Summary
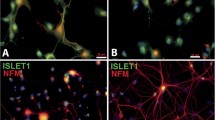
A protocol for the isolation, purification and culture of motor neurons from newborn rat spinal cord was described and the effect of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) on the growth of neurite of motor neurons was investigated in vitro. Spinal motor neurons (SMNs) were dissociated from ventral spinal cord of postnatal day 1 rats. The culture system for SMNs was established by density gradient centrifugation, differential adhesion, and use of serum-free defined media and addition of exogenous GDNF. After 72-h culture, the cells displayed the characteristic morphology of motor neurons, exhibited extensive neuritic processes and were positive for choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) expression. The neurite length of SMNs in GDNF groups was significantly longer than that in control group (P<0.05). This protocol can be adapted for various postnatal motor neurons studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henderson C, Bloch-Gallego E, Camu W. Purified embryonic motor neurons. In: Cohen J, Wilkin G (Eds.), Neural Cell Culture. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995.69–81
Das M, Rumsey JW, Gregory CA, et al. Embryonic motoneuron-skeletal muscle co-culture in a defined system. Neuroscience, 2007,146(2):481–488
Das M, Molnar P, Devaraj H, et al. Electrophysiological and morphological characterization of rat embryonic motoneurons in a defined system. Biotechnol Prog, 2003, 19(6):1756–1761
Kuhn TB. Growing and working with spinal motor neurons. Methods Cell Biol, 2003,71:67–87
Camu W, Henderson C E. Purification of embryonic rat motoneurons by panning on a monoclonal antibody to the low-affinity NGF receptor. J Neurosci Methods, 1992, 44(1):59–70
Bataille S, Portalier P, Coulon P, et al. Influence of acetylcholinesterase on embryonic spinal rat motoneurones growth in culture: a quantitative morphometric study. Eur J Neurosci, 1998,10(2):560–572
Anderson KN, Potter AC, Piccenna LG, et al. Isolation and culture of motor neurons from the newborn mouse spinal cord. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc, 2004,12(3): 132–136
Arce V, Garces A, de Bovis B, et al. Cardiotrophin-1 requires LIFRbeta to promote survival of mouse motoneurons purified by a novel technique. J Neurosci Res, 1999,55(1):119–126
Hoffer BJ, Hoffman A, Bowenkamp K, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor reverses toxin-induced injury to midbrain dopaminergic neurons in vivo. Neurosci Lett, 1994,182(1):107–111
Beck KD, Valverde J, Alexi T, et al. Mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons protected by GDNF from axotomy-induced degeneration in the adult brain. Nature, 1995,373(6512):339–341
Bilak MM, Kuncl RW. Delayed application of IGF-I and GDNF can rescue already injured postnatal motor neurons. Neuroreport, 2001,12(11):2531–2535
Ho TW, Bristol LA, Coccia C, et al. TGFbeta trophic factors differentially modulate motor axon outgrowth and protection from excitotoxicity. Exp Neurol, 2000,161(2): 664–675
Orike N, Thrasivoulou C, Cowen T. Serum-free culture of dissociated, purified adult and aged sympathetic neurons and quantitative assays of growth and survival. J Neurosci Methods, 2001,106(2):153–160
Ren D, Miller J D. Primary cell culture of suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res Bull, 2003,61(5):547–553
Zheng J, Buxbaum RE, Heidemann SR. Measurements of growth cone adhesion to culture surfaces by micromanipulation, J Cell Biol, 2000,127(6):2049–2060
Tisay KT, Key B. The extracellular matrix modulates factory neurite outgrowth on ensheaththing cell. Neurosci, 1999,19(22):9890–9899
Song XQ, Wu SY, Wang LQ, et al. Influence of substrates coated on the cultured spinal motorneurons. Chin J Anatomy (Chinese), 2004,27(1):102–105
Xue QS, Xiao YP. Principles and techniques of culture in vitro. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. 656–670
Davies AM. The survival and growth of embryonic proprioceptive neurons is promoted by a factor present in skeletal muscle. Dev Biol, 1986,115(1):56–67
Brewer GJ. Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Methods, 1997,71(2):143–155
Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, et al. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res, 1993,35(5):567–576
Cronin AS, Horan TL, Spergel DJ, et al. Neurotrophic effects of BDNF on embryonic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons. Eur J Neurosci, 2004,20(2): 338–344
deLapeyrière O, Henderson CE. Motoneuron differentiation, survival and synaptogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 1997,7(5):642–650
Ullian EM, Harris BT, Wu A, et al. Schwann cells and astrocytes induce synapse formation by spinal motor neurons in culture. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2004,25(2): 241–251
Rakowicz W P, Staples C S, Milbrandt J, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promotes the survival of early postnatal spinal motor neurons in the lateral and medial motor columns in slice culture. J Neurosci, 2002, 22(10):3953–3962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from National Research Program of Basic Medicine of China (No. 2003CB 515304).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, S., Shi, Y., Hai, B. et al. Culture of motor neurons from newborn rat spinal cord. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 413–416 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0404-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0404-x