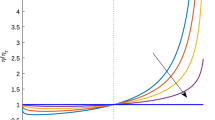
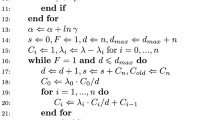Abstract
We study the practical identifiability of parameters, i.e., the accuracy of the estimation that can be hoped, in a model of HIV dynamics based on a system of non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE). This depends on the available information such as the schedule of the measurements, the observed components, and the measurement precision. The number of patients is another way to increase it by introducing an appropriate statistical “population” framework. The impact of each improvement of the experimental condition is not known in advance but it can be evaluated via the Fisher Information Matrix (FIM). If the non-linearity of the biological model, as well as the complex statistical framework makes computation of the FIM challenging, we show that the particular structure of these models enables to compute it as precisely as wanted. In the HIV model, measuring HIV viral load and total CD4+ count were not enough to achieve identifiability of all the parameters involved. However, we show that an appropriate statistical approach together with the availability of additional markers such as infected cells or activated cells should considerably improve the identifiability and thus the usefulness of dynamical models of HIV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, A., Donev, A., 1992. Optimum Experimental Designs. Oxford University Press, London.
Audoly, S., Bellu, G., D’Angio, L., Saccomani, M., Cobelli, C., 2001. Global identifiability of nonlinear models of biological systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48, 55–65.
Auranen, K., Arjas, E., Leino, T., Takala, A., 2000. Transmission of pneumococcal carriage in families: a latent Markov process model for binary longitudinal data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 95.
Banks, H., Grove, S., Hu, S., Ma, Y., 2005. A hierarchical Bayesian approach for parameter estimation in HIV models. Inverse Probl. 21, 1803–1822.
Bortz, D., Nelson, P., 2006. Model selection and mixed-effects modeling of HIV infection dynamics. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 2005–2025.
Box, G.E.P., Draper, N.R., 1959. A basis for the selection of a response surface design. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 54, 622–654.
Cauchemez, S., Temime, L., Guillemot, D., Varon, E., Valleron, A., Thomas, G., Boëlle, P., 2006. Investigating heterogeneity in pneumococcal transmission: a Bayesian MCMC approach applied to a follow-up of schools. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101, 946–958.
Chun, T.W., Carruth, L., Finzi, D., Shen, X., DiGiuseppe, J.A., Taylor, H., Hermankova, M., Chadwick, K., Margolick, J., Quinn, T.C., Kuo, Y.H., Brookmeyer, R., Zeiger, M.A., Barditch-Crovo, P., Siliciano, R.F., 1997. Quantification of latent tissue reservoirs and total body viral load in HIV-1 infection. Nature 387, 183–188.
Commenges, D., Jacqmin-Gadda, H., Proust, C., Guedj, J., 2006. A Newton-like algorithm for likelihood maximization: the robust variance scoring algorithm. arXiv:math.ST/0610402.
Davidian, M., Giltinian, D.M., 1995. Nonlinear Models for Repeated Measurements Data. Chapman & Hall, London.
Fedorov, V.V., 1972. Theory of Optimal Experiments. Academic, San Diego
Genz, A., Keister, B.D., 1996. Fully symmetric interpolatory rules for multiple integrals over infinite regions with Gaussian weight. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 71, 299–311.
Grossman, Z., Meier-Schellersheim, M., Sousa, A.E., Victorino, R.M.M., Paul, W.E., 2000. CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV infection: are we closer to understanding the cause? Nat. Med. 8, 319–323.
Guedj, J., Thiébaut, R., Commenges, D., 2007. Maximum likelihood estimation in dynamical models of HIV. Biometrics, Epub 2007 May 8.
Han, C., Chaloner, K., 2004. Bayesian experimental design for nonlinear mixed-effects models with application to HIV dynamic. Biometrics 60, 25–33.
Ho, D.D., Neumann, A.U., Perelson, A.S., Chen, W., Leonard, J.M., Markowitz, M., 1995. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373, 123–126.
Holmberg, A., 1982. On the practical identifiability of microbial growth models incorporating Michaelis-Menten type nonlinearities. Math. Biosci. 62, 23–43.
Huang, Y., Liu, D., Wu, H., 2006. Hierarchical Bayesian methods for estimation of parameters in a longitudinal HIV dynamic system. Biometrics 63, 413–423.
Huang, Y., Wu, H., 2006. A Bayesian approach for estimating antiviral efficacy in HIV dynamic models. J. Appl. Stat. 33, 155–174.
Julien, S., Barbary, J., Lessard, P., 1997. Theoretical and practical identifiability of a reduced order model in an activated sludge process doing nitrification and denitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 37, 309–316.
Kiefer, J., 1974. General equivalence theory for optimum designs (approximate theory). Ann. Stat. 2, 849–879.
Knight, K., 2001. Mathematical Statistics. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London/Boca Raton.
Louis, T., 1982. Finding the observed Information matrix when using the EM algorithm. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 44, 226–233.
Mclean, A.R., Michie, C.A., 1995. In vivo estimates of division and death rates of human t lymphocytes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3707–3711.
Mentré, F., Mallet, A., Baccar, D., 1997. Optimal design in random-effects regression models. Biometrika 84, 429–442.
Patterson, B.K., Mosiman, V.L., Cantarero, L., Furtado, M., Bhattacharya, M., Goolsby, C., 1998. Detection of HIV-RNA-positive monocytes in peripheral blood of HIV-positive patients by simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of intracellular HIV RNA and cellular immunophenotype. Cytometry 31, 265–274.
Perelson, A.S., 2002. Modelling viral and immune system dynamics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 28–36.
Perelson, A.S., Neumann, A.U., Markowitz, M., Leonard, J.M., Ho, D., 1996. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Science 271, 1582–1586.
Petersen, B., Gernaey, K., Vanrolleghem, P.A., 2001. Practical identifiability of model parameters by combined respirometric-titrimetric measurements. Water Sci. Technol. 43, 347–355.
Piatak, M., Saag, M., Yang, L.C., Clark, S.J., Kappes, J.C., Luk, K.C., Hahn, B.H., Shaw, G.M., Lifson, J.D., 1993. High levels of HIV-1 in plasma during all stages of infection determined by competitive PCR. Science 259, 1749–1754.
Pinheiro, J.C., Bates, D.M., 2000. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-PLUS. Springer, London.
Pohjanpalo, H., 1978. System identifiability based on the power series expansion of the solution. Math. Biosci. 41.
Putter, H., Heisterkamp, S.H., Lange, J.M.A., de Wolf, F., 2002. A Bayesian approach to parameter estimation in HIV dynamic models. Stat. Med. 21, 2199–2214.
Radhakrishnan, K., Hindmarsh, A.C., 1993. Description and use of LSODE, the livermore solver for ordinary differential equations. LLNL Report UCR-ID-113855 Livermore, CA 4.
Ramratnam, B., Bonhoeffer, S., Binley, J., Hurley, A., Zhang, L., Mittler, J.E., Markowitz, M., Moore, J.P., Perelson, A.S., Ho, D.D., 1999. Rapid production and clearance of HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus assessed by large volume plasma apheresis. Lancet 354, 1782–1786.
Retout, S., Dufull, S., Mentr, F., 2001. Development and implementation of the population Fisher information matrix for the evaluation of population pharmacokinetic designs. Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 65, 141–151.
Ribeiro, R.M., Mohri, H., Ho, D.D., Perelson, A.S., 2002. In vivo dynamics of T cell activation, proliferation, and death in HIV-1 infection: Why are CD4 but not CD8 T cells depleted? Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 24, 15572–15577.
Rothenberg, T.J., 1971. Identification in parametric models. Econometrica 39, 577–591.
Rusert, P., Fischer, M., Joos, B., Leemann, C., Kuster, H., Flepp, M., Bonhoeffer, S., Gunthard, H.F., Trkola, A., 2004. Quantification of infectious HIV-1 plasma viral load using a boosted in vitro infection protocol. Virology 326, 113–129.
Stafford, M.A., Corey, L., Cao, Y., Daar, E.S., Ho, D.D., Perelson, A.S., 2000. Modeling plasma virus concentration during primary HIV infection. J. Theor. Biol. 203, 285–301.
Thiébaut, R., Guedj, J., Jacqmin-Gadda, H., Chêne, G., Trimoulet, P., Neau, D., Commenges, D., 2006. Estimation of dynamical model parameters taking into account undetectable marker values. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 6, 1–10, http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/6/38.
Thiébaut, R., Jacqmin-Gadda, H., Leport, C., Katlama, C., D., C., Le Moing, V., Morlat, P., Chene, G., the APROCO Study Group, 2003. Bivariate longitudinal model for the analysis of the evolution of HIV RNA and CD4 cell count in HIV infection taking into account left censoring of HIV RNA measures. J. Biopharm. Stat. 13, 271–282.
Vajda, S., Rabitz, H., Walter, E., Lecourtier, Y., 1989. Qualitative and quantitative identifiability analysis of nonlinear chemical kinetic models. Chem. Eng. Commun. 83, 191–219.
Walter, E., Pronzato, L., 1997. Identification of Parametric Models from Experimental Data. Springer, Berlin.
Wei, X., Ghosh, S.K., E., T.M., Johnson, V.A., Emini, E.A., Deutsch, P., Lifson, J.D., Bonhoeffer, S., Nowak, N.A., Hahn, B.H., Saag, M.S., Shaw, G.M., 1995. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 373, 117–122.
Wu, H., 2005. Statistical methods for HIV dynamic studies in AIDS clinical trials. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 14, 1–22.
Xia, X., Moog, C.H., 2003. Identifiability of nonlinear systems with applications to HIV/AIDS models. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 48, 330–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guedj, J., Thiébaut, R. & Commenges, D. Practical Identifiability of HIV Dynamics Models. Bull. Math. Biol. 69, 2493–2513 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-007-9228-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-007-9228-7