Abstract
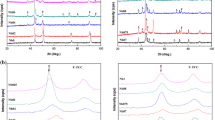
CoFe2NiMn0.3Alx (x = 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.00) alloys were prepared using the arc melting method, and their crystal structure, microstructure, and mechanical properties were systematically studied. The results show that a greater Al content beneficially alters the crystal structure of the alloys from a single FCC phase to a mixture of FCC + BCC phases. With increasing Al content, the volume fraction of the BCC phase increases steadily, whereas the volume fraction of the FCC phase substantially decreases. With increasing Al content, the yield strength and hardness of the CoFe2NiMn0.3Alx alloys increases, whereas their ductility gradually decreases. Among the studied alloys, that with x = 0.75 exhibits both high strength and good ductility and its yield strength, fracture strength, and fracture strain are 1100 MPa, 2335 MPa, and 33.24%, respectively. Measurements of magnetic properties indicated that the saturation magnetization increases from 90 emu g−1 for the Al0.25 alloy to 148 emu g−1 for the Al1.00 alloy. The results show that the CoFe2NiMn0.3Alx high-entropy alloys are potential candidates to serve as magnetic materials in industrial applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Engin. Mater., 2004, 6(5), p 299–303
Z.M. Li, K.G. Pradeep, Y. Deng, D. Raabe, and C.C. Tasan, Metastable High-entropy Dual-phase Alloys Overcome the Strength-ductility Trade-off, Nature, 2016, 534, p 227–230
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and Properties of High-entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93
H. Jiang, D.X. Qiao, Y.P. Lu, Z. Ren, Z.Q. Cao, T.M. Wang, and T.J. Li, Direct Solidification of Bulk Ultrafine-Microstructure Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys with Outstanding Thermal Stability, Scripta Mater., 2019, 165, p 145–149
Y.P. Lu, H.F. Huang, X.Z. Gao, C.R. Ren, J. Gao, H.Z. Zhang, S.J. Zheng, Q.Q. Jin, Y.H. Zhao, C.Y. Lu, T.M. Wang, and T.J. Li, A Promising New Class of Irradiation Tolerant Materials: Ti2ZrHfV0.5Mo0.2 High-entropy Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35(3), p 369–373
F. He, D. Chen, B. Han, Q.F. Wu, Z.J. Wang, S.L. Wei, D.X. Wei, J.C. Wang, C.T. Liu, and J.J. Kai, Design of D022 Superlattice with Superior Strengthening Effect in High Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2019, 167, p 275–286
M.B. Kivy, M.A. Zaeem, and S. Lekakh, Investigating Phase Formations in Cast AlFeCoNiCu High Entropy Alloys by Combination of Computational Modeling and Experiments, Mater. Des., 2017, 127, p 224–232
Y.P. Lu, X.Z. Gao, L. Jiang, Z.N. Chen, T.M. Wang, J.C. Jie, H.J. Kang, Y.B. Zhang, S. Guo, H.H. Ruan, Y.H. Zhao, Z.Q. Cao, and T.J. Li, Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with Balanced Strength and Ductility in a Wide Temperature Range, Acta Mater., 2017, 124, p 143–150
O.N. Senkov, S.V. Senkova, and C. Woodward, Effect of Aluminum on the Microstructure and properties of Two Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2014, 68, p 214–228
P.H. Wu, N. Liu, W. Yang, Z.X. Zhu, Y.P. Lu, and X.J. Wang, Microstructure and Solidification Behavior of Multicomponent CoCrCuxFeMoNi High-entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2015, 642, p 142–149
M. Zhu, K. Li, Y.Q. Liu, Z.J. Wang, L.J. Yao, Y. Fa, and Z.Y. Jian, Microstructure, Corrosion Behaviour and Microhardness of Non-equiatomic Fe1.5CoNiCrCux (0.5 ≤ x ≤ 2.0) High-entropy Alloys, Trans. Indian Ins. Metals, 2019, 73(2), p 389–397
Z.J. Wang, Y.Y. Huang, Y. Yang, J.C. Wang, and C.T. Liu, Atomic-size Effect and Solid Solubility of Multicomponent Alloys, Scripta Mater., 2015, 94, p 28–31
P.F. Yu, L.J. Zhang, H. Cheng, H. Zhang, M.Z. Ma, Y.C. Li, G. Li, P.K. Liaw, and R.P. Liu, The High-entropy Alloys with High Hardness and Soft Magnetic Property Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and High-pressure Sintering, Intermetallics, 2016, 70, p 82–87
C.Z. Yao, P. Zhang, M. Liu, G.R. Li, J.Q. Ye, P. Liu, and Y.X. Tong, Electrochemical Preparation and Magnetic Study of Bi-Fe-Co-Ni-Mn High Entropy Alloy, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(28), p 8359–8365
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Y.Q. Cheng, and P.K. Liaw, High-entropy Alloys with High Saturation Magnetization, Electrical Resistivity, and Malleability, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, p 1455
Q. Zhang, H. Xu, X.H. Tan, X.L. Hou, S.W. Wu, G.S. Tan, and L.Y. Yu, The Effects of Phase Constitution on Magnetic and Mechanical Properties of FeCoNi(CuAl)x (x = 0–1.2) High-entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 693, p 1061–1067
P.P. Li, A.D. Wang, and C.T. Liu, Composition Dependence of Structure, Physical and Mechanical Properties of FeCoNi(MnAl)x High Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2017, 87, p 21–26
Y.F. Kao, S.K. Chen, T.J. Chen, P.C. Chu, J.W. Yeh, and S.J. Lin, Electrical, Magnetic, and Hall Properties of AlxCoCrFeNi High-entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509(5), p 1607–1614
T.T. Zuo, M.C. Gao, L.Z. Ouyang, X. Yang, Y.Q. Cheng, R. Feng, S.Y. Chen, P.K. Liaw, J.A. Hawk, and Y. Zhang, Tailoring Magnetic Behavior of CoFeMnNiX (X = Al, Cr, Ga, and Sn) High Entropy Alloys by Metal Doping, Acta Mater., 2017, 130, p 10–18
C. Liu, W.Y. Peng, C.S. Jiang, H.M. Guo, J. Tao, X.H. Deng, and Z.X. Chen, Composition and Phase Structure Dependence of Mechanical and Magnetic Properties for AlCoCuFeNix High Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35(6), p 1175–1183
Y.J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, F.J. Wang, and G.L. Chen, Phase Transformation Induced by Lattice Distortion in Multiprincipal Component CoCrFeNiCuxAl1−x Solid-solution Alloys, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92, p 241917
B. Chanda and J. Das, Composition Dependence on the Evolution of Nanoeutectic in CoCrFeNiNbx (0.45 ≤ x ≤ 0.65) High Entropy Alloys, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, 20(4), p 1700908
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, Prediction of High-entropy Stabilized Solid-solution in Multi-component Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 132(2–3), p 233–238
G. Qin, S. Wang, R.R. Chen, H.T. Zheng, L. Wang, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Improvement of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrCuFeNi High-entropy Alloys by V Addition, J. Mater. Engin. Perform., 2019, 28, p 1049–1056
G. Qin, Z.B. Li, R.R. Chen, H.T. Zheng, C.L. Fan, L. Wang, Y.Q. Su, H.S. Ding, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, CoCrFeMnNi High-entropy Alloys Reinforced with Laves Phase by Adding Nb and Ti Elements, J. Mater. Res., 2019, 34(6), p 1011–1020
N.Y. Yurchenko, N.D. Stepanov, D.G. Shaysultanov, M.A. Tikhonovsky, G.A. Salishcheva, Effect of Al Content on Structure and Mechanical Properties of the AlxCrNbTiVZr (x = 0; 0.25; 0.5; 1) High-entropy Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2016, 121, p 125–134
S. Guo, C.P. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu, Effect of Valence Electron Concentration on Stability of fcc or bcc Phase in High Entropy Alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109(10), p 103505
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, and J. Shi, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiTiAlx High-entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 508(1–2), p 214–219
C.J. Tong, M.R. Chen, J.W. Yeh, S.J. Lin, S.K. Chen, T.T. Shun, and S.Y. Chang, Mechanical Performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi High-entropy Alloy System with Multiprincipal Elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36, p 1263–1271
J.M.D. Coey, Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010, p 195–244
Acknowledgment
This research work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51301125, 51971166, 51904218), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020JM-557), and the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing in NWPU (No. SKLSP201811).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Yao, L., Zhu, M. et al. Structural Evolution and Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Nonequiatomic CoFe2NiMn0.3Alx (0.25 ≤ x ≤ 1.00) High-Entropy Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 1472–1478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05411-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05411-7