Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical efficacy of acupoint pressure plus long-snake moxibustion for upper-limb spastic hemiplegia after cerebral infarction.
Methods
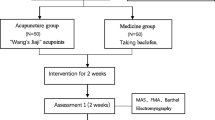
A total of 100 patients were randomized into a control group and an observation group, with 50 cases in each group. Both groups were treated with the same conventional internal medicine and rehabilitation training. The control group was treated with additional acupoint pressure therapy, and the observation group was treated with long-snake moxibustion on the basis of the treatment given to the control group. The Ashworth grade, Fugl-Meyer assessment upper limb scale (FMA-UL) and Barthel index (BI) were evaluated, and the root mean square (RMS) values of biceps brachii and flexor carpi radialis on the affected side were measured before and after treatment. The efficacy was evaluated after treatment.
Results
After treatment, the total effective rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, the Ashworth grade of the observation group was superior to that of the control group (P<0.05). The scores of FMA-UL and BI in both groups increased compared with those before treatment (all P<0.05), and the scores of FMA-UL and BI in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (both P<0.05). The RMS values of biceps brachii and flexor carpi radialis in both groups decreased compared with those before treatment (all P<0.05), and the RMS values of biceps brachii and flexor carpi radialis in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (both P<0.05).
Conclusion
Based on conventional internal medicine and rehabilitation training, acupoint pressure plus long-snake moxibustion has great therapeutic efficacy for upper-limb spastic hemiplegia after cerebral infarction. It can improve the degree of spasticity of the affected upper limb, reduce the muscle tone of biceps brachii and flexor carpi radialis on the affected side, and enhance the mobility of the affected limb and the activities of daily living.
【摘要】
目的: 观察点穴加长蛇灸治疗脑梗死后上肢痉挛性偏瘫的临床疗效。方法: 将100例患者随机分为对照组和观察组, 每组50例。两组均接受相同的常规内科治疗及康复训练, 对照组在此基础上加用点穴疗法, 观察组在对照组治疗基础上加用长蛇灸。治疗前后评定Ashworth分级、Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表(FMA-UL)及Barthel指数(BI), 测定患肢肱二头肌及桡侧腕屈肌的均方根(RMS)值。治疗结束后进行疗效评价。结果: 治疗后, 观察组总有效率明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。治疗后, 观察组Ashworth分级优于对照组(P<0.05); 两组FMA-UL及BI评分均较本组治疗前升高(均P<0.05), 观察组FMA-UL及BI评分均高于对照组(均P<0.05); 两组肱二头肌及桡侧腕屈肌RMS值均较本组治疗前降低(均P<0.05), 观察组肱二头肌及桡侧腕屈肌RMS值均低于对照组(均P<0.05)。结论: 在常规内科治疗及康复训练基础上加用点穴和长蛇灸治疗脑梗死后上肢痉挛性偏瘫疗效显著, 可改善患肢痉挛程度, 降低患肢肱二头肌及桡侧腕屈肌肌张力, 提升患肢活动能力及日常生活能力。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knutson JS, Fu MJ, Sheffler LR, Chae J. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for motor restoration in hemiplegia. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am, 2015, 26(4): 729–745.
Yen JT, Li S. Altered force perception in stroke survivors with spastic hemiplegia. J Rehabil Med, 2015, 47(10): 917–923.
Morreale M, Marchione P, Pili A, Lauta A, Castiglia SF, Spallone A, Pierelli F, Giacomini P. Early versus delayed rehabilitation treatment in hemiplegic patients with ischemic stroke: proprioceptive or cognitive approach. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med, 2016, 52(1): 81–89.
Xu H, Wang KF, Wen LN. Research progress of moxibustion in the treatment of stroke sequelae. Hebei Zhongyi, 2016, 38(1): 142––144.
Zhang XD. Clinical observation on softening tendon by finger-pointing manipulation plus rehabilitation training for spastic cerebral palsy. Zhongguo Minjian Liaofa, 2019, 27(1): 33–34.
Fan ZL, Jiang HQ. Effect of finger acupoints in early rehabilitation of stroke hemiplegia. Zhongguo Jixu Yixue Jiaoyu, 2019, 11(24): 145–147.
Rao ML. China Guideline for Cerebrovascular Diseases Prevention and Treatment. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2007: 7–9.
Zhu XH, Zhang F, Dai JL, Zhu RH, Wang JL, Dou ZC, Yang M, Bi H, Shi Y. Therapeutic effect of acupoint catgut embedding combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation in treating post-stroke upper limb spasm. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2019, 35(12): 37–40.
Lundquist CB, Maribo T. The Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity: reliability, responsiveness and validity of the Danish version. Disabil Rehabil, 2017, 39(9): 934–939.
van Meijeren-Pont W, Volker G, Vliet Vlieland T, Goossens P. Comparison of the responsiveness of the Utrecht scale for evaluation of rehabilitation (USER) and the Barthel index in stroke patients. Clin Rehabil, 2019, 33(10): 1672–1681.
Hong HY, Yu XC, Liu T. Clinical observation on 35 cases of spastic paralysis after stroke treated by needle scalpel in relaxing and promoting triggering spot of muscular fascia. Gansu Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2019, 36(3): 67–71.
Wang CL. Ju-needling Combined with Conventional Spastic Hemiplegia of Cerebral Infarction at Restoration Stage Treated by Acupuncture Curative Effect Observation. Guangzhou: Master Thesis of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2016.
Zhou X, Chu SF, Wan JF, Chen C, Zhang DY, Chen NH. Research progress of SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis in the treatment of ischemic stroke with stem cells. Yaoxue Xuebao, 2018, 53(7): 1054–1059.
Du LJ, Yang Y, Yang GK, Ma ZH, Li GJ, Wan J. The role of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/protein kinase B in stromal cell derived factor-1 induced migration of endothelial tip cell. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi, 2018, 35(7): 1199–1202.
Hao ZP. Clinical Observation on Treatment of Spastic Paralysis of Upper Limbs after Stroke with Pricking Twelve Jing-Well Acupoint Combined with Acupuncture. Harbin: Master Thesis of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, 2019.
Gao Y, Zhao JF, Guo CX. Effect of Governor Vessel moxibustion for restless legs syndrome of maintenance hemodialysis: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2016, 36(6): 597–600.
Tang X, Chen MX, Meng FY, Liu Y, Zhao HB. Bioinformatics analysis of muscle spasticity related genes in children with cerebral palsy. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2018, 33(5): 499–505.
Wang J, Zhao M, Zhang M, Liu CM, Xu MY. Therapeutic observation of finger-pointing manipulation for upper-limb spasticity in patients with stroke. Zhongguo Shiyong Shenjing Jibing Zazhi, 2015, 18(15): 112–113.
Hubert P, Killick R, Chung A, Padovese LR. A Bayesian binary algorithm for root mean squared-based acoustic signal segmentation. J Acoust Soc Am, 2019, 146(3): 1799.
Cabral EEA, Fregonezi GAF, Melo L, Basoudan N, Mathur S, Reid WD. Surface electromyography (sEMG) of extra diaphragm respiratory muscles in healthy subjects: a systematic review. J Electromyogr Kinesiol, 2018, 42: 123–135.
Acknowledgments
There was no project-fund supporting for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author: Wang Yu-chun, bachelor, nurse-in-charge.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu-chun, W., Hai-yan, S. Clinical observation on acupoint pressure plus long-snake moxibustion for upper-limb spastic hemiplegia after cerebral infarction. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 19, 187–192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1242-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1242-z
Keywords
- Acupuncture-moxibustion Therapy
- Acupoint Pressure Therapy
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Governor Vessel
- Cerebral Infarction
- Poststroke Syndrome
- Hemiplegia
- Muscle Spasticity