Abstract
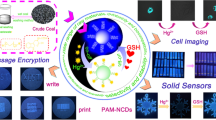
The efficient utilization of natural lignin, which is the main by-product of the cellulose industry, is crucial for enhancing its economic value, alleviating the environmental burden, and improving ecological security. By taking advantage of the large sp2 hybrid domain of lignin and introducing amino functional groups, new lignin-derived carbon dots (SPN-CDs) with red fluorescence were successfully synthesized. Compared with green and blue fluorescent materials, red SPN-CDs have desirable anti-interference properties of short-wave background and exhibit superior luminescence stability. The SPN-CDs obtained exhibited sensitive and distinctive visible color with fluorescence-dual responses toward hypochlorite. Considering this feature, a portable, low-cost, and sensitive fluorescence sensing paper with a low limit of detection of 0.249 µmol·L−1 was fabricated using the SPN-CDs for hypochlorite detection. Furthermore, a new type of visible-light and fluorescence dual-channel information encryption platform was constructed. Low-concentration hypochlorite can be employed as an accessible and efficient information encryption/decryption stimulus, as well as an information “eaaser”, facilitating a safe and diversified transmission and convenient decryption of information. This work opens new avenues for high-value-added applications of lignin-based fluorescent materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Espina-Casado J, Fernández-González A, Díaz-García M E, Badía-Laíño R. Smart carbon dots as chemosensor for control of water contamination in organic media. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2021, 329: 129262
Ahmed F, Iqbal S, Zhao L, Xiong H. “On-off-on” fluorescence switches based on N,S-doped carbon dots: facile hydrothermal growth, selective detection of Hg2+, and as a reversive probe for guanine. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2021, 1183: 338977
Li L, Ren X, Bai P, Liu Y, Xu W, Xie J, Zhang R. Near-infrared emission carbon dots for bio-imaging applications. New Carbon Materials, 2021, 36(3): 632–638
Wan J, Zhang X, Fu K, Zhang X, Shang L, Su Z. Highly fluorescent carbon dots as novel theranostic agents for biomedical applications. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(41): 17236–17253
Xie A Q, Guo J, Zhu L, Chen S. Carbon dots promoted photonic crystal for optical information storage and sensing. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 415: 128950
Muthamma K, Sunil D, Shetty P. Carbon dots as emerging luminophores in security inks for anti-counterfeit applications—an up-to-date review. Applied Materials Today, 2021, 23: 101050
Zhang J, He B, Hu Y, Alam P, Zhang H, Lam J W Y, Tang B Z. Stimuli-responsive AIEgens. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(32): 2008071
Zhou H, Han J, Cuan J, Zhou Y. Responsive luminescent MOF materials for advanced anticounterfeiting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 134170
Liu H, Wang Y, Mo W, Tang H, Cheng Z, Chen Y, Zhang S, Ma H, Li B, Li X. Dendrimer-based, high-luminescence conjugated microporous polymer films for highly sensitive and selective volatile organic compound sensor arrays. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(13): 1910275
Li X, Zhao S, Li B, Yang K, Lan M, Zeng L. Advances and perspectives in carbon dot-based fluorescent probes: mechanism, and application. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 431: 213686
Kateshiya M R, Malek N I, Kumar Kailasa S. Green fluorescent carbon dots functionalized MoO3 nanoparticles for sensing of hypochlorite. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 351: 118628
Kailasa S K, Koduru J R. Perspectives of magnetic nature carbon dots in analytical chemistry: from separation to detection and bioimaging. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 33: e00153
Ashrafizadeh M, Mohammadinejad R, Kailasa S K, Ahmadi Z, Afshar E G, Pardakhty A. Carbon dots as versatile nanoarchitectures for the treatment of neurological disorders and their theranostic applications: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 278: 102123
Yu H, Shi R, Zhao Y, Waterhouse G I N, Wu L Z, Tung C H, Zhang T. Smart utilization of carbon dots in semiconductor photocatalysis. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(43): 9454–9477
Wilhelm N, Kaufmann A, Blanton E, Lantagne D. Sodium hypochlorite dosage for household and emergency water treatment: updated recommendations. Journal of Water and Health, 2017, 16(1): 112–125
Wu H, Zhang W, Wu Y, Liu N, Meng F, Xie Y, Yan L A. 7-Diethylaminocoumarin-based chemosensor with barbituric acid for hypochlorite and hydrazine. Microchemical Journal, 2020, 159:105461
Yang G, Wan X, Su Y, Zeng X, Tang J. Acidophilic S-doped carbon quantum dots derived from cellulose fibers and their fluorescence sensing performance for metal ions in an extremely strong acid environment. Journal of Materials Chemistry A: Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2016, 4(33): 12841–12849
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Song J, Li M, Yang Y, Gu W, Xu X, Xu H, Wang S. A highly specific and sensitive turn-on fluorescence probe for hypochlorite detection based on anthracene fluorophore and its bioimaging applications. Dyes and Pigments, 2019, 161: 172–181
Ji D, Li G, Zhang S, Zhu M, Li C, Qiao R. Mitochondria-targeted fluorescence probe for endogenous hypochlorite imaging in living cells and zebrafishs. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 259:816–824
Hu Q, Qin C, Huang L, Wang H, Liu Q, Zeng L. Selective visualization of hypochlorite and its fluctuation in cancer cells by a mitochondria-targeting ratiometric fluorescent probe. Dyes and Pigments, 2018, 149: 253–260
Tang C, Gao Y, Liu T, Lin Y, Zhang X, Zhang C, Li X, Zhang T, Du L, Li M. Bioluminescent probe for detecting endogenous hypochlorite in living mice. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2018, 16(4): 645–651
Zhu B, Wu L, Zhang M, Wang Y, Liu C, Wang Z, Duan Q, Jia P. A highly specific and ultrasensitive near-infrared fluorescent probe for imaging basal hypochlorite in the mitochondria of living cells. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2018, 107: 218–223
Xi L L, Guo X F, Wang C L, Wu W L, Huang M F, Miao J Y, Zhao B X. A near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid and selective detection of hypochlorous acid in aqueous solution and living cells. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 255: 666–671
Yue Y, Huo F, Yin C, Escobedo J O, Strongin R M. An recent progress in chromogenic and fluorogenic chemosensors for hypochlorous acid. Analyst, 2016, 141(6): 1859–1873
Chen X, Wang F, Hyun J Y, Wei T, Qiang J, Ren X, Shin I, Yoon J. Recent progress in the development of fluorescent, luminescent and colorimetric probes for detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(10): 2976–3016
Feng Y, Li S, Li D, Wang Q, Ning P, Chen M, Tian X, Wang X. Rational design of a diaminomaleonitrile-based mitochondria-targeted two-photon fluorescent probe for hypochlorite in vivo: solvent-independent and high selectivity over Cu2+. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 254: 282–290
Wang Z X, Jin X, Gao Y F, Kong F Y, Wang W J, Wang W. Fluorometric and colorimetric determination of hypochlorite using carbon nanodots doped with boron and nitrogen. Mikrochimica Acta, 2019, 186(6): 328
Duan C, Won M, Verwilst P, Xu J, Kim H S, Zeng L, Kim J S. In vivo imaging of endogenously produced HClO in zebrafish and mice using a bright, photostable ratiometric fluorescent probe. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(6): 4172–4178
Hu H C, Xu H, Wu J, Li L, Yue F, Huang L, Chen L, Zhang X, Ouyang X. Secondary bonds modifying conjugate-blocked linkages of biomass-derived lignin to form electron transfer 3D networks for efficiency exceeding 16% nonfullerene organic solar cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(23): 2001494
Agarwal A, Rana M, Park J H. Advancement in technologies for the depolymerization of lignin. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 181: 115–132
Ding Z, Li F, Wen J, Wang X, Sun R. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots derived from lignin biomass. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(6): 1383–1390
Jiang X, Shi Y, Liu X, Wang M, Song P, Xu F, Zhang X. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped lignin/DES carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for the detection of Fe3+ ions. Polymers, 2018, 10(11): 1282
Zhang B, Liu Y, Ren M, Li W, Zhang X, Vajtai R, Ajayan P M, Tour J M, Wang L. Sustainable synthesis of bright green fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from alkali lignin. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(18): 4202–4210
Zhu X, Yuan X, Han L, Liu H, Sun B. A smartphone-integrated optosensing platform based on red-emission carbon dots for realtime detection of pyrethroids. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2021, 191: 113460
Wang X, Cheng Z, Zhou Y, Tammina S K, Yang Y. A double carbon dot system composed of N, Cl-doped carbon dots and N, Cu-doped carbon dots as peroxidase mimics and as fluorescent probes for the determination of hydroquinone by fluorescence. Mikrochimica Acta, 2020, 187(6): 350
Fan Y Z, Tang Q, Liu S G, Yang Y Z, Ju Y J, Xiao N Luo H Q, Li N B. A smartphone-integrated dual-mode nanosensor based on novel green-fluorescent carbon quantum dots for rapid and highly selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol and pH. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 492: 550–557
Pathak A, Pv S, Stanley J, Satheesh Babu T G. Correction to: multicolor emitting N/S-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for imaging pathogenic bacteria and human buccal epithelial cells. Mikrochimica Acta, 2019, 186(9): 645
Lu H, Xu S, Liu J. One pot generation of blue and red carbon dots in one binary solvent system for dual channel detection of Cr3+ and Pb2+ based on ion imprinted fluorescence polymers. ACS Sensors, 2019, 4(7): 1917–1924
Jia R, Jin K, Zhang J, Zheng X, Wang S, Zhang J. Colorimetric and fluorescent detection of glutathione over cysteine and homocysteine with red-emitting N-doped carbon dots. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 321: 128506
Lu S, Sui L, Liu J, Zhu S, Chen A, Jin M, Yang B. Near-infrared photoluminescent polymer-carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(15): 1603443
Yang J, Jin X, Cheng Z, Zhou H Gao L, Jiang D, Jie X, Ma Y Chen W. Facile and green synthesis of bifunctional carbon dots for detection of Cu2+ and ClO− in aqueous solution. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(39): 13206–13214
Zhang P, Wang Y, Chen L, Yin Y. Bimetallic nanoclusters with strong red fluorescence for sensitive detection of hypochlorite in tap water. Mikrochimica Acta, 2017, 184(10): 3781–3787
Wang Z X, Ding S N. One-pot green synthesis of high quantum yield oxygen-doped, nitrogen-rich, photoluminescent polymer carbon nanoribbons as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for sensitive and selective detection of silver(I) and mercury(II) ions. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(15): 7436–7445
Acknowledgements
Yixuan Chang and Fanwei Kong contributed equally to the work. We are grateful for the financial support by the Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovations by NEFU (Grant No. 202110225105), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51903031), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2572021CG05), Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (Grant No. 2019QNRC001), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (Grant Nos. 2022T150102, 2021M700735, 2019T120249, 2018M630331), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund (Grant Nos. LBH-Z18010, LBH-TZ1001), the Key Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. ZD2021C001), the 111 Project (Grant No. B20088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., Kong, F., Zhu, Z. et al. Lignin-derived dual-function red light carbon dots for hypochlorite detection and anti-counterfeiting. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 17, 966–975 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2244-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2244-1