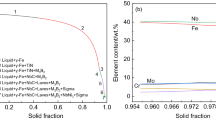
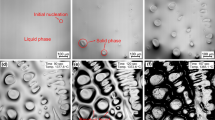
Abstract
The effects of solution temperature and soaking time on the grain growth and precipitates in a novel iron-base superalloy were investigated. Abnormal grain growth occurs at the solution temperature of 1473 K (1200 °C) irrespective of the niobium content and soaking time, which is attributed to the dissolution and coarsening of NbC precipitates. The amount of NbC particles increases with increasing niobium content of the superalloy, which has a strong pinning effect on grain boundary migration. Fe2Nb-type Laves phase is fully dissolved in the superalloy containing 0.64 and 1.00 mass pct Nb, whereas eutectic carbide NbCs are partially dissolved regardless of the solution temperatures. Both Fe2Nb-type Laves phase and eutectic carbide NbC are partially dissolved in the superalloy with 1.40 mass pct Nb after the solution at 1443 K (1170 °C) because of the competitive dissolution of Fe2Nb-type Laves phase and eutectic carbide NbC. The amount of eutectic carbides NbC after the solution at 1473 K (1200 °C) is larger than that at 1443 K (1170 °C) because of higher soluble niobium content in the superalloy matrix contributed by the complete dissolution of Fe2Nb-type Laves phase. A model for predicting the austenite grain growth of the superalloy with varying niobium contents during solution is developed. The role of niobium on the hardness of the superalloy was discussed.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02505-6
References
M. Seifollahi, S.H. Razavi, Sh. Kheirandish, and S.M. Abbasi: Phys. Met. Metall., 2020, vol. 121, pp. 284–90.
B.S. Rho, S.W. Nam, and X. Xie: J. Mater. Sci., 2002, vol. 37, pp. 203–09.
P.D. Tiedra, Ó. Martín, and M. San-Juan: J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 673, pp. 231–36.
K. Kobayashi, K. Yamaguchi, M. Hayakawa, and M. Kimura: Int. J. Fatigue., 2008, vol. 30, pp. 1978–84.
Y. Ning, S. Huang, M.W. Fu, and J. Dong: Mater. Charact., 2015, vol. 109, pp. 36–42.
M. Zhao, Z. Guo, H. Liang, and L. Rong: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2010, vol. 527, pp. 5844–51.
Y. Toda, Y. Nakamura, N. Harada, A. Kaseya. N. Kobata, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, and O. Umezawa: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, vol. 797, pp. 140104.
Z. Sun, P.D. Edmondson, and Y. Yamamoto: Acta Mater., 2018, vol. 144, pp. 716–27.
S. Sui, Z. Li, C. Zhong, Q. Zhang, A. Gasser, J. Chen, Y. Chew, and G. Bi: Compos. Part B., 2021, vol. 215, p. 108819.
S. Chen, C. Zhang, Z. Xia, H. Ishikawa, and Z. Yang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2014, vol. 616, pp. 183–88.
Q. Yu and Y. Sun: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2006, vol. 420, pp. 34–38.
Y. Zhang, X. Li, Y. Liu, C. Liu, J. Dong, L. Yu, and H. Li: Mater. Charact., 2020, vol. 169, p. 110612.
E. Pu, W. Zheng, Z. Song, K. Zhang, F. Yang, H. Lu, and H. Dong: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, vol. 705, pp. 335–47.
B. Piekarski: Mater. Charact., 2001, vol. 47, pp. 181–6.
H. Lu, H. G, W. Liang, J. Li, G. Zhang, and T. Li: Mater. Des., 2020, vol. 188, pp. 108477.
Y. Zhang, H. Wang, H. Sun, and G. Chen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2020, vol. 798, p. 140236.
C. Dong, Z. Liu, Z. Chen, H. Bao, X. Wang, and Z. Liu: J. Alloys Compd., 2020, vol. 825, p. 154106.
Y. Xu, J. Liu, Y. Zhao, and Y. Jiao: Philos. Mag., 2021, vol. 101, pp. 77–95.
M. Shirdel, H. Mirzadeh, and M.H. Parsa: Mater. Charact., 2014, vol. 97, pp. 11–17.
A. Chamanfar, S.M. Chentouf, M. Jahazi, and L.P. Lapierre-Boire: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 9, pp. 12102–14.
M. Maalekian, R. Radis, M. Militzer, A. Moreau, and W.J. Poole: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 1015–26.
E.J. Palmiere, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. Ardo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 1994, vol. 25, pp. 277–86.
P.R. Rios: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 1785–89.
P.R. Rios and M.E. Glicksman: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 5313–21.
V.Y. Novikov: Mater. Lett., 2012, vol. 68, pp. 413–15.
D. Zhou, W. Zhao, H. Mao, Y. Hu, X. Xu, X. Sun, and Z. Lu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2015, vol. 622, pp. 91–100.
C. Wagner: Thermodynamics of Alloys, Addison-Wesley Press, Cambridge, 1952, p. 51.
R.C. Sharma, V.K. Lakshmanan, and J.S. Kirkaldy: Metall. Trans. A., 1984, vol. 15, pp. 545–53.
G. Solis-Bravo, M. Merwin, and C.I. Garcia: Metals., 2020, vol. 10, p. 89.
L.M. Fu, H.R. Wang, W. Wang, and A.D. Shan: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 996–1001.
H.R. Wang and W. Wang: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 24, pp. 228–32.
I.M. Lifshitz and V.V. Slyozov: J. Phys. Chem. Solids., 1961, vol. 19, pp. 35–50.
Q.L. Yong: Second Phases in Structural Steel, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006.
G.S. Rohrer: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2010, vol. 41, pp. 457–94.
B.R. Patterson and Y. Liu: Metall. Trans. A., 1992, vol. 23, pp. 2481–82.
T. Gladman and D. Dulieu: Met. Sci., 1974, vol. 8, pp. 167–76.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier, New York, 2012.
P.A. Beck, J.C. Kremer, and L. Demer: Phys. Rev., 1947, vol. 71, p. 555.
E. Anelli: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 440–49.
N. Raghunathan and T. Sheppard: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1989, vol. 5, pp. 542–47.
K.A. Annan, C.W. Siyasiya, and W.E. Stumpf: ISIJ Int., 2018, vol. 58, pp. 333–39.
W.J. Liu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 1995, vol. 26, pp. 1641–57.
S. Uhm, J. Moon, C. Lee, J. Yoon, and B. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 1230–37.
E.O. Hall: Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B London., 1951, vol. 64, pp. 747–53.
N.J. Petch: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, vol. 174, pp. 25–28.
Acknowledgments
The financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51874026 and 52074027) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. FRF-AT-20-13) is greatly acknowledged. The authors are also grateful to the financial support from the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy (Grant No. 41621024).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Figure 7b was corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Shi, C., Zhu, X. et al. Effect of Solution Treatment on Grain Growth and Precipitates in Electroslag Remelted 15Cr-22Ni Iron-Base Superalloy. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 877–894 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02421-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02421-1