Abstract
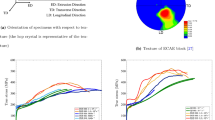
The microscopic damage mechanisms operating in a hot-rolled magnesium alloy AZ31B are investigated under both uniaxial and controlled triaxial loadings. Their connection to macroscopic fracture strains and fracture mode (normal vs shear) is elucidated using postmortem fractography, interrupted tests, and microscopic analysis. The fracture locus (strain-to-failure vs stress triaxiality) exhibits a maximum at moderate triaxiality, and the strain-to-failure is found to be greater in notched specimens than in initially smooth ones. A transition from twinning-induced fracture under uniaxial loading to microvoid coalescence fracture under triaxial loading is evidenced. It is argued that this transition accounts in part for the observed greater ductility in notched bars. The evolution of plastic anisotropy with stress triaxiality is also investigated. It is inferred that anisotropic plasticity at a macroscopic scale suffices to account for the observed transition in the fracture mode from flat (triaxial loading) to shear-like (uniaxial loading). Damage is found to initiate at second-phase particles and deformation twins. Fracture surfaces of broken specimens exhibit granular morphology, coarse splits, twin-sized crack traces, as well as shallow and deep dimples, in proportions that depend on the overall stress triaxiality and fracture mode. An important finding is that AZ31B has a greater tolerance to ductile damage accumulation than has been believed thus far, based on the fracture behavior in uniaxial specimens. Another finding, common to both tension and compression, is the increase in volumetric strain, the microscopic origins of which remain to be elucidated.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Spatial nonuniformity, notably of triaxiality, is greater after crack initiation.
References
Stalmann A, Sebastian W, Friedrich H, Schumann S, Droder K (2001) Adv. Eng. Mater. 3:969–74
Agnew SR, Tome CN, Brown DW, Holden TM, Vogel SC (2003) Scripta Mater. 48:1003–08
Koike J, Kobayashi T, Mukai T, Watanabe H, Suzuki M, Maruyama K, Higashi K (2003) Acta Mater. 51:2055–65
Koike J (2005) Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A:1689–96
Yi SB, Davies CHJ, Brokmeier HG, Bolmaro RE, Kainer KU, Homeyer J (2006) Acta Mater. 54:549–62
Gao X, Nie JF (2007) Scripta Mater. 56:645–48
Capolungo L, Beyerlein IJ, Tome CN (2009) Scripta Mater. 60:32–35
Al-Maharbi M, Karaman I, Beyerlein IJ, Foley D, Hartwig KT, Kecskes LJ, Mathaudhu SN (2011) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528:7616–27
Pineau A (2006) Int. J. Fract. 138:139–66
Benzerga AA, Leblond J-B (2010) Adv. Appl. Mech. 44:169–305
Barnett MR (2007) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464:8–16
Al-Samman T, Gottstein G (2008) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 488:406–14
H. Watanabe: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013.
Marya M, Hector LG, Verma R, Tong W (2006) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 418:341–56
Somekawa H, Singh A, Mukai T (2009) Philos. Mag. Lett. 89:2–10
Lugo M, Tschopp MA, Jordon JB, Horstemeyer MF (2011) Scripta Mater. 64:912–15
Steglich D, Morgeneyer T (2013) Int. J. Fract. 183:105–12
Yoo MH (1981) Metall. Trans. 12:409–18
Ando D, Koike J, Sutou Y (2010) Acta Mater. 58:4316–24
Somekawa H, Mukai T (2005) Effect of texture on fracture toughness in extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Scripta Mater. 53:541–45
J. Rice: in 14th International Congress on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, W. Koiter, ed., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1976, pp. 207–20.
B. Kondori and A.A. Benzerga: Exp. Mech., 2014, DOI:10.1007/s11340-013-9812-8.
R.T. DeHoff: in Quantitative Microscopy, R.T. DeHoff and F.N. Rhines, eds., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1968, pp. 128–48.
Benzerga AA, Besson J, Pineau A (2004) Acta Mater. 52:4623–38
Benzerga AA, Besson J, Pineau A (2004) Acta Mater. 52:4639–50
Hosokawa A, Wilkinson DS, Kang J, Maire E (2013) Acta Mater. 61:1021–36
Laser T, Nurnberg M, Janz A, Hartig C, Letzig D, Schmid-Fetzer R, Bormann R (2006) Acta Mater. 54:3033–41
Hort N, Huang YD, Kainer KU (2006) Adv. Eng. Mater. 8:235–40
S. Basu and A.A. Benzerga: Unpublished research.
Chun YB, Davies CHJ (2011) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528:4941–46
Mukai T, Yamanoi M, Watanabe H, Higashi K (2001) Scripta Mater. 45:89–94
Bron F, Besson J, Pineau A (2004) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 380:356–64
Benzerga AA, Besson J, Batisse R, Pineau A (2002) Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 10:73–102
P. Achon: Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole des Mines de Paris, 1994.
Barnett MR, Keshavarz Z, Beer AG, Atwell D (2004) Acta Mater. 52:5093–5103
Lou XY, Li M, Boger RK, Agnew SR, Wagoner RH (2007) Int. J. Plast. 23:44–86
Barnett MR (2007) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464:1–7
El Kadiri H, Oppedal AL (2010) J. Mech. Phys. Solids 58:613–24
Keshavarz Z, Barnett MR (2006) Scripta Mater. 55:915–18
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the NPRP Grant No 4-1411-2-555 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 9, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondori, B., Benzerga, A.A. Effect of Stress Triaxiality on the Flow and Fracture of Mg Alloy AZ31. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 3292–3307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2211-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2211-7