LIU Wei, GENG Peng, LI Shi-qing, et al. Tuning electronic configuration of WP2 nanosheet arrays via nickel doping for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 55: 17–24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.06.068.
LIU Wei, GENG Peng, LI Shi-qing, et al. Self-supported three-dimensional WP2 (WP) nanosheet arrays for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(53): 28576–28585. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.144.
PFEIFFER H, TANCRET F, BICHAT M P, et al. Air stable copper phosphide (Cu3P): A possible negative electrode material for lithium batteries [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2004, 6(3): 263–267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2003.12.012.
WANG Rui, DONG Xi-yan, DU Jiao, et al. MOF-derived bifunctional Cu3 P nanoparticles coated by a N, P-codoped carbon shell for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction [J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(6): 1703711. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201703711.
ZHOU Xin, ZHOU Xiao-liang, LIU Li-min, et al. Self-supported Cu3P nanowire electrode as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction [J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(54): 34137–34143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA05526G.
TIAN Jing-qi, LIU Qian, CHENG Ning-yan, et al. Self-supported Cu3P nanowire arrays as an integrated high-performance three-dimensional cathode for generating hydrogen from water [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2014, 53(36): 9577–9581. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201403842.
WEI Shu-ting, QI Kun, JIN Zhao, et al. One-step synthesis of a self-supported copper phosphide nanobush for overall water splitting [J]. ACS Omega, 2016, 1(6): 1367–1373. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.6b00366.
DANG Rui, SONG Ling-ling, DONG Wen-jun, et al. Synthesis and self-assembly of large-area Cu nanosheets and their application as an aqueous conductive ink on flexible electronics [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(1): 622–629. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/am404708z.
ZHANG Ke, XIONG Zhi-ping, LI Shu-min, et al. Cu3P/RGO promoted Pd catalysts for alcohol electro-oxidation [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 706: 89–96. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.179.
HOU Chun-chao, CHEN Qian-qian, WANG Chuan-jun, et al. Self-supported cedarlike semimetallic Cu3P nanoarrays as a 3D high-performance Janus electrode for both oxygen and hydrogen evolution under basic conditions [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(35): 23037–23048. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b06251.
ZHEN Wen-long, JIAO Wen-jun, WU Yu-qi, et al. The role of a metallic copper interlayer during visible photocatalytic hydrogen generation over a Cu/Cu2O/Cu/TiO2 catalyst [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(21): 5028–5037. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY01432E.
FU Zhong-yuan, MA Xin-yi, XIA Bing, et al. Efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution over Cu and Cu3P co-modified TiO2 nanosheet [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(37): 19373–19384. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.03.089.
ZHANG Hong-wei, TAN Hui-ru, JAENICKE S, et al. Highly efficient and robust Cu catalyst for non-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethanol to acetaldehyde and hydrogen [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 389: 19–28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2020.05.018.
LIN Jia, ZENG Cheng-hui, LIN Xiao-ming, et al. CNT-assembled octahedron carbon-encapsulated Cu3P/Cu heterostructure by in situ MOF-derived engineering for superior lithium storage: Investigations by experimental implementation and first-principles calculation [J]. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 2020, 7(14): 2000736. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202000736.
KOU Yu-li, WANG Kang-kang, WUMAER M, et al. Synthesis of hollow Cu@Cu3 P core-shell nanostructure as dual-functional catalyst with copper vacancy for enhancing chemical reduction and photocatalytic performance [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 589: 153031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153031.
LI Xiao-lin, ZHANG Jia-ling, ZHANG Yu, et al. Copper induced phosphide for enhanced electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(41): 21422–21430. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.213.
MA Lian-bo, SHEN Xiao-ping, ZHOU Hu, et al. Synthesis of Cu3P nanocubes and their excellent electrocatalytic efficiency for the hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic solution [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(12): 9672–9677. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA24427G.
HAO Jin-hui, YANG Wen-shu, HUANG Zhi-peng, et al. Superhydrophilic and superaerophobic copper phosphide microsheets for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution [J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3(16): 1600236. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201600236.
RONG Jian, XU Jin-chao, QIU Feng-xian, et al. Sea urchinlike MOF-derived formation of porous Cu3P@C as an efficient and stable electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution and hydrogen evolution reactions [J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2019, 6(14): 1900502. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201900502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Project(21905232) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Contributors
DANG Rui provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. DANG Rui and XU Xiufeng validated the proposed method with practical experiments. XIE Meng-meng accomplished writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
DANG Rui, XU Xiu-feng and XIE Mengmeng declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, R., Xu, Xf. & Xie, Mm. Fabrication of triangular Cu3P nanorods on Cu nanosheets as electrocatalyst for boosted electrocatalytic water splitting. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3870–3883 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-023-5243-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-023-5243-6