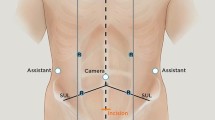
Abstract
When a familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) patient’s rectal polyp undergoes malignant transformation, the surgeon needs to consider how to balance the quality of surgery with the patient’s quality of life. Here, we present a case of robotic surgery in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis and ultra-low rectal cancer. Fiberoptic colonoscopy found that hundreds of polyp-like bulges were diffusely distributed throughout the colon, and a malignant mass was found at the end of the rectum. The patient underwent total colectomy with abdominoperineal extended radical resection for rectal cancer using the Xi robotic platform. The patient recovered well in the postoperative period. The ileostomy was well used. And the patient was in good health and metastasis free at 9 months postoperatively. We identified total colectomy combined with extended radical rectal resection under the assistance of the da Vinci robot platform is of great benefit to the patient.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and information are saved in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, and the information is true, credible and available. The datasets is availability from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Rhodes M, Bradburn DM (1992) Overview of screening and management of familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 33(1):125–131
Parascandola SA, Horsey ML, Hota S, Paull JO, Graham A, Pudalov N et al (2021) The robotic colorectal experience: an outcomes and learning curve analysis of 502 patients. Colorectal Dis 23:226–236
Aliyev V, Goksel S, Bakir B, Guven K, Asoglu O (2021) Sphincter-saving robotic total mesorectal excision provides better mesorectal specimen and good oncological local control compared with laparoscopic total mesorectal excision in male patients with mid-low rectal cancer. Surg Technol Int 38:160–166
Zhu Y, Xiong H, Chen Y, Liu Z, Jiang Z, Huang R et al (2021) Comparison of natural orifice specimen extraction surgery and conventional laparoscopic-assisted resection in the treatment effects of low rectal cancer. Sci Rep 11(1):9338
Kim MJ, Park SC, Park JW, Chang HJ, Kim DY, Nam BH et al (2018) Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer: a phase II open label prospective randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 267(2):243–251
McLaughlin SD, Clark SK, Tekkis PP, Ciclitira PJ, Nicholls RJ (2008) Review article: restorative proctocolectomy, indications, management of complications and follow-up–a guide for gastroenterologists. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27(10):895–909
Campos FG, Real Martinez CA, Monteiro de Camargo MG, Cesconetto DM, Nahas SC, Cecconello I (2018) Laparoscopic versus open restorative proctocolectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 28(1):47–52
Wang X (2021) Natural orifice specimen extraction surgery. Springer, Singapore
Jimenez-Rodriguez RM, Quezada-Diaz F, Tchack M, Pappou E, Wei IH, Smith JJ et al (2019) Use of the Xi robotic platform for total abdominal colectomy: a step forward in minimally invasive colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 33(3):966–971
Aliyev V, Arslan NC, Goksoy B, Guven K, Goksel S, Asoglu O (2022) Is robotic da Vinci Xi® superior to the da Vinci Si® for sphincter-preserving total mesorectal excision? Outcomes in 150 mid-low rectal cancer patients. J Robot Surg 16(6):1339–1346
Acknowledgements
This study was approved by Institutional Review Board of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. All methods were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the approved guidelines. The patient provided written informed consent.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Operative procedure, material preparation and data collection were performed by all authors. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HX and JW, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, H., Wang, J., Hu, H. et al. Application of the Xi robotic platform for familial adenomatous polyposis with ultra-low rectal cancer: exploration of minimally invasive and refined therapies. J Robotic Surg 17, 1843–1846 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01587-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01587-x