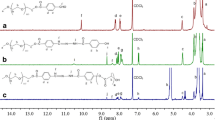
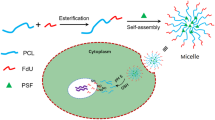
Abstract
In this paper, we present a simple and feasible drug self-assembled delivery system with pH responsiveness and targeting function for cancer therapy. The drug delivery system is composed of an anticancer drug and an amphiphilic random copolymer based on phenylboronic acid, galactose, and polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether acrylate molecules and achieved through reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. The micelles present targeting function by introducing galactose molecules and show pH sensitivity on the basis of the interactions between phenylboronic acid and galactose molecules. Particle size, transmission electron microscopy, and drug release assays show the pH-responsive behavior of micelles at pH 6.0. Cellular uptake assay demonstrates that micelles can internalize HepG2 cells via receptor-mediated interaction. In addition, the drug-loaded micelles can considerably inhibit cancer cell proliferation as indicated by in vivo antitumor assay. The synthesized micelles may facilitate the development of valid drug delivery systems for cancer therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander JL, Wilson ID, Teare J, Marchesi JR, Nicholson JK, Kinross JM (2017) Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(6):356
An J, Dai X, Wu Z, Zhao Y, Lu Z, Guo Q, Zhang X, Li C (2015) An acid-triggered degradable and fluorescent nanoscale drug delivery system with enhanced cytotoxicity to cancer cells. Biomacromol 16(8):2444
Arouri A, Hansen AH, Rasmussen TE, Mouritsen OG (2013) Lipases, liposomes and lipid-prodrugs. Curr Opin Coll Interface ence 18(5):419
Ashwell G, Harford J (1982) Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver. Annu Rev Biochem 51(1):531
Becker S, Spiess M, Klenk HD (1995) The asialoglycoprotein receptor is a potential liver-specific receptor for Marburg virus. J Gen Virol 76(Pt 2):393
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394
Cheng C, Zhang X, Wang Y, Sun L, Li C (2012) Phenylboronic acid-containing block copolymers: synthesis, self-assembly, and application for intracellular delivery of proteins. New J Chem 36(6):1413
Cheng W, Nie J, Xu L, Liang C, Peng Y, Liu G, Wang T, Mei L, Huang L, Zeng X (2017) pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(22):18462
Cheng YJ, Qin SY, Ma Y, Chen XS, Zhang AQ, Zhang XZ (2019) Super-pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based drug delivery system for effective combination cancer therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:1878
Chen H, Liu Z, Wei B, Huang J, You X, Zhang J, Yuan Z, Tang Z, Guo Z, Wu J (2021) Redox responsive nanoparticle encapsulating black phosphorus quantum dots for cancer theranostics. Bioactive Mater 6(3):655
Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen ZG, Shin DM (2008) Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1310
Duan Q, Cao Y, Li Y, Hu X, Xiao T, Lin C, Pan Y, Wang L (2013) pH-responsive supramolecular vesicles based on water-soluble pillar[6]arene and ferrocene derivative for drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 135(28):10542
Duan X, Chen H, Fan L, Kong J (2016) Drug self-assembled delivery system with dual responsiveness for cancer chemotherapy. ACS Biomater Ence Eng 21:2347
Fallon RJ, Schwartz AL (1988) Asialoglycoprotein receptor phosphorylation and receptor-mediated endocytosis in hepatoma cells Effect of phorbol esters. J Biol Chem 263(26):13159
Fang S, Niu Y, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Yu L, Li X (2015) Liposomes assembled from a dual drug-tailed phospholipid for cancer therapy. Chem Asian J 10(5):1232
Gao X, Zhai M, Guan W, Liu J, Liu Z, Damirin A (2017) Controllable synthesis of a smart multifunctional nanoscale metal-organic framework for magnetic resonance/optical imaging and targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(4):3455
Guo Q, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhang P, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Li C, Jiang S, Zhang X (2019) In situ real-time tracing of hierarchical targeting nanostructures in drug resistant tumors using diffuse fluorescence tomography. Chem Sci 10(34):7878
Han Y, Yin W, Li J, Zhao H, Zha Z, Ke W, Wang Y, He C, Ge Z (2018) Intracellular glutathione-depleting polymeric micelles for cisplatin prodrug delivery to overcome cisplatin resistance of cancers. J Control Release: Official J Control Release Soc 273:30
Hashida M, Nishikawa M, Yamashita F, Takakura Y (2001) Cell-specific delivery of genes with glycosylated carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 52(3):187
He L, Read ES, Armes SP, Adams DJ (2007) Direct synthesis of controlled-structure primary amine-based methacrylic polymers by living radical polymerization. Macromolecules 40(13):4429
Koyamatsu Y, Hirano T, Kakizawa Y, Okano F, Takarada T, Maeda M (2014) pH-responsive release of proteins from biocompatible and biodegradable reverse polymer micelles. J Control Release: Official J Control Release Soc 173:89
Lee MC, Kabilan S, Hussain A, Yang X, Blyth J, Lowe CR (2004) Glucose-sensitive holographic sensors for monitoring bacterial growth. Anal Chem 76(19):5748
Lepenies B, Lee J, Sonkaria S (2013) Targeting C-type lectin receptors with multivalent carbohydrate ligands. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(9):1271
Lin X, Li AM, Li YH, Luo RC, Zou YJ, Liu YY, Liu C, Xie YY, Zuo S, Liu Z et al (2020) Silencing MYH9 blocks HBx-induced GSK3β ubiquitination and degradation to inhibit tumor stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):13
Li Y, Xiao W, Xiao K, Berti L, Luo J, Tseng HP, Fung G, Lam KS (2012) Well-defined, reversible boronate crosslinked nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in response to acidic pH values and cis-diols. Angewandte Chemie (Int ed in English) 51(12):2864
Li M, Song W, Tang Z, Lv S, Lin L, Sun H, Li Q, Yang Y, Hong H, Chen X (2013) Nanoscaled poly(L-glutamic acid)/doxorubicin-amphiphile complex as pH-responsive drug delivery system for effective treatment of nonsmall cell lung cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(5):1781
Li X, Wang X, Sha L, Wang D, Shi W, Zhao Q, Wang S (2018) Thermosensitive lipid bilayer-coated mesoporous carbon nanoparticles for synergistic thermochemotherapy of tumor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(23):19386
Pan J, Li PJ, Wang Y, Chang L, Wan D, Wang H (2018) Active targeted drug delivery of MMP-2 sensitive polymeric nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb) 54(79):11092
Saw PE, Xu X, Zhang M, Cao S, Farokhzad OC, Wu J (2020) Nanostructure engineering by simple tuning of lipid combinations. Angewandte Chemie (Int ed in English) 59(15):6249
Su J, Chen F, Cryns VL, Messersmith PB (2011) Catechol polymers for pH-responsive, targeted drug delivery to cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc 133(31):11850
Tan YF, Lao LL, Xiong GM, Venkatraman S (2018) Controlled-release nanotherapeutics: state of translation. J Control Release: Off J Control Release Soc 284:39
Wang H, Lu Z, Wang L, Guo T, Wu J, Wan J, Zhou L, Li H, Li Z, Jiang D et al (2017b) New generation nanomedicines constructed from self-assembling small-molecule prodrugs alleviate cancer drug toxicity. Can Res 77(24):6963
Wang H, Wu J, Xu L, Xie K, Chen C, Dong Y (2017a) Albumin nanoparticle encapsulation of potent cytotoxic therapeutics shows sustained drug release and alleviates cancer drug toxicity. Chem Commun (Camb) 53(17):2618
Yao C, Wang P, Li X, Hu X, Hou J, Wang L, Zhang F (2016) Near-infrared-triggered azobenzene-liposome/upconversion nanoparticle hybrid vesicles for remotely controlled drug delivery to overcome cancer multidrug resistance. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 28(42):9341
Zhang P, Wang Y, Lian J, Shen Q, Wang C, Ma B, Zhang Y, Xu T, Li J, Shao Y et al (2017b) Engineering the surface of smart nanocarriers using a pH-/Thermal-/GSH-responsive polymer zipper for precise tumor targeting therapy in vivo. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 29:36
Zhang Z, Shi L, Wu C, Su Y, Qian J, Deng H, Zhu X (2017a) Construction of a supramolecular drug-drug delivery system for non-small-cell lung cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(35):29505
Zhang M, Song CC, Su S, Du FS, Li ZC (2018) ROS-activated ratiometric fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles for self-reporting drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(9):7798
Zhang M, Ma Y, Wang Z, Han Z, Gao W, Zhou Q, Gu Y (2019) A CD44-targeting programmable drug delivery system for enhancing and sensitizing chemotherapy to drug-resistant cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(6):5851
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Effect of serum exosome circ-RPPH1 on paclitaxel resistance of breast cancer and its mechanism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhong, R., Fu, Y. et al. Simple and feasible design of a polymeric nanoparticle for efficient anticancer drug delivery. Chem. Pap. 75, 4035–4044 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01589-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01589-9