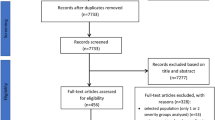
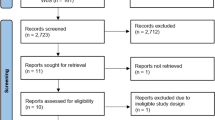
Abstract
Pancreatic encephalopathy (PE) is a lethal complication of acute pancreatitis (AP), but its clinical characteristics and prognosis remain obscure. Herein, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the incidence and outcomes of PE in AP patients. PubMed, EMBASE, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched. Based on the data from cohort studies, the incidence and mortality of PE in AP patients were pooled. Based on the individual data from case reports, logistic regression analyses were performed to identify the risk factors for death in PE patients. Among 6702 papers initially identified, 148 were included. Based on 68 cohort studies, the pooled incidence and mortality of PE in AP patients were 11% and 43%, respectively. The causes of death were clearly reported in 282 patients, of which the most common was multiple organ failure (n = 197). Based on 80 case reports, 114 AP patients with PE were included. The causes of death were clearly reported in 19 patients, of which the most common was multiple organ failure (n = 8). Univariate analyses showed that multiple organ failure (OR = 5.946; p = 0.009) and chronic cholecystitis (OR = 5.400; p = 0.008) were the significant risk factors of death among patients with PE. PE is not a rare complication of AP and indicates poor prognosis. Such a high mortality of PE patients may be attributed to its coexistence of multiple organ failure.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data reported in this study were available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- PE:
-
Pancreatic encephalopathy
- AP:
-
Acute pancreatitis
- SAP:
-
Severe acute pancreatitis
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
- CNKI:
-
China National Knowledge Infrastructure
- APACH II:
-
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II
- NOS:
-
Newcastle–Ottawa Scale
- JBI:
-
Joanna Briggs Institute
- OR:
-
Odds ratios
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
References
Minhas P, Brown B (2020) Pancreatic encephalopathy and cerebral hemorrhage in patient with severe acute pancreatitis. Chest 158(4):A758
Ohkubo T, Shiojiri T, Matsunaga T (2004) Severe diffuse white matter lesions in a patient with pancreatic encephalopathy. J Neurol 251(4):476–478
Gill D, Sheikh N, Shah A, Ruiz VG, Savici D (2017) Diffuse cerebral edema from acute pancreatitis induced by hypertriglyceridemia. Am J Med 130(5):e211–e212
Bartha P, Shifrin E, Levy Y (2006) Pancreatic encephalopathy–a rare complication of a common disease. Eur J Intern Med 17(5):382
Zhang XP, Tian H (2007) Pathogenesis of pancreatic encephalopathy in severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 6(2):134–140
Zhong X, Gong S (2017) Fatal cerebral hemorrhage associated with acute pancreatitis: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(50):e8984
Cui HW, Zhang BA, Peng T, Liu Y, Liu YR (2012) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a patient with acute pancreatitis: unusual cortical involvement and marvelous prognosis. Neurol Sci 33(3):615–618
Ding X, Liu CA, Gong JP, Li SW (2004) Pancreatic encephalopathy in 24 patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 3(4):608–611
Qiu F, Lu XS, Huang YK (2012) Protective effect of low-molecular-weight heparin on pancreatic encephalopathy in severe acute pancreatic rats. Inflamm Res 61(11):1203–1209
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS (2013) American college of gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 108(9):1400–15
Greenberg JA, Hsu J, Bawazeer M et al (2016) Clinical practice guideline: management of acute pancreatitis. Can J Surg 59(2):128–140
Pezzilli R, Zerbi A, Campra D et al (2015) Consensus guidelines on severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis 47(7):532–543
Jha RK, Ma Q, Sha H, Palikhe M (2009) Protective effect of resveratrol in severe acute pancreatitis-induced brain injury. Pancreas 38(8):947–953
Zerem E (2014) Treatment of severe acute pancreatitis and its complications. World J Gastroenterol 20(38):13879–13892
Wang X, Zhuang X, Wei R, Wang C, Xue X, Mao L (2015) Protective effects of Acanthopanax vs. Ulinastatin against severe acute pancreatitis-induced brain injury in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 24(2):285–298
Lin R, Li M, Luo M, Teng T, Pan Y, Huang H (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells decrease blood-brain barrier permeability in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:43
Sinha S, Kataria A, Kolla BP, Thusius N, Loukianova LL (2019) Wernicke encephalopathy-clinical pearls. Mayo Clin Proc 94(6):1065–1072
Sun GH, Yang YS, Liu QS, Cheng LF, Huang XS (2006) Pancreatic encephalopathy and Wernicke encephalopathy in association with acute pancreatitis: a clinical study. World J Gastroenterol 12(26):4224–4227
Bubber P, Ke ZJ, Gibson GE (2004) Tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes following thiamine deficiency. Neurochem Int 45(7):1021–1028
Sechi G, Serra A (2007) Wernicke’s encephalopathy: new clinical settings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol 6(5):442–455
Ruggieri RM, Lupo I, Piccoli F (2002) Pancreatic encephalopathy: a 7-year follow-up case report and review of the literature. Neurol Sci 23(4):203–205
Jingmin O, Xiping Z, Chun W, Ping Y, Qian Y (2012) Study of dexamethasone, baicalin and octreotide on brain injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflamm Res 61(3):265–275
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C et al (2013) Classification of acute pancreatitis–2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62(1):102–111
Funding
Dr. Hongyu Li received the funding from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC1315901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XQ; Methodology: YM, XZ, FG, and XQ; Data curation: YM, XZ, FG, and LC; Formal analysis and data interpretation: YM, XZ, FG, LC, JQ, HL, and XQ; Writing-original draft: YM and XQ; Writing-review and editing: YM, XZ, FG, LC, JQ, HL, and XQ; Supervision: HL and XQ. All authors have made an intellectual contribution to the manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal comnsent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Zheng, X., Gao, F. et al. Incidence and outcomes of pancreatic encephalopathy in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern Emerg Med 18, 1203–1212 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-023-03243-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-023-03243-6