Abstract
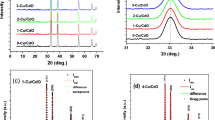
This work explores the structural, optical and dielectric properties and the magnetic behaviour of copper (Cu) (0–4%)-doped tin dioxide (SnO2) nanoparticles, synthesized by the sol–gel method using methanol as solvent. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed the tetragonal structure of SnO2. The inclusion of Cu in the SnO2 lattice enhanced the crystallite size of the Cu-doped SnO2 nanoparticles, as determined by the Scherrer method, and crystallite sizes were found to be consistent with the Williamson–Hall method. The morphology, observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), revealed the formation of uniformly distributed nanoparticles of spherical shape. The formation of a characteristic peak in the range of 480–750 cm−1 was associated with an antisymmetric O-Sn-O bridge functional group of SnO2. The reduced band gap is in accordance with the quantum confinement effect in synthesized samples. Strain-influenced dielectric studies conducted at room temperature within a frequency range of 1 Hz to 7 MHz revealed a relatively high dielectric constant, AC conductivity and low dielectric loss. Here, for the first time, electric modulus formalism is adapted to analyse the relaxation mechanism in Cu-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. The relaxation peak shift towards lower frequency (\( \approx 1\;{\hbox{kHz}}) \) in the investigated samples indicates the short-range mobility of ions and longer relaxation times. The transition from a diamagnetic to a paramagnetic state is confirmed by the addition of Cu content in the SnO2 lattice. The observed paramagnetism of the Cu-doped SnO2 nanoparticles is correlated with lattice strain. Cu doping led to an increase in magnetic moment on the order of 10−1 emu/g. The synthesized samples with high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and paramagnetic behaviour are found to be efficient candidates for high-frequency devices and biomedical applications. The longer relaxation times may make them suitable for future memory materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Seabra and N. Durán, Nanotoxicology of metal oxide nanoparticles. Metals 5, 934 (2015).
S.K. Tripathy and T.N.V. Prabhakara Rao, J. Nano Electron. Phys. 9, 02019 (2017).
S. Sarmah and A. Kumar, Indian J. Phys. 84, 1211 (2010).
M.S. Pereira, F.A.S. Lima, C.B. Silva, P.T.C. Freire, and I.F. Vasconcelos, J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 84, 206 (2017).
S. Nilavazhagan, S. Muthukumaran, and M. Ashokkumar, Microstruct. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 26, 3989–3996 (2015).
M. Parthibavarman, V. Hariharan, C. Sekar, and V.N. Singh, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 12, 1894 (2010).
S. Zulfiqar, Z. Iqbal, and L. Jianguo, Chin. Phys. B 26, 126104 (2017).
A. Ayeshamariam, V.S. Vidhya, S. Sivaranjani, M. Bououdina, R. PerumalSamy, and M. Jayachandran, J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 8, 1 (2013).
M. Aziz, W. Rosemaria, and W. Baharom, J. Mater. Lett. 91, 31–34 (2013).
H.-C. Chiu and C.-S. Yeh, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 7256–7259 (2007).
S. Tazikeh, A. Akbar, A. Taleb, and E. Taleb, Mater. Sci. Poland 32, 98 (2014).
W.B. Soltan, S. Nasri, M.S. Lassoued, and S. Ammar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 6649–6656 (2017).
G. Lu, K.L. Huebner, L.E. Ocola, M. Gajdardziska-Josifovska, J. Chen, and Hindawi Publishing Corporation, J. Nanomater. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/JNM/2006/60828.
Q. Zhao, L. Ma, Q. Zhang, C. Wang, and X. Xijin, J. Nanomater. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/850147.
Z. Dai, M. Peng, X. Cai, Y. Fu, X. Yu, S. Liu, B. Deng, and K. Hany, J. Power Sources 247, 8673–8680 (2014).
E. Pradyumna, N. Sreelekha, D. Amaranatha, K.R. Gunasekhar, and K. Subramanyam, Int. J. Adv. Eng. Nano Technol. 2, 22 (2015).
A. Kolmakov, Y.X. Zhang, G.S. Cheng, and M. Moskovits, Adv. Mater. 15, 997 (2003).
S. PhilKim, M. YongChoi, and H. ChulChoi, Mater. Res. Bull. 74, 85 (2016).
C.W. Zhang, H. Kao, and J.M. Dong, Phys. Lett. A 373, 2592 (2009).
R. Zulfiqar, Y. Yuan, Z. Iqbal, J. Yang, W. Wang, Z. Ye, and J. Lu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 12 (2016).
M.P. Rajeeva, C.S. Naveen, A.R. Lamani, and H.S. Jayamma, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 21 (2017).
A. Ahmed, M. Naseem Siddique, T. Ali, P. Tripathi, in AIP Conference Proceedings, pp. 1–4 (2018).
F.A. Mir, K.M. Batoo, I. Chatterjee, and G.M. Bhat, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 3 (2014).
S.K. Pandian, K. Karthik, K. Sureshkumar, and N. Victor Jaya, Mater. Manuf. Process. 27, 130 (2012).
R. Singh and B.C. Yadav, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 20, 5 (2010).
S. Benzitouni, M. Zaabat, A. Khial, D. Rechem, A. Benaboud, D. Bouras, A. Mahdjoub, M. Toubane, and R. Coste, Adv. Nanopart. 5, 140 (2016).
S. S. Roy, J. Podder, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering (2009), pp. 26–28.
S. Sagadevan, Z.Z. Chowdhury, M. Johan, R. Bin, F.A. Aziz, L.S. Roselin, J. Podder, J.A. Lett, and R. Selvin, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 7139 (2019).
P.P. Sahay, R.K. Mishra, S.N. Pandey, S. Jha, and M. Shamsuddin, Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 479 (2013).
J. Zhang, Y. Zhang, K.W. Xu, and V. Ji, Solid State Commun. 139, 87 (2006).
S. Sagadevan, J. Nano Res. 3, 91 (2015).
A. Sharma, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 093918 (2010).
K. Subramanyam, N. Sreelekha, G. Murali, D. Amaranatha Reddy, and R.P. Vijayalakshmi, Phys. B 454, 86 (2014).
S. Gupta, V. Ganesan, N. P. Lalla, I. Sulania B. Das, Cond-Mat. Mtrl-Sci. arXiv:1709.05930 (2017).
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N. Madhusudhana Rao, N. Sai, M. Rigana Begam, M. Shobana, and Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/284237.
J.M.D. Coey, A.P. Douvalis, C.B. Fitzgerald, and M. Venkatesan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 23 (2004).
M. Sharma, S. Kumar, R.N. Aljawfi, S. Dalela, S.N. Dolia, A. Alshoaibi, and P.A. Alvi, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 8181 (2019).
R. Toy and E. Karathanasis, Nano Materials in Pharmacology, ed. Z.R. Lu and S. Sakuma (New York: Springer Link Books, 2016), p. 113.
O. Wiranwetchayan, S. Promnopas, T. Thongtem, A. Chaipanich, and S. Thongtem, Surf. Coat. Technol. 326, 310–315 (2017).
M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghia and N. Shahtahmasebia, Phys. B 403, 2431 (2008).
V.S. Jahnavi, S.K. Tripathy, and A.V.N. Ramalingeswara, Phys. B 565, 61 (2019).
K. Bhuyan, A. Bhattacharjee, D.M. Bhuyan, and P.R. Alapa, Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3, 10 (2007).
G. Mulongo, J. Mbabazi, and S. Hak-Chol, Res. J. Chem. Sci. 1, 18 (2011).
G.E. Patil, D.D. Kajale, S.D. Shinde, V.G. Wagh, V.B. Gaikwad, and G.H. Jain, Advancement in Sensing Technology, ed. S.C. Mukhopadhyay, K.P. Jayasundera, and A. Fuchs (Berlin: Springer, 2013), p. 299.
N. Bhardwaj, A. Pandey, B. Satpati, M. Tomar, V. Gupta, and S. Mohapatra, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 18846 (2016).
J. Hays and A. Punnoose, Phys. Rev. B 72, 075203 (2005).
A. Punnoose, J. Hays, A. Thurber, M.H. Engelhard, R.K. Kukkadapu, C. Wang, V. Shutthanandan, and S. Thevuthasan, Phys. Rev. B 72, 054402 (2005).
J. Kaur, V. Gupta, R.K. Kotnala, and K.C. Verma, Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 50, 57 (2012).
B. Venugopal, B. Nandan, A. Ayyachamy, V. Balaji, S. Amirthapandian, B.K. Panigrahi, and T. Paramasivam, RSC Adv. 4, 6141 (2014).
N. Mazumder, A. Bharati, S. Saha, D. Sen, and K.K. Chattopadhyay, Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 975 (2012).
M.A. Dar, K.M. Batoo, V. Verma, W.A. Siddiqui, and R.K. Kotnala, J. Alloy. Compd. 493, 553 (2009).
K. Manikandan, S. Dhanuskodi, A.R. Thomas, N. Maheswari, G. Muralidharan, and D. Sastikumar, Supercapacitor Opt. Limiter. 6, 90559 (2016).
A.R. Razeghizadeh, L. Zalaghi, I. Kazeminezhad, and V. Rafee, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 36, 1 (2017).
K. Sakthiraj, B. Karthikeyan, and K. Balachandrakumar, Int. J. Chem. Technol. Res. 7, 1481 (2014).
Y. Wang, J.-c. Zhao, S. Zhang, Q.-j. Liu, and X. Wu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 1477 (2005).
J. Pal and P. Chauhan, Materials Charcterization 61, 575 (2010).
S.S. Roy and J. Podder, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 12, 1479 (2010).
V. Agrahari, A.K. Tripathi, M.C. Mathpal, A.C. Pandey, S.K. Mishra, R.K. Shukla, and A. Agarwal, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 9571 (2015).
K.G. Saw, N.M. Aznan, F.K. Yam, S.S. Ng, and S.Y. Pung, PLoS ONE 10, 0141180 (2015).
S. Bandyopadhyay, G.K. Paul, and S.K. Sen, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 71, 103 (2002).
A.H. Virpal, N. Kohli, J. Kaur, A. Kaur, J. Singh, S. Sharma, and R.C. Singh, Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 8, 16 (2017).
W. Grimesy and R.W. Grimesz, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 3029 (1998).
H.M. El-MallahTju, Acta Phys. Pol. A 122, 174 (2012).
M. Sumaira Mehraj and A. Shahnawaze Ansari, J. Nano Eng. Nano Manuf. 3, 229 (2013).
V.D. Nithya and R. Kalai Selvan, Phys. B 406, 24 (2011).
R. Bargougui, A. Oueslati, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, S. Colis, F. Hlel, and S. Ammar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 2066 (2014).
R. Khan and F. Ming-Hu, Chin. Phys. B 24, 127803-1 (2015).
N. Ahmad, S. Khan, and M.M.N. Ansari, Mater. Res. Expr. 5, 22 (2018).
W.-H. Jung and Hindawi Publishing Corporation, J. Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/169528.
J. Liua, C.-G. Duan, W.-G. Yin, W.N. Mei, and R.W. Smith, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 2812 (2003).
R. Tripathi, A. Dutta, S. Das, and A. Kumar, Appl. Nanosci. 6, 175 (2016).
M. Coskun, O. Polat, F.M. Coskun, Z. Durmus, M. Çaglard, and A. Turuta, RSC Adv. 8, 4634 (2018).
P. Mohanapriya, N. Padmanathan, R. Pradeepkumar, and K. Rahulan, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 13057 (2016).
V. Agrahari, L.K. Gaur, M.C. Mathpal, and A. Agarwal, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17, 8752 (2017).
V. Kumar, S. Uma, and R. Nagarajan, Turk. J. Phys. 38, 450 (2014).
P. Pascariu, A. Airinei, M. Grigoras, N. Fifere, L. Sacarescu, N. Lupu, and L. Stoleriu, J. Alloy. Compd. 668, 65 (2016).
V. Agrahari, M.C. Mathpal, S. Kumar, and A. Agarwal, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 3053 (2016).
V. Agrahari, M.C. Mathpal, S. Kumar, M. Kumar, and A. Agarwal, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 6020 (2016).
S. Bhuvana, H.B. Ramalingam, G. Thilakavathi, and K. Vadivel, Mater. Technol. 32, 1 (2016).
N. Nithyaa and N. Victor Jaya, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 31, 4117 (2018).
J. Fan, E. Menéndez, M. Guerrero, A. Quintana, E. Weschke, E. Pellicer, and J. Sort, Nanomaterials 7, 348 (2017).
D.C. Agarwal, U.B. Singh, S. Gupta, R. Singhal, P.K. Kulriya, F. Singh, A. Tripathi, J. Singh, U.S. Joshi, and D.K. Avasthi, Sci. Rep. 9, 6675 (2019).
H. Bayrakdar, O. Yalçın, S. Vural, and K. Esmer, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 343, 86 (2013).
J. Ma and K. Chen, Phys. Lett. A 380, 3313 (2016).
A.T. Apostolov, I.N. Apostolova, and J.M. Wesselinowa, Phys. Status Solidi B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201800179.
R. Kumar and M. Kar, Ceram. Int. 42, 6640 (2016).
Acknowledgments
The authors are ever grateful to the management of G.V.P. College of Engineering for supporting us, and we also extend our thanks to Andhra University for providing structural and optical characterization techniques, STIC, Cochin India for providing TEM facilities, Sathyabama University for providing impedance analysis facilities, and IIT Madras for providing VSM facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahnavi, V.S., Tripathy, S.K. & Rao, A.V.N.R. Study of the Structural, Optical, Dielectric and Magnetic Properties of Copper-Doped SnO2 Nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 3540–3554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08028-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08028-7