Abstract
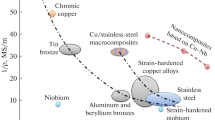
In this study, strength and electrical conductivity of Cu-9Fe-1.2X (X = Ag or Cr) microcomposite wires obtained by cold drawing combined with intermediate heat treatments have been investigated. During cold working, the primary and secondary dendrite arms are aligned along the drawing direction and elongated into filaments. The addition of Ag was found to reduce the filament spacings at the given draw ratio throughout the drawing processing. The ultimate tensile strength and the conductivity of the Cu-Fe-Ag microcomposites were higher than those of Cu-Fe-Cr microcomposites, suggesting the refinement of the filaments is more effective than the strengthening of the filaments in strengthening the microcomposites. The strength of Cu-Fe-Xi microcomposites is dependent on the spacing of the Fe filaments in accord with a Hall-Petch relationship. The fracture surfaces of all the specimens showed ductile-type fracture and iron filaments occasionally observed on the fracture surfaces. The good mechanical and electrical properties in Cu-Fe-Ag wires may be associated with the more uniform distribution of the filaments than in Cu-Fe-Cr wires. The increase of the conductivity in Cu-Fe-Ag and Cu-Fe-Cr after intermediate heat treatments is attributed to the precipitation of Fe, Cr, or Ag particles, which dissolved during heavy deformation processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.A. Spitzig, A.R. Pelton, and F.C. Laabs: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 2427–42.
C. Biselli and D.G. Morris: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 493–504.
P.D. Funkenbusch and T.H. Courtney: Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 913–21.
J.D. Verhoeven, L.S. Chumbley, F.C. Laabs, and W.A. Spitzig: Acta Metall., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 2825–34.
C.L. Trybus and W.A. Spitzig: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 1971–81.
S.I. Hong and M.A. Hill: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4111–22.
S.I. Hong: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 39, pp. 1685–91.
J.D. Verhoeven, W.A. Spitzig, L.L. Jones, H.L. Downing, C.L. Trybus, E.D. Gibson, L.S. Chumbly, L.S. Fritzemeier, and G.D. Schnittgrund: J. Mater. Eng., 1990, vol. 12, pp. 127–39.
C. Biselli and D.G. Morris: Acta Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 163–76.
Y.S. Go and W.A. Spitzig: J. Mater. Sci., 1991, vol. 26, pp. 163–71.
J.D. Verhoeven, S.C. Chueh, and E.D. Gibson: J. Mater. Sci., 1989, vol. 24, pp. 1748–52.
W.A. Spitzig, L.S. Chumbley, J.D. Verhoeven, Y.S. Go, and H.L. Downing: J. Mater. Sci., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 2005–11.
W. Hodge, R.A. Happe, and B.W. Gonser: Wire Wire Prod., 1951, vol. 26, pp. 1033–38.
L.J. Swartzendruber: in Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed., T.B. Massalski, H. Okamoto, R.R. Subramanian, and L. Kacprzak, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1990, vol. 1, p. 35.
M.S. Lim, J.S. Song, and S.I. Hong: J. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 4557–61.
W.A. Spitzig: Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 1085–90.
W.A. Spitzig: Scripta Metall., 1989, vol. 23, pp. 1177–83.
P.D. Courtney and T.H. Courtney: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 1183–89.
S.I. Hong and M.A. Hill: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 737–42.
J.D. Verhoeven, H.L. Downing, L.S. Chumbly, and E.D. Gibson: J. Appl. Phys., 1989, vol. 65, pp. 1293–1301.
G.A. Jerman, I.E. Anderson, and J.D. Verhoeven: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 35–42.
A.R. Pelton, F.C. Laabs, W.A. Spitzig, and C.C. Cheng: Ultramicroscopy, 1987, vol. 22, pp. 251–66.
S.I. Hong and M.A. Hill: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. 256, pp. 321–29.
S. Horibe, J.K. Lee, and C. Laird: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. 63, pp. 257–64.
J. Bevk, J.P. Harbison, and J.L. Bell: J. Appl. Phys., 1978, vol. 49, pp. 6031–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S.I., Song, J.S. Strength and conductivity of Cu-9Fe-1.2X (X = Ag or Cr) filamentary microcomposite wires. Metall Mater Trans A 32, 985–991 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0356-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0356-7