Abstract
Objective
To explore the mechanism of moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by observing the metabolite changes in urine using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based metabolomic analysis.
Methods
Twenty-four rats were randomly divided into a control group, a model group, and a moxibustion group. Rats in the model and moxibustion groups were established as collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) models. The control and model groups did not receive any intervention; rats in the moxibustion group received moxibustion at Shenshu (BL23) and Zusanli (ST36). After three weeks of intervention, ankle joint, serum, and urine samples were collected for pathological examinations and metabolomic tests.
Results
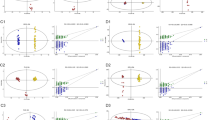
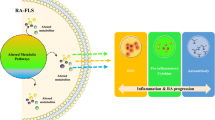
After moxibustion treatment, the CIA rats showed increased body mass, reduced swelling of the hind paws and arthritis score, decreased serum cytokine levels, and improved histopathological evaluation of the ankle joint. Twenty-four significantly altered metabolites were found, mainly involved in alanine metabolism, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, tricarboxylic acid cycle, phenylalanine metabolism, tyrosine metabolism, and primary bile acid biosynthesis. These metabolites may serve as potential biomarkers for RA.
Conclusion
Moxibustion can effectively resist inflammation in CIA rats. The potential biomarkers and the abnormal metabolic pathways of RA can be identified by LC-MS-based metabolomics. Metabolomics may be an effective way to explain the mechanism of moxibustion in treating RA.
摘要
目的
通过代谢组学液相色谱-质谱法(LC-MS)比较尿液代谢物的变化, 以探索艾灸治疗类风湿关节炎(RA)的机 制。
方法
将24 只大鼠随机分为对照组, 模型组和艾灸组。模型组和艾灸组大鼠建立胶原性关节炎(CIA)模型。对照 组和模型组不干预; 艾灸组大鼠接受艾灸肾俞和足三里治疗。干预3 周后, 收集踝关节, 血清和尿液标本进行病理学 和代谢组学检测。
结果
艾灸治疗后, CIA大鼠体质量增加, 后足肿胀度减轻, 关节炎评分及血清细胞因子水平降低, 踝 关节的组织病理形态改善。共发现24 种显著变化的代谢产物, 主要涉及丙氨酸代谢, 牛磺酸和次牛磺酸代谢, 三羧 酸循环, 苯丙氨酸代谢, 酪氨酸代谢和初级胆汁酸的生物合成。这些代谢物可作为RA的潜在生物标记。
结论
艾灸治 疗可以有效抵抗CIA大鼠的炎症。RA的潜在生物标志物和异常代谢途径可通过代谢组学LC-MS被确定。代谢组学可 能是解释艾灸治疗RA机制的有效途径。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FILIPOWICZ-SOSNOWSKA A. Drug-free remission: the goal of the future in management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatologia, 2017, 55(6): 284–289.
ZHAI W, MA Z, WANG W, SONG L, YI J. Paeoniflorin inhibits Rho kinase activation in joint synovial tissues of rats with collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 255–259.
VILLANUEVA-ROMERO R, GUTIÉRREZ-CAñAS I, CARRIóN M, PÉREZ-GARCíA S, SEOANE IV, MARTíNEZ C, GOMARIZ R P, JUARRANZ Y. The anti-inflammatory mediator, vasoactive intestinal peptide, modulates the differentiation and function of Th subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 6043710.
WANG X, LI D, JIANG M, PEI Z, XUL. K nearest neighbor algorithm coupled with metabonomics to study the therapeutic mechanism of Sendeng-4 in adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis rat. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2018, 2018: 2484912.
XU F, HUANG M, JIN Y, KONG Q, LEI Z, WEI X. Moxibustion treatment for primary osteoporosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One, 2017, 12(6): e0178688.
ZHONG Y M, CHEN Y, LUO X C, ZHOU H Y. Research progress on mechanism of moxibustion in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi, 2021, 28(3): 133–137.
TANG X W, YANG L, HOU Y. Effects of mild moxibustion on curative efficacy of cold dampness blockage type rheumatoid arthritis and clinical immune index. Shijie Zhongyiyao, 2019, 14(2): 481–485.
HUANG A, PANG Y, TANG Q, XU J, LIN J, LI J. Clinical therapeutic effects on rheumatoid arthritis treated with the assisted therapy of acupuncture at the points detected with thermosensitive moxibustion in Zhuang medicine. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2018, 38(3): 245–250.
ZHANG W, CHEN M R, HU J Y. Medicinal-powder-separated long-snake moxibustion over the Governor Vessel with different skin vesiculation conditions for treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2016, 41(4): 327–333.
LIN X, LIU X, XU J, CHENG K K, CAO J, LIU T, LIU Q, ZHONG H, SHEN G, DONG J, CHANG X. Metabolomics analysis of herb-partitioned moxibustion treatment on rats with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Chin Med, 2019, 14: 18.
XU J, ZHENG X, CHENG K K, CHANG X, SHEN G, LIU M, WANG Y, SHEN J, ZHANG Y, HE Q, DONG J, YANG Z. NMR-based metabolomics reveals alterations of electro-acupuncture stimulations on chronic atrophic gastritis rats. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 45580.
WISHART D S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2016, 15(7): 473–484.
GUMA M, TIZIAN S, FIRESTEIN G S. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: desperately seeking biomarkers. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2016, 12(5): 269–281.
XIE H H, XU J Y, XIE T, MENG X, LIN L L, HE L L, WU H, SHAN J J, WANG S C. Effects of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Berit. on the metabolomic profiles of placenta and amniotic fluid in pregnant rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016, 183: 38–45.
PIRHAJI L, MILANI P, LEIDL M, CURRAN T, AVILAPACHECO J, CLISH C B, WHITE F M, SAGHATELIAN A, FRAENKEL E. Revealing disease-associated pathways by network integration of untargeted metabolomics. Nat Methods, 2016, 13(9): 770–776.
YAN B, HUANG J, DONG F, YANG L, HUANG C, GAO M, SHI A, ZHA W, SHI L, HU X. Urinary metabolomic study of systemic lupus erythematosus based on gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr, 2016, 30(11): 1877–1881.
LI Y, LIU N, LI P, ZHENG X X. Establishment and optimization of rat collagen-induced arthritis model. Fujian Yiyao Zazhi, 2013, 35(1): 45–48, 181.
REMMERS E F, JOE B, GRIFFITHS M M, DOBBINS D E, DRACHEVA S V, HASHIRAMOTO A, FURUYA T, SALSTROM J L, WANG J, GULKO P S, CANNON G W, WILDER R L. Modulation of multiple experimental arthritis models by collagen-induced arthritis quantitative trait loci isolated in congenic rat lines: different effects of non-major histocompatibility complex quantitative trait loci in males and females. Arthritis Rheum, 2002, 46(8): 2225–2234.
PENG L X, SHAN J J, QIAN W J, XIE T, KANG A, DI Q L. Interventional effects of Zushima tablets on lipid metabolomic disorder of rheumatoid arthritis in rats based on UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS. Zhongcaoyao, 2018, 49(18): 4356–4365.
SHAN J, PENG L, QIAN W, XIE T, KANG A, GAO B, DI L. Integrated serum and fecal metabolomics study of collagen-induced arthritis rats and the therapeutic effects of the Zushima tablet. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 891.
HE M, HARMS A C, VAN WIJK E, WANG M, BERGER R, KOVAL S, HANKEMEIER T, VAN D E R, GREEF J. Role of amino acids in rheumatoid arthritis studied by metabolomics. Int J Rheum Dis, 2019, 22(1): 38–46.
SAFFARPOUR S, NASIRINEZHAD F. Functional interaction between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and ascorbic acid during neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol, 2017, 28(6): 601–608.
PRENTICE H, PAN C, GHARIBANI P M, MA Z, PRICE A L, GIRALDO G S, RETZ H M, GUPTA A, CHEN P C, CHIU H, MODI J, MENZIE J, TAO R, WU J Y. Analysis of neuroprotection by taurine and taurine combinations in primary neuronal cultures and in neuronal cell lines exposed to glutamate excitotoxicity and to hypoxia/reoxygenation. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 975(Pt 1): 207–216.
LIU Y, LI F, ZHANG L, WU J, WANG Y, YU H. Taurine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by antiinflammation and antioxidants in rats. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(5): 6512–6517.
CAO P J, JIN Y J, LI M E, ZHOU R, YANG M Z. PGC-1α may associated with the anti-obesity effect of taurine on rats induced by arcuate nucleus lesion. Nutr Neurosci, 2016, 19(2): 86–93.
LI S Q, LI X Y. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Radix Angelicae Sinensis (Dang Gui). Dajia Jiankang (Xueshuban), 2016, 10(2): 283.
WANG H, SUN N. Analysis on the research progress of effective chemical components and pharmacological action of Radix Angelicae Sinensis (Dang Gui). Shandong Huagong, 2017, 46(18): 59–60.
MA R, XIE Q, WANG J, HUANG L H, TANG J F, LI W X, MA X, CHEN N, DONG T W. Metabolomics study on effects of compatibility of alcohol extracts of Magnolia Officinalis and Polygala Tenuifolia on urine metabolites in rats. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao, 2019, 35(6): 870–877.
REN J G, SETH P, YE H, GUO K, HANAI J I, HUSAIN Z, SUKHATME V P. Citrate suppresses tumor growth in multiple models through inhibition of glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the IGF-1R pathway. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 4537.
ALONSO A, JULIÀ A, VINAIXA M, DOMÈNECH E, FERNÁNDEZ-NEBRO A, CAñETE J D, FERRÁNDIZ C, TORNERO J, GISBERT J P, NOS P, CASBAS A G, PUIG L, GONZÁLEZ-ÁLVARO I, PINTO-TASENDE J A, BLANCO R, RODRíGUEZ M A, BELTRAN A, CORREIG X, MARSAL S; IMID Consortium. Urine metabolome profiling of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. BMC Med, 2016, 14(1): 133.
CHEN R L, HE Y L, JIANG H Y, LIU H Y, WEI Q N, LUO G X, PENG Y X, ZHU Y. Mechanism of action of blood-pricking therapy combined with medicated thread moxibustion in rats with acute gouty arthritis: a study based on urine metabolomics. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2019, 39(2): 234–240.
CAI X, YUAN Y, LIAO Z, XING K, ZHU C, XU Y, YU L, WANG L, WANG S, ZHU X, GAO P, ZHANG Y, JIANG Q, XU P, SHU G. α-Ketoglutarate prevents skeletal muscle protein degradation and muscle atrophy through PHD3/ADRB2 pathway. FASEB J, 2018, 32(1): 488–499.
LENG Y F, HE J, LI C, CHEN B, WANG D W, CHEN F Q, XIE T, XU X, SUN Z L. Urinary metabolomics reveals the therapeutic mechanism of moxibustion on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Eur J Integr Med, 2020, 37: 101160.
PALERMO L, MACDONALD A, LIMBACK E, ROBERTSON L, HOWE S, GEBERHIWOT T, ROMANI C. Emotional health in early-treated adults with phenylketonuria (PKU): relationship with cognitive abilities and blood phenylalanine. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol, 2020, 42(2): 142–159.
HERIAN M, KAMLŃSKA K, ŚWIT P, SKAWSKI M, WOJTAS A, SOBOCIŃSKA M, GOŁEMBIOWSKA K. Effect of 4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxy-N-(2-methoxybenzyl) phenethylamine on brain neurotransmitters and rats’ locomotor activity. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2020, 31(Suppl 1): S23–S24.
SHEN D, MA N, YANG Y, LIU X, QIN Z, LI S, JIAO Z, KONG X, LI J. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based plasma metabolomics to evaluate the effects of aspirin eugenol ester on blood stasis in rats. Molecules, 2019, 24(13): 2380.
LI Z. Preliminary Study on the Intervention of HDAC Inhibitors on Intracellular Metabolomics of Hela Cells. Xiamen: Master Thesis of Xiamen University, 2019.
LAI L C, CHEN F L, WANG S L, CAO C. UPLC-Q/TOF-MS based serum metabolomic study on rats with calcium oxalate renal stones intervened by Desmodii Styracifolii Herba. Zhongyao Xinyao Yu Linchuang Yaoli, 2020, 31(8): 950–959.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金项目, No. 81774383, No. 81904274); Nursing Advantageous Discipline Construction Project in Jiangsu Universities (江苏省高校护理优势学科建设项目, No. 2019YSHL008, No. 2019YSHL021); Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (江苏省研究生科研创新计划项目, No. KYCX21_1802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
First Author: PANG Xiangtian, master degree candidate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, X., Leng, Y., Yao, Y. et al. Study on the mechanism of moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 20, 247–256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-022-1321-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-022-1321-9