Abstract
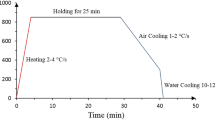
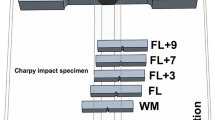
Mechanical properties and microstructure transformation for welded joints in EH40 ship plate steel were investigated after an electro-gas vertical welding and welding thermal simulation. Effect of the inclusions on the prior to austenite grain size and nucleation of intragranular ferrites (IGFs) was examined. Results indicated that the experimental steel has a good ability for high-heat input welding. Excellent impact toughness at testing temperature of − 20 °C was obtained. An increase in impact energies at − 20 °C for the position away from fusion line (FL) is observed. The average impact energy (177 J) for heat-affected zone by simulation with heat input of 120 kJ/cm is similar with that (165 J) for FL+1 mm by electro-gas vertical welding with heat input of 207 kJ/cm. The TiN particle lost the pinning effect when the peak temperature reached 1400 °C. However, the titanium oxide particles play an important role in inhibiting the austenite grain growth because of the high melting point. Three IAFs nucleated on the TiOx-Al2O3-MgO-MnS particle with the size of 7.6 μm were observed. The inclusion size is not the dominant requirement for the nucleation of IGFs and IAFs. The MnAl2O4 and TiO particle have good lattice matching with ferrite, they have a strong ability to promote the nucleation of IAF.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.H. Shi, X.G. Yuan, H.J. Huang, and S. Zhang, Effect of Zr Addition on the Microstructure and Toughness of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone with High-Heat Input Welding Thermal Cycle in Low-Carbon Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., 2017, 26(7), p 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2758-8
W.Z. Mu, P.G. Jonsson, and K. Nakajima, Recent Aspects on the Effect of Inclusion Characteristics on the Intragranular Ferrite Formation in Low Alloy Steels: A Review, High Temp. Mater. Proc., 2017, 36(4), p 309–325. https://doi.org/10.1515/htmp-2016-0175
J. Kobayashi, D. Ina, A. Futamura, and K. Sugimoto, Fracture Toughness of an Advanced Ultrahigh-strength TRIP-aided Steel, ISIJ Int., 2014, 54(4), p 955–962. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.54.955
K. Seo, H. Ryoo, and H.J. Kim, Local Variation of Impact Toughness in Tandem Electro-Gas Welded Joint, Weld. World, 2020, 64(3), p 457–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00844-8
M.H. Lee, R. Kim, and J.H. Park, Effect of Nitrogen on Grain Growth and Formability of Ti-Stabilized Ferritic Stainless Steels, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), p 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42879-3
Q.Y. Sha and Z.Q. Sun, Grain Growth Behavior of Coarse-Grained Austenite in a Nb-V-Ti Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2009, 523, p 77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.05.037
S.F. Medina, M. Chapa, P. Valles, A. Quispe, and M.I. Vega, Influence of Ti and N Contents on Austenite Grain Control and Precipitate Size in Structural Steels, ISIJ Int., 1999, 39(9), p 930–936. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.39.930
K. He and T.N. Baker, Effect of Zirconium Additions on Austenite Grain Coarsening of C-Mn and Microalloy Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1998, 256, p 111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)00804-1
Y. Liu, G.Q. Li, X.L. Wan, X.G. Zhang, Y. Shen and K.M. Wu, Toughness Improvement by Zr Addition in the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2019, 46, p 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2017.1353763
X.B. Li, T.S. Zhang, Y. Min, C.J. Liu and M.F. Jiang, Effect of Magnesium Addition in Low-Carbon Steel Part 1: Behaviour of Austenite Grain Growth, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2019, 46, p 292–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2017.1368953
M.H. Shi, K. Rangasayee, J. Zhang, X.G. YuanzL.J. Li, Effect of Zr Microalloying on Austenite Grain Size of Low-Carbon Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, 50(6), p 2574–2585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01701-1
J.W. Lei, K.M. Wu, Y. Li, T.P. Hou, X. Xie, and R.D.K. Misra, Effects of Zr Addition on Microstructure and Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2019, 26(10), p 1117–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00319-6
M.H. Shi, P.Y. Zhang, C. Wang, and F.X. Zhu, Effect of High Heat Input on Toughness and Microstructure of Coarse Grain Heat Affected Zone in Zr Bearing Low Carbon Steel, ISIJ Int, 2014, 54(4), p 932–937. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.54.932
G. An, J. Park, and I. Han, Effects of High Toughness and Welding Residual Stress for Unstable Fracture Prevention, Appl. Sci., 2020, 10(23), p 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238613
V. Richter-Trummer, P.M.G.P. Moreira, J. Ribeiro, and P.M.S.T. Castro, The Contour Method for Residual Stress Determination Applied to an Friction Stir Butt Weld, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2011, 681, p 177–181. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.681.177
K. Seo, H. Ryoo, and H.J. Kim, Characterization of the local Brittle Layer Formed in Electro-Gas Weld Metals, Weld. World, 2021, 65, p 513–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-01032-9
B.D. Meester, The weldability of modern structural TMCP steels, ISIJ Int, 1997, 37(6), p 537–551. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.37.537
N. Rykalin, Calculation of Heat Processes in Welding, 1st ed. Mashgiz, Moscow, 1960, p 4–6
M.H. Shi, P.Y. Zhang, and F.X. Zhu, Toughness and Microstructure of Coarse Grain Heat Affected Zone with High Heat Input Welding in Zr-bearing Low Carbon Steel, ISIJ Int., 2014, 54(1), p 188–192. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.54.188
Y. Tanimoto, H. Terasaki, and Y.I. Komizo, In-situ Observation of Microstructure Evolution in Heat-Affected-Zone of Ti-Killed Steel Weld, Q. J. Jpn. Weld. Soc, 2009, 27, p 122–125. https://doi.org/10.2207/qjjws.27.122s
N. Fujiyama, T. Nishibata, H. Hirata, and A. Seki, Analysis of γ Grain Growth Behavior with TiN Dissolution, Prep. Nat. Meet. JWS, 2013, 21, p 176–177
M. Koda, K. Amano, Y. Funahashi, C. Shiga, and S. Ueda, Relation Between Solution Behavior of TiN Particles and Austenite Grain Size in Synthetic HAZ (Properties of Iron and Steel), Tetsu. Hagane., 1984, 70, p S1265
T. Koseki and G. Thewlis, Overview Inclusion Assisted Microstructure Control in C-Mn and Low Alloy Steel Welds, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2005, 21(8), p 867–879. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328405×51703
R.A. Ricks, P.R. Howell, and G.S. Barritte, The Nature of Acicular Ferritein HSLA Steel Weld Metals, J. Mater. Sci., 1982, 17, p 732–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540369
F.J. Barbaro, P. Krauklis, and K.E. Eastering, Formation of Acicular Ferrite at Oxide Particles in Steels, Mater. Sci. Tech., 1989, 5, p 1057–1068. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708389790340888
S.G. Hong, K.J. Kang, and C.G. Park, Strain-Induced Precipitation of NbC in Nb and Nb-Ti Microalloyed HSLA Steels, Scr. Mater., 2002, 6, p 163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01214-3
Y.T. Pan and J.L. Lee, Development of TiOx-bearing steels with superior heat-affected zone toughness, Mater. Des., 1994, 15, p 331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/0261-3069(94)90027-2
J. Takamura, S. Mizoguchi, Roles of Oxides in Steel Performance, in proceedings of the 6th internal iron and steel congress. (Nagoya, ISIJ, 1999), pp. 591–597
Hori. Effect of Chemical Composition on Strength and Toughness of Welds Made by Large Heat Input Submerged Arc Welding. PhD Thesis, Osaka University, 1995
S. Tsushima, S. Ohkita, and Y. Hori, Effects of Oxygen on the Toughness of Ti-B Containing AC-MIG Weld Metal Development of AC-MIG Welding Process (Report 3), Q. J. Jpn. Weld. Soc., 1992, 10, p 264–271. https://doi.org/10.2207/qjjws.10.264
J.M. Dowling, J.M. Corbett, and H.W. Kerr, Inclusion Phases and the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in Submerged arc Welds in HIGH Strength Low Alloy Steels, Metal. Mater. Trans. A., 1986, 17A, p 1611–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650098
Y. Tomonori, Study on inclusion composition and acicular ferrite formation behavior in weld metal of Ti-B low carbon alloy steel. PhD Thesis, Osaka University, 88–89, 2009
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a grant from National Natural Science Foundation Project of China (Grant Number 51674004) and Key research and development projects of Anhui Science and Technology Department (Grant Number 202104a05020020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Zhang, J. & Li, B. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Transformation Behavior for Welded Joints in Ship Plate Steel with High-Heat Input Welding. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 944–952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06224-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06224-y