Abstract
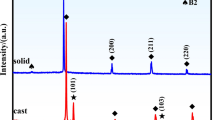
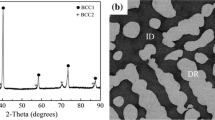
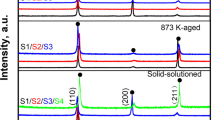
This paper reports the effect of the solution annealing heat treatment process on the microstructure evolution, hardness changes, and creep behavior of high-entropy refractory alloy (RHEA) AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr. Solution annealing was performed on the as-cast samples in the temperature range (1400-1550) °C for 24 h. Observations showed that the alloy consists of a dendritic structure such that a dual body-centered cubic (BCC)/B2 matrix (dendritic region) is surrounded by Al-Zr-rich intermetallic phases (inter-dendritic region). The significant tendency of Zr in respect of separation from the matrix was found as the main reason for the causing thermal instability. The results showed that with the increase in heat treatment temperature, the volume fraction of inter-dendritic phases decreases and causes a decrease in hardness. It is also the microstructure of the alloy adjacent to the creep indentation process verified that no significant phase deformation takes place in the area beneath the indenter face; while, an obvious phase compression besides the indenter edge was evident for severe shear stresses at this area. Using the constitutive equations, the stress exponent and activation energy of the creep were determined as ~ 141 and 1233 kJ/mol, respectively. The abnormal value of stress exponent was attributed to the lattice distortion, nano-scaled structure, ordered B2 phase, and Al-Zr intermetallic phase, all restricting the dislocation glide in the alloy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.J. Pickering and N.G. Jones, High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Assessment of Their Founding Principles and Future Prospects, Int. Mater. Rev., 2016, 61(3), p 183–202.
I. Florea, R.M. Florea, O. Balţatescu, V. Soare, R. Chelariu, and I. Carcea, High entropy alloys, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater., 2013, 15, p 761–767.
R. Kozak, A. Sologubenko, and W. Steurer, Single-Phase High-Entropy Alloys–An Overview, Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater., 2015, 230(1), p 55–68.
M.H. Tsai, Physical Properties of High Entropy Alloys, Entropy, 2013, 15(12), p 5338–5345.
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6(5), p 299–303.
S.J.C.S. Ranganathan, Alloyed Pleasures: Multimetallic Cocktails, Curr. Sci., 2003, 85(5), p 1404–1406.
J.W. Yeh, Recent Progress in High Entropy Alloys, Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat., 2006, 31, p 633–648.
Z. Lyu, C. Lee, S.Y. Wang, X. Fan, J.W. Yeh, and P.K. Liaw, Effects of Constituent Elements and Fabrication Methods on Mechanical Behavior of High-Entropy Alloys: A Review, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, 50(1), p 1–28.
M. Todai, T. Nagase, T. Hori, A. Matsugaki, A. Sekita, and T. Nakano, Novel TiNbTaZrMo High-Entropy Alloys for Metallic Biomaterials, Scr. Mater., 2017, 129, p 65–68.
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, and Q.J. Zhang, Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl High-Entropy Solid Solution Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 485(1–2), p L31–L34.
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, S.W. Lee, and K. Niihara, Characterization of Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiTiAl High-Entropy Solid Solution Processed by Mechanical Alloying, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 495(1), p 33–38.
O.N. Senkov, D.B. Miracle, K.J. Chaput, and J.P. Couzinie, Development and Exploration of Refractory High Entropy Alloys—A Review, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 33(19), p 3092–3128.
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory MoNbHfZrTi High-Entropy Alloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 81, p 87–94.
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory High Entropy (Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi) BCC/M5Si3 In-Situ Compound, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 660, p 197–203.
H. Chen, A. Kauffmann, S. Laube, I.C. Choi, R. Schwaiger, Y. Huang, and K. Lichtenberg et al., Contribution of Lattice Distortion to Solid Solution Strengthening in a Series of Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, 49(3), p 772–781.
N.D. Stepanov, N.Y. Yurchenko, E.S. Panina, M.A. Tikhonovsky, and S.V. Zherebtsov, Precipitation-Strengthened Refractory Al0.5CrNbTi2V0.5 High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2017, 188, p 162–164.
Y. Zhang, High-Entropy Materials: Advances and Applications, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2023.
B. Gorr, M. Azim, H.J. Christ, T. Mueller, D. Schliephake, and M. Heilmaier, Phase Equilibria, Microstructure, and High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Novel Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 624, p 270–278.
C.M. Lin, C.C. Juan, C.H. Chang, C.W. Tsai, and J.W. Yeh, Effect of Al Addition on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 624, p 100–107.
H. Wang, W. Chen, Z. Fu, C. Chu, Z. Tian, Z. Jiang, and H. Wen, Lightweight Ti-Zr-Nb-Al-V Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with Superior Strength-Ductility Synergy and Corrosion Resistance, Int. J. Refract Met. Hard Mater., 2023, 116, p 106331.
J. Brechtl, R. Feng, P.K. Liaw, B. Beausir, H. Jaber, T. Lebedkina, and M. Lebyodkin, Mesoscopic-Scale Complexity in Macroscopically-Uniform Plastic Flow of an Al0.3CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy, Acta Mater., 2023, 242, p 118445.
C. Cao, J. Fu, T. Tong, Y. Hao, P. Gu, H. Hao, and L. Peng, Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy, Entropy, 2018, 20(12), p 960.
A.E. Karantzalis, D. Sioulas, A. Poulia, C. Mathiou, and E. Georgatis, A First Approach on the Assessment of the Creep Behavior of MoTaNbVxTi High Entropy Alloys by Indentation Testing, SN Appl. Sci., 2020, 2(5), p 1–10.
Y. Ma, Y.H. Feng, T.T. Debela, G.J. Peng, and T.H. Zhang, Nanoindentation Study on the Creep Characteristics of High-Entropy Alloy Films: Fcc Versus Bcc Structures, Int. J. Refract Met. Hard Mater., 2016, 54, p 395–400.
S.G. Ma, Creep Resistance and Strain-Rate Sensitivity of a CoCrFeNiAl0.3 High-Entropy Alloy by Nanoindentation, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(12), p 126508.
M. Sadeghilaridjani, S. Muskeri, M. Pole, and S. Mukherjee, High-Temperature Nano-indentation Creep of Reduced Activity High Entropy Alloys Based on 4-5-6 Elemental Palette, Entropy, 2020, 22(2), p 230.
O.N. Senkov, C. Woodward, and D.B. Miracle, Microstructure and Properties of Aluminum-Containing Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, JOM, 2014, 66(10), p 2030–2042.
O.N. Senkov, S.V. Senkova, and C.J.A.M. Woodward, Effect of Aluminum on the Microstructure and Properties of Two Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2014, 68, p 214–228.
P.S. Ocaño, S.G. Fries, I. Lopez-Galilea, R.D. Kamachali, J. Roik, and L.A. Jácome, The AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr Refractory High Entropy Superalloy: Experimental Findings and Comparison with Calculations Using the CALPHAD Method, Mater. Des., 2022, 217, p 110593.
J.K. Jensen, Characterization of a High Strength, Refractory High Entropy Alloy, AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr, The Ohio State University, Columbus, 2017.
D.X. Qiao, H. Jiang, W.N. Jiao, Y.P. Lu, Z.Q. Cao, and T.-J. Li, A Novel Series of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Ti2ZrHf0.5VNbx with High Specific Yield Strength and Good Ductility, Acta Metall. Sin. (English Letters), 2019, 32, p 925–931.
Z. Zarei, M. Zohrevand, A. Momeni, S. Sadeghpour, and M. Somani, Effect of Heat Treatment Regime on Microstructure and Phase Evolution of AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2023, 949, p 169818.
J. Zhang, C. Gadelmeier, S. Sen, R. Wang, X. Zhang, Y. Zhong, U. Glatzel, B. Grabowski, G. Wilde, and S.V. Divinski, Zr Diffusion in BCC Refractory High Entropy Alloys: A Case of ‘Non-Sluggish’diffusion Behavior, Acta Mater., 2022, 233, p 117970.
H.U. Prasanna and K.R. Udupa, Indentation Creep Studies to Evaluate the Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel Welds, Aust. J. Mech. Eng., 2016, 14(1), p 39–43.
D. Matschkal-Amberger, M. Kolb, S. Neumeier, S. Gao, A. Hartmaier, K. Durst, and M. Göken, New Flat-Punch Indentation Creep Testing Approach for Characterizing the Local Creep Properties at High Temperatures, Mater. Des., 2019, 183, p 108090.
O.N. Senkov, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, and A.L. Pilchak, Development of a Refractory High Entropy Superalloy, Entropy, 2016, 18(3), p 102.
R. Gupta and B.S.S. Daniel, Impression Creep Behaviour of Ultrasonically Processed In-Situ Al3Ti Reinforced Aluminium Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 733, p 257–266.
L. Zhang, P. Yu, H. Cheng, H. Zhang, H. Diao, Y. Shi, and B. Chen, Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of an Al0.3CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, 47(12), p 5871–5875.
H. Rouault-Rogez, M. Dupeux, and M. Ignat, High Temperature Tensile Creep of CMSX-2 Nickel Base Superalloy Single Crystals, Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, 42(9), p 3137–3148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soltanalinezhad, M., Omidvar, H. & Farzadi, A. Microstructural and Mechanical Investigations in the Solution Annealing Heat Treatment of AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09480-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09480-w