Abstract
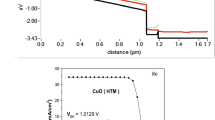
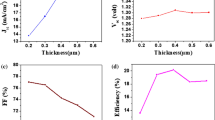
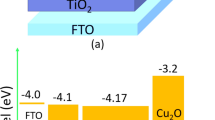
Lead-based organic–inorganic perovskite (OIP) materials have shown great possibilities as absorber materials in photovoltaic devices. Despite its better power conversion efficiency (PCE), the toxicity of lead limits its application in photovoltaic organic solar cells. This limitation has encouraged researchers to find an alternative lead-free organic perovskite material that must be eco-friendly. Therefore, in this present research work, we have proposed a lead-free OIP heterostructure solar cell using CH3NH3SnI3 as the absorber layer, Cu2O as the hole transport layer (HTL), TiO2 as the electron transport layer (ETL), and FTO as a transparent conducting oxide (TCO) layer. Further, we have carried out a simulation study using SCAPS software to obtain a good performance of the proposed cell by optimizing various parameters. Thus, the obtained simulated results show that a moderate temperature of 305 K is necessary to achieve better cell efficiency. A significant decrease in efficiency is observed upon increasing the operating device temperature. Further, Gaussian energy distribution in the absorber OIP layer, CH3NH3SnI3 , shows better possibilities for obtaining a good performance from the proposed cell. On varying the Gaussian peak defect density from 1 × 1016 cm−3 to 6 × 1020 cm−3, the best-simulated result is offered at a concentration of 1.079 × 1016 cm−3. In addition, on varying the electron affinity of the active layer, we obtained the best result in its class at a value of 4.13 eV. Further, on energy band gap optimization of the active layer, we observed the maximum open-circuit voltage of 1.5 eV. Finally, all the performance parameters for the proposed OIP cell were found to be: PCE 18.27%, short-circuit current density 32.47 mA/cm2, open-circuit voltage 0.7397 V, and FF 76.06%. Thus, we can proudly say that the present analysis may open a modern doorway for attaining clean energy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.K. Markose, M. Shaji, S. Bhatia, P.R. Nair, K.J. Saji, A. Antony, and M.K. Jayaraj, Novel boron-doped p-type Cu2O thin films as a hole-selective contact in c-Si solar cells. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 12972–12981 (2020).
Y. Li, M.D. Cole, Y. Gao, T. Emrick, Z. Xu, Y. Liu, and T.P. Russell, High-performance perovskite solar cells with a non-doped small molecule hole transporting layer. Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 1634–1641 (2019).
H.H. Huang, Y.C. Shih, L. Wang, and K.F. Lin, Boosting the ultra-stable unencapsulated perovskite solar cells by using montmorillonite/CH3NH3PbI3 nanocomposite as a photoactive layer. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 1265–1273 (2019).
W.S. Yang, B.W. Park, E.H. Jung, N.J. Jeon, Y.C. Kim, D.U. Lee, S.S. Shin, J. Seo, E.K. Kim, J.H. Noh, and S.I. Seok, Iodide management in formamidinium-lead-halide-based perovskite layers for efficient solar cells. Science 356, 1376–1379 (2017).
Y.C. Shih, Y.B. Lan, C.S. Li, H.C. Hsieh, L. Wang, C. Wu, and K.F. Lin, Amino-acid-induced preferential orientation of perovskite crystals for enhancing interfacial charge transfer and photovoltaic performance. Small 13, 1604305–1604314 (2017).
H.S. Kim, S.H. Im, and N.G. Park, Organolead halide perovskite: new horizons in solar cell research. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 5615–5625 (2014).
F. Gao, C. Li, L. Qin, L. Zhu, X. Huang, H. Liu, L. Liang, Y. Hou, Z. Lou, Y. Hu, and F. Teng, Enhanced performance of tin halide perovskite solar cell by addition of lead thiocyanate. RSC Adv. 8, 14025–14030 (2018).
M. Lyu, J.H. Yun, P. Chen, M. Hao, and L. Wang, Addressing toxicity of lead: progress and applications of low-toxic metal halide perovskites and their derivatives. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602512–1602537 (2017).
L. Lanying, N. Chengsheng, M. Cassidya, and J.T.S. Irvine, Demonstration of high performance in a perovskite oxide supported solid oxide fuel cell based on La and Ca co-doped SrTiO3. Mater. Chem. A 4, 11708–11718 (2016).
H. Kleineberg, M. Eisenacher, H. Lange, H. Strutz, and R. Palkovits, Perovskites and metal nitrides as catalysts in the base-catalyzed aldol addition of isobutyraldehyde to formaldehyde. Catal. Sci. Technol. 6, 6057–6065 (2016).
S.D. Stranks, G.E. Eperon, G. Grancini, C. Menelaou, M.J.P. Alcocer, T. Leijtens, L.M. Herz, A. Petrozza, and H.J. Snaith, Electron–hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013).
A.K. Sharma, N.K. Chourasia, and R.K. Chourasia, Optical, temperature, and bulk analysis theoretically in p-Si/n-CdS heterojunction solar cell. Mater. Today: Proc. 67, 632–636 (2022).
P.K. Jha, N.K. Chourasia, A.K. Sharma, and R.K. Chourasia, Optimization of electrical properties for performance analysis of p-Si/n-CdS/ITO heterojunction photovoltaic cell. Mater. Today: Proc. 67, 620–624 (2022).
M. Weiss, J. Horn, C. Richter, and D. Schlettwein, Preparation and characterization of methylammonium tin iodide layers as photovoltaic absorbers. Phys. Status Solidi A 213, 975–981 (2016).
N.K. Noel, S.D. Stranks, A. Abate, C. Wehrenfennig, S. Guarnera, A.A. Haghighirad, A. Sadhanala, G.E. Eperon, S.K. Pathak, M.B. Johnston, A. Petrozza, L.M. Herza, and H.J. Snaith, Lead-free organic–inorganic tin halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3061–3068 (2014).
M. Kumar, A. Raj, A. Kumar, and A. Anshul, An optimized lead-free formamidinium Sn-based perovskite solar cell design for high power conversion efficiency by SCAPS simulation. Opt. Mater. 108, 110213 (2020).
M. Kumar, A. Raj, A. Kumar, and A. Anshul, Computational analysis of bandgap tuning, admittance and impedance spectroscopy measurements in lead-free MASnI3 perovskite solar cell device. Int. J. Energy Res. 46(8), 1–14 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7942.
Y. Guo, Y. Xue, X. Li, C. Li, H. Song, Y. Niu, H. Liu, X. Mai, J. Zhang, and Z. Guo, Effects of transition metal substituents on the interfacial and electronic structure of CH3NH3PbI3/TiO2 interface: a firstprinciples comparative study. Nanomaterials 9, 966–979 (2019).
H.Y. Yang, W.Y. Rho, S.K. Lee, S.H. Kim, and Y.B. Hahn, TiO2 nanoparticles/nanotubes for efficient light harvesting in perovskite solar cells. Nanomaterials 9, 326–335 (2019).
L. Lin, L. Jiang, P. Li, B. Fan, and Y. Qiu, A modelled perovskite solar cell structure with a Cu2O hole- transporting layer enabling over 20% efficiency by low-cost low-temperature processing. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 14, 205–211 (2019).
S. Abdelaziz, A. Zekry, A. Shaker, and M. Abouelatta, Investigating the performance of formamidinium tin-based perovskite solar cell by SCAPS device simulation. Opt. Mater. 101, 109738 (2020).
Y.H. Khattak, F. Baig, S. Ullah, B. Marí, S. Beg, and K. Khan, Effect of Cu2O hole transport layer and improved minority carrier lifetime on the efficiency enhancement of Cu2NiSnS4 based experimental solar cell. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 10, 043502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5037471.
W. Yu, F. Li, H. Wang, E. Alarousu, Y. Chen, B. Lin, L. Wang, M.N. Hedhili, Y. Li, K. Wu, X.W. Omar, F. Mohammedc, and T. Wu, Ultrathin Cu2O as an efficient inorganic hole transporting material for perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8(11), 6173–6179 (2016).
Q. Qiu, S. Li, J. Jiang, D. Wang, Y. Lin, and T. Xie, Improved electron transfer between TiO2 and FTO interface by N-doped anatase TiO2 nanowires and its applications in quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 121(39), 21560–21570 (2017).
H.J. Du, W.C. Wang, and J.Z. Zhu, Device simulation of lead-free CH3NH3SnI3 perovskite solar cells with high efficiency. Chin. Phys. B 25, 108802–188809 (2016).
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductor Devices (NewYork: John Wiley and Sons, 1981), p.264.
M.A. Green, Solar Cells (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1982), p.88.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Marc Burgelman, University of Gent, Belgium, for the SCAPS-1D simulation software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PKJ: Writing—original draft, Formal analysis; NKC: Writing—original draft, Formal analysis; AS: Writing—original draft, Formal analysis; AKS: Formal analysis; RK: Formal analysis; SS: Formal analysis; MK: Review original draft, Formal analysis; RKC: Visualization, Supervision, Writing—original draft, Formal analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Prakash Kumar Jha and Nitesh K. Chourasia contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, P.K., Chourasia, N.K., Srivastava, A. et al. Study of Eco-Friendly Organic–Inorganic Heterostructure CH3NH3SnI3 Perovskite Solar Cell via SCAPS Simulation. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 4321–4329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10267-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10267-3