Abstract
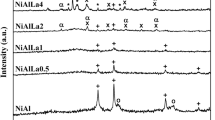
La0.8A0.2NiO3 (A=K, Ba, Y) catalysts supported on the microwave-absorbing ceramic heating carrier were prepared by the sol-gel method. The crystalline phase and the catalytic activity of the La0.8A0.2NiO3 catalysts were characterized by XRD and H2 temperature-programmed reduction (TPR). The effects of reaction temperature, oxygen concentration, and gas flow rate on the direct decomposition of nitric oxide over the synthesized catalysts were studied under microwave irradiation (2.45 GHz). The XRD results indicated that the La0.8A0.2NiO3 catalysts formed an ABO3 perovskite structure, and the H2-TPR results revealed that the relative reducibility of the catalysts increased in the order of La0.8K0.2NiO3 > La0.8Ba0.2NiO3 > La0.8Y0.2NiO3. Under microwave irradiation, the highest NO conversion amounted to 98.9%, which was obtained with the La0.8K0.2NiO3 catalyst at 400 °C. The oxygen concentration did not inhibit the NO decomposition on the La0.8A0.2NiO3 catalysts, thus the N2 selectivity exceeded 99.8% under excess oxygen at 550 °C. The NO conversion of the La0.8A0.2NiO3 catalysts decreased linearly with the increase in the gas flow rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kampa M, Castanas E. Human Health Effects of Air Pollution[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 151(2): 362–367
Liu X, Zhang B, Zhao W, et al. Comparative Effects of Sulfuric and Nitric Acid Rain on Litter Decomposition and Soil Microbial Community in Subtropical Plantation of Yangtze River Delta Region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 601–602: 669–678
Galloway J N, Townsend A R, Erisman J W, et al. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5878): 889–892
Balat M. Influence of Coal as an Energy Source on Environmental Pollution[J]. Energy Sources, Part A. Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2007, 29(7): 581–589
Chen L, Si Z, Wu X, et al. Rare Earth Containing Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia: A Review[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2014, 32(10): 907–917
Liu Z, Yu F, Ma C, et al. A Critical Review of Recent Progress and Perspective in Practical Denitration Application[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(9): 771
Imanaka N, Masui T. Advances in Direct NOx Decomposition Catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2012, 431–432: 1–8
Zhang Y, Cao G, Yang X. Advances in De-NOx Methods and Catalysts for Direct Catalytic Decomposition of NO: A Review[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(8): 6 443–6 464
Roy S, Hegde M S, Madras G. Catalysis for NOx Abatement[J]. Applied Energy, 2009, 86(11): 2 283–2 297
Shen Q, Dong S, Li S, et al. A Review on the Catalytic Decomposition of NO by Perovskite-Type Oxides[J]. Catalysts, 2021, 11(5): 622
Wu R J, Chou T Y, Yeh C T. Enhancement Effect of Gold and Silver on Nitric Oxide Decomposition over Pd/Al2O3 Catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 1995, 6(2): 105–116
Haneda M, Kintaichi Y, Nakamura I, et al. Comprehensive Study Combining Surface Science and Real Catalyst for NO Direct Decomposition[J]. Chemical Communications, 2002, 2(23): 2 816–2 817
Iwamoto M, Yokoo S, Sakai K, et al. Catalytic Decomposition of Nitric Oxide over Copper(II)-exchanged, Y-type Zeolites[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1981, 77(7): 1 629–1 638
Iwamoto M, Furukawa H, Mine Y, et al. Copper(II) Ion-Exchanged ZSM-5 Zeolites as Highly Active Catalysts for Direct and Continuous Decomposition of Nitrogen Monoxide[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical communications, 1986, (16): 1 272–1 273
Iwamoto S, Takahashi R, Inoue M. Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide over Ba Catalysts Supported on CeO2-based Mixed Oxides[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 70(1): 146–150
Winter E R S. The Catalytic Decomposition of Nitric Oxide by Metallic Oxides[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1971, 22(2): 158–170
Winter E R S. The Catalytic Decomposition of Nitric Oxide by Metallic Oxides: II, The Effect of Oxygen[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1974, 34(3): 440–444
Pârvulescu V I, Centeno M A, Grange P, et al. NO Decomposition over Cu − Sm − ZSM-5 Zeolites Containing Low-Exchanged Copper[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2000, 191(2): 445–455
Amirnazmi A, Benson J E, Boudart M. Oxygen Inhibition in the Decomposition of NO on Metal Oxides and Platinum[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1973, 30(1): 55–65
Zhu J, Li H, Zhong L, et al. Perovskite Oxides: Preparation, Characterizations, and Applications in Heterogeneous Catalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(9): 2 917–2 940
Zhu J, Thomas A. Perovskite-Type Mixed Oxides as Catalytic Material for NO Removal[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 92(3–4): 225–233
Tofan C, Klvana D, Kirchnerova J. Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide over Perovskite-Type Catalysts: Part I, Activity When No Oxygen Is Added to the Feed[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2002, 223(1): 275–286
Tofan C, Klvana D, Kirchnerova J. Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide over Perovskite-Type Catalysts: Part II. Effect of Oxygen in the Feed on the Activity of Three Selected Compositions[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2002, 226(1): 225–240
Chemat-Djenni Z, Hamada B, Chemat F. Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Assisted Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions[J]. Molecules, 2007, 12(7): 1 399–1 409
Crosswhite M, Hunt J, Southworth T, et al. Development of Magnetic Nanoparticles as Microwave-Specific Catalysts for the Rapid, Low-Temperature Synthesis of Formalin Solutions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(6): 1 318–1 323
Kappe C O, Pieber B, Dallinger D. Microwave Effects in Organic Synthesis: Myth or Reality?[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(4): 1 088–1 094
Xu L, Fan L, Hou C, et al. Effect of Adding Microwave Absorber on Structures and Properties of Hypercoal-Based Activated Carbons[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology -Materials Science Edition, 2020, 35(3): 488–494
Ma S, Jin X, Wang M, et al. Experimental Study on Removing NO from Flue Gas Using Microwave Irradiation over Activated Carbon Carried Catalyst[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2011, 54(12): 3 431–3 436
Xu W, Zhou J, Li H, et al. Microwave-Assisted Catalytic Reduction of NO into N2 by Activated Carbon Supported Mn2O3 at Low Temperature under O2 Excess[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 127: 1–6
Wei Z, Niu H, Ji Y. Simultaneous Removal of SO2 and NOx by Microwave with Potassium Permanganate over Zeolite[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2009, 90(2): 324–329
Wei Z, Zeng G, Xie Z, et al. Microwave Catalytic NOx and SO2 Removal Using FeCu/zeolite as Catalyst[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(4): 1 599–1 603
Tang J, Zhang T, Liang D, et al. Direct Decomposition of NO by Microwave Heating over Fe/NaZSM-5[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2002, 36(1): 1–7
Xu W, Cai J, Zhou J, et al. Microwave Irradiation Coupled with MeOx/Al2O3 (Me=Cu, Mn, Ce) Catalysts for Nitrogen Monoxide Removal from Flue Gas at Low Temperatures[J]. Energy Technology, 2016, 4(7): 856–863
Xu W, Shi N, You Z, et al. Low-Temperature NO Decomposition through Microwave Catalysis on BaMnO3-based Catalysts under Excess Oxygen: Effect of A-site Substitution by Ca, K and La[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 167: 205–214
Xu W, Cai J, Zhou J, et al. Highly Effective Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide by Microwave Catalysis over BaMeO3 (Me=Mn, Co, Fe) Mixed Oxides at Low Temperature under Excess Oxygen[J]. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(2): 417–425
Xu W, Zhou J, Ou Y, et al. Microwave Selective Effect: A New Approach Towards Oxygen Inhibition Removal for Highly-Effective NO Decomposition by Microwave Catalysis over BaMn(x)Mg(1 − x)O3 Mixed Oxides at Low Temperature under Excess Oxygen.[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(19): 4 073–4 076
Xu W, Zhou J, You Z, et al. Microwave Irradiation Coupled with Physically Mixed MeOx (Me=Mn, Ni) and Cu-ZSM-5 Catalysts for the Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide under Excess Oxygen[J]. ChemCatChem, 2015, 7(3): 450–458
Cruz R M G D L, Falcón H, Peña M A, et al. Role of Bulk and Surface Structures of La1−xSrxNiO3 Perovskite-Type Oxides in Methane Combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2001, 33(1): 45–55
Arvanitidis I, Siche D, Seetharaman S. A Study of the Thermal Decomposition of BaCO3[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1996, 27(3): 409–416
Lima S M, Assaf J M, Peña M A, et al. Structural Features of La1−xCex NiO3 Mixed Oxides and Performance for the Dry Reforming of Methane[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2006, 311(1): 94–104
Zhao B, Wang R, Yang X. Simultaneous Catalytic Removal of NOx and Diesel Soot Particulates over La1−xCexNiO3 Perovskite Oxide Catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2009, 10(7): 1 029–1 033
Mousavi M, Nakhaei P A, Gholizadeh M, et al. Dry Reforming of Methane by La0.5Sr0.5NiO3 Perovskite Oxides: Influence of Preparation Method on Performance and Structural Features of the Catalysts[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2020, 95(11): 2 911–2 920
Yokoi Y, Uchida H. Catalytic Activity of Perovskite-Type Oxide Catalysts for Direct Decomposition of NO: Correlation between Cluster Model Calculations and Temperature-Programmed Desorption Experiments[J]. Catalysis Today, 1998, 42(1): 167–174
Datta A K, Rakesh V. Principles of Microwave Combination Heating[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2013, 12(1): 24–39
Conner W C, Tompsett G A. How Could and Do Microwaves Influence Chemistry at Interfaces?[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2008, 112(7): 2 110–2 118
Tang J W, Zhang T, Liang D B, et al. Microwave Discharge-Assisted Catalytic Conversion of NO to N2[J]. Chemical Communications, 2000, (19): 1 861–1 862
Ishihara T. Direct Decomposition of NO into N2 and O2 over La(Ba) Mn(In)O3 Perovskite Oxide[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 220(1): 104–114
Teraoka Y, Kagawa T H A S. Reaction Mechanism of Direct Decomposition of Nitric Oxide over Co- and Mn-based Perovskite-Type Oxides[J]. Faraday Transactions, 1998, 94(13): 1 887–1 891
Zhu J, Xiao D, Li J, et al. Recycle—New Possible Mechanism of NO Decomposition over Perovskite(-Like) Oxides[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2005, 233(1–2): 29–34
Wang X, Hou W, Wang X, et al. Preparation, Characterization and Activity of Novel Silica-Pillared Layered Titanoniobate Supported Copper Catalysts for the Direct Decomposition of NO[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2002, 35(3): 185–193
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.cn/) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhao, Z., Duan, X. et al. Efficient Direct Decomposition of NO over La0.8A0.2NiO3 (A=K, Ba, Y) Catalysts under Microwave Irradiation. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 39, 17–23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-024-2849-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-024-2849-y