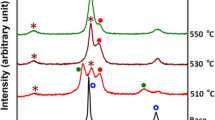
Abstract
The modified layers were prepared on the 65Mn steel surface by pulse detonation-plasma technology (PDT) treatment. The effects of PDT on the morphology, phase structure, microhardness, and crystallographic orientation of 65Mn steel were studied. The modified layer with uniform thickness, compact structure and high hardness can be formed on the surface of 65Mn steel after PDT treatment. It was found that the grains are refined in modified layer, the residual austenite is formed with different physical processes, and the element of electrode is implanted into the surface to cause microalloying effects. Moreover, the microhardness and the wear resistance of the modified layer improve with increasing of treatment pulse. The maximum microhardness of modified layer is up to 794.9HV, and the wear resistance can be improved to be 2.1 times that of the substrate, which might due to grain refinement, dislocation increase and impact hardening. The possible mechanisms of the changes of microstructure and properties in modified layer after PDT treatment were discussed in this paper.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, T.V. Pastukhova et al., Modification of Steel Surface by Pulsed Plasma Heating [J], Probl. Atom. Sci. Technol., 2017, 110(4), p 97–102.
S. Romankov, A. Mamaeva, S.D. Kaloshkin et al., Pulsed Plasma Treatment of Ti-Al Coatings Produced by Mechanical Alloying Method [J], Mater. Lett., 2007, 61(30), p 5288–5291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.04.055
A.N. Bandura, O.V. Byrka, V.V. Chebotarev et al., Alloying and Modification of Structural Materials under Pulsed Plasma Treatment [J], Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, 5(1), p 2–6.
Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, T.V. Pastukhova et al., Phase-structural Composition of Coating Obtained by Pulsed Plasma Treatment Using Eroded Cathode of T1 High Speed Steel[J], Probl. Atom. Sci. Technol., 2016, 102(4), p 102–106.
K.A. Yushchenko, Y.S. Borisov, Y.N. Tyurin et al., Theory and Practice of Plasma Detonation Modification of the Surface of Machine and Tool Components[J], Weld. Int., 1995, 9(1), p 56–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507119509548754
A.D. Pogrebnjak and Y.N. Tyurin, Modification of Material Properties and Coating Deposition Using Plasma Jets [J], Phys. Usp., 2005, 48(5), p 487–514. https://doi.org/10.1070/PU2005v048n05ABEH002055
Y.N. Tyurin, S.N. Kul, O.V. Kolisnichenko et al., Improving the Wear Resistance of Hard-alloy Rolling Disks by Pulsed-plasma Treatment [J], Steel in, Translation, 2009, 39(10), p 948–951. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091209100283
S.N. Bratushka, Y. Tyurin, O.V. Kolisnichenko et al., Structure and Tribological Characteristics of Steel Under Melting by Plasma Flow and Simultaneous Mo and W Alloying [J], J. Frict. Wear, 2012, 33(1), p 22–33. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366612010047
H.Y. Wang, Y.F. Zhao, X.J. Xu et al., Effects of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Boriding Layer on 65Mn Steel [J], Trans. Mater. Heat Treat., 2012, 33(12), p 142–146. https://doi.org/10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2012.12.027
A. Li, Hu. Mengjuan et al., Microstructure and Properties of 65Mn Steel After Austenite Inverse Phase Transformation by Sub-temperature Quenching [J], Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 194–196, p 89–94.
X.M. Yuan, H.Y. Wang, Y.F. Zhao et al., Process Design of Strengthening and Toughening Treatment for 65Mn Steel by Powder RE-Boronizing Method under Low Temperature [J], Adv. Mater. Res., 2014, 941–944, p 1414–1419.
C. Dong, J. Zhang, J. Xu et al., Microstructures and Properties of Electrical Discharge Strengthened Layers on 65Mn Steel [J], Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257(7), p 2843–2849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.078
H.L. Wang, Y.J. Shen, Q.D. Li et al., Effect of Laser Hardening Process Parameters on Hardened Layer Depth of 65Mn Steel [J], Trans. Mater. Heat Treat., 2015, 36(9), p 213–218. https://doi.org/10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2015.09.037
J.M. Luo, Y.H. Chen, J.L. Xu et al., Effect of Plasma-pulses Detonation Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of the Ti-6Al-4V Surface [J], Surf. Coat. Technol., 2019, 366, p 164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.03.033
L.I. Markashova, Y.N. Tyurin, O.V. Kolisnichenko et al., Influence of Structure Parameters of Mechanical Properties of R6M5 Steel Under the Conditions of Strengthening Surface Treatment [J], Paton Weld. J., 2013, 12, p 16–21.
M.A. Li, Influence of Pretreatment Process on Microstructure and Properties of 65Mn Steel after Subcritical Quenching [J], Appl. Mech. Mater., 2013, 310, p 55–58.
Z.H. Zheng, W.L. Zhang, D.X. Zhu et al., Inverse Heat Conduction Ananlysis of Surface Heat Transfer Coefficients for Typical Steels During Quenching with Phase Transformation [J], Trans. Mater. Heat Treat., 2010, 31(5), p 143–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60008-6
F. Landry and P. Schaaf, Laser Nitriding of Iron: Influence of the Spatial Laser Intensity Distribution [J], Appl. Surf. Sci., 1999, 138, p 266–270.
Y. Ivanov, W. Matz, V. Rotshtein et al., Pulsed Electron-beam Melting of High-speed Steel: Structural Phase Transformations and Wear Resistance [J], Surf. Coat. Technol., 2002, 150(2–3), p 188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(01)01542-0
G. Stahli and C.H. Sturzenegger, On the Formation of Austentic Boundary Layers by Short Laser-pulse Reaction with Steel[J], Scr. Metall., 1978, 12(7), p 617–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/0036-9748(78)90273-9
C.A. Apple and G. Krauss, The Effect of Heating Rate on the Martensite to Austenite Transformation in Fe-Ni-C Alloys [J], Acta Metall., 1972, 20(7), p 849–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(72)90077-6
Y.B. Xu, Y. Zou et al., Correlation Between Deformation Behavior and Austenite Characteristics in a Mn-Al Type TRIP Steel [J], Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 698, p 126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.05.058
W.J. Kaluba, R. Taillard and J. Foct, The Bainitic Mechanism of Austenite Formation During Rapid Heating [J], Acta Mateialia, 1998, 46(16), p 5917–5927. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00210-9
A.N. Valyaev, V.S. Ladysev, D.R. Mendygaliev et al., Defects in α-Fe Induces by Intense- Pulsed Ion Beam (IPIB) [J], Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B, 2000, 171(4), p 481–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(00)00294-9
G.E. Remnev, I.F. Isakov, M.S. Opekounov et al., High Intensity Pulsed Ion Beam Sources and Their Industrial Applications [J], Surf. Coat. Technol., 1999, 114(2/3), p 206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(99)00058-4
X. Jin, B.Q. Fu, C.L. Zhang and W. Liu, Evolution of the Texture and Mechanical Properties of 2060 Alloy During Bending [J], Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2015, 22, p 966–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1156-1
A.T. Lim, D.J. Srolovitz, M. Haataja et al., Low-angle Grain Boundary Migration in the Presence of Eatrinsic Dislocations [J], Acta Mater., 2009, 57(17), p 5013–5022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.07.003
Y.S. Borisov, O.V. Kolisnichenko et al., Effect of Plasma-detonation Treatment of Surface on Thermal State and Phase Composition of Modified Layers of Steel U8 [J], Sci. Tech., 2003, 4, p 22–25.
A. Ludwig, B. Pustal and D.M. Herlach, General Concept for a Stability Analysis of a Planar Interface Under Rapid Solidification Conditions in Multi-component Alloy Systems [J], Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, 304–306, p 277–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)01451-9
S. Takaki, Reversion of Deformation Induced Materials to Austenite and Mechanism of Ultra Grain Refining [J], Tetsu- to- Hagane, 2010, 80(12), p 529–535. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.463751
Xu. Cao Yupeng, F.A. Ying et al., Experimental study of residual stress formation mechanism of 7050 aluminum alloy sheet by laser shock processing [J], Chin. J. Lasers, 2016, 43(7), p 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3788/CJL201643.0702008
A. Leyland and A. Matthews, On the Significance of the H/E Ratio in Wear Control: A Nanocomposite Coating to Optimized Tribological Behavior [J], Wear, 2000, 246(1–2), p 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(00)00488-9
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (2013DFR50900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51701089, 51961015), Jiangxi Province Science and Technology Department (20194ABC28011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, L. et al. Microstructure and Properties of Modified Layer on the 65Mn Steel Surface by Pulse Detonation-Plasma Technology. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1562–1572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06258-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06258-2