Abstract
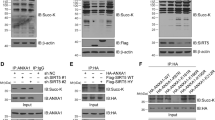
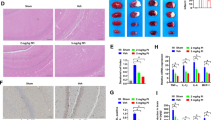
In our previous study, we concluded that sirtuin 5 (SIRT5) was highly expressed in microglia following ischaemic stroke, which induced excessive neuroinflammation and neuronal injury. Therefore, SIRT5-targeting interventions should reduce neuroinflammation and protect against ischaemic brain injury. Here, we showed that treatment with a specific SIRT5 inhibitor, MC3482, alleviated microglia-induced neuroinflammation and improved long-term neurological function in a mouse model of stroke. The mice were administrated with either vehicle or 2 mg/kg MC3482 daily for 7 days via lateral ventricular injection following the onset of middle cerebral artery occlusion. The outcome was assessed by a panel of tests, including a neurological outcome score, declarative memory, sensorimotor tests, anxiety-like behavior and a series of inflammatory factors. We observed a significant reduction of infarct size and inflammatory factors, and the improvement of long-term neurological function in the early stages during ischaemic stroke when the mice were treated with MC3482. Mechanistically, the administration of MC3482 suppressed the desuccinylation of annexin-A1, thereby promoting its membrane recruitment and extracellular secretion, which in turn alleviated neuroinflammation during ischaemic stroke. Based on our findings, MC3482 offers promise as an anti-ischaemic stroke treatment that targets directly the disease's underlying factors.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Balkaya M, Krober J, Gertz K, Peruzzaro S, Endres M (2013) Characterization of long-term functional outcome in a murine model of mild brain ischemia. J Neurosci Methods 213:179–187
Boltze J, Lukomska B, Jolkkonen J, consortium M-I, (2014) Mesenchymal stromal cells in stroke: improvement of motor recovery or functional compensation? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:1420–1421
Boudhraa Z, Bouchon B, Viallard C, D’Incan M, Degoul F (2016) Annexin A1 localization and its relevance to cancer. Clin Sci (lond) 130:205–220
Bouet V, Freret T, Toutain J, Divoux D, Boulouard M, Schumann-Bard P (2007) Sensorimotor and cognitive deficits after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse. Exp Neurol 203:555–567
Caron D, Maaroufi H, Michaud S, Tanguay RM, Faure RL (2013) Annexin A1 is regulated by domains cross-talk through post-translational phosphorylation and SUMOYlation. Cell Signal 25:1962–1969
Collaborators GBDS (2021) Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol 20:795–820
D’Acunto CW, Gbelcova H, Festa M, Ruml T (2014) The complex understanding of Annexin A1 phosphorylation. Cell Signal 26:173–178
Du J, Zhou Y, Su X, Yu JJ, Khan S, Jiang H, Kim J, Woo J, Kim JH, Choi BH, He B, Chen W, Zhang S, Cerione RA, Auwerx J, Hao Q, Lin H (2011) Sirt5 is a NAD-dependent protein lysine demalonylase and desuccinylase. Science 334:806–809
Finkel T, Deng CX, Mostoslavsky R (2009) Recent progress in the biology and physiology of sirtuins. Nature 460:587–591
Fransen PS et al (2016) Time to Reperfusion and Treatment Effect for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol 73:190–196
Gao Y, Wang ZY, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Huo H, Wang T, Jiang T, Wang S (2014) RVG-peptide-linked trimethylated chitosan for delivery of siRNA to the brain. Biomacromol 15:1010–1018
Guan J, Jiang X, Gai J, Sun X, Zhao J, Li J, Li Y, Cheng M, Du T, Fu L, Li Q (2020) Sirtuin 5 regulates the proliferation, invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells through acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1. J Cell Mol Med 24:14039–14049
Kim JS (2019) tPA Helpers in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Are They Ready for Clinical Use? J Stroke 21:160–174
Kwon OK, Bang IH, Choi SY, Jeon JM, Na AY, Gao Y, Cho SS, Ki SH, Choe Y, Lee JN, Ha YS, Bae EJ, Kwon TG, Park BH, Lee S (2022) SIRT5 Is the desuccinylase of LDHA as novel cancer metastatic stimulator in aggressive prostate cancer. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 21:177–189
Li X, Zhao Y, Xia Q, Zheng L, Liu L, Zhao B, Shi J (2016) Nuclear translocation of annexin 1 following oxygen-glucose deprivation-reperfusion induces apoptosis by regulating Bid expression via p53 binding. Cell Death Dis 7:e2356
Li L, Xu L, Chen W, Li X, Xia Q, Zheng L, Duan Q, Zhang H, Zhao Y (2018) Reduced Annexin A1 Secretion by ABCA1 Causes Retinal Inflammation and Ganglion Cell Apoptosis in a Murine Glaucoma Model. Front Cell Neurosci 12:347
Li Q, Cheng Z, Zhou L, Darmanis S, Neff NF, Okamoto J, Gulati G, Bennett ML, Sun LO, Clarke LE, Marschallinger J, Yu G, Quake SR, Wyss-Coray T, Barres BA (2019) Developmental Heterogeneity of Microglia and Brain Myeloid Cells Revealed by Deep Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Neuron 101(207–223):e210
Li X, Xia Q, Mao M, Zhou H, Zheng L, Wang Y, Zeng Z, Yan L, Zhao Y, Shi J (2021) Annexin-A1 SUMOylation regulates microglial polarization after cerebral ischemia by modulating IKKalpha stability via selective autophagy. Sci Adv 7:eabc5539
Luo ZZ, Gao Y, Sun N, Zhao Y, Wang J, Tian B, Shi J (2014) Enhancing the interaction between annexin-1 and formyl peptide receptors regulates microglial activation to protect neurons from ischemia-like injury. J Neuroimmunol 276:24–36
Mao M, Xia Q, Zhan GF, Chu QJ, Li X, Lian HK (2022) SENP6 induces microglial polarization and neuroinflammation through de-SUMOylation of Annexin-A1 after cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Biosci 12:113
Mattson MP, Culmsee C, Yu ZF (2000) Apoptotic and antiapoptotic mechanisms in stroke. Cell Tissue Res 301:173–187
Molinari F, Feraco A, Mirabilii S, Saladini S, Sansone L, Vernucci E, Tomaselli G, Marzolla V, Rotili D, Russo MA, Ricciardi MR, Tafuri A, Mai A, Caprio M, Tafani M, Armani A (2021) SIRT5 Inhibition Induces Brown Fat-Like Phenotype in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Cells 10:1126
Mori M, Cazzaniga G, Meneghetti F, Villa S, Gelain A (2022) Insights on the Modulation of SIRT5 Activity: A Challenging Balance. Molecules 27:4449
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198
Pan J, Konstas AA, Bateman B, Ortolano GA, Pile-Spellman J (2007) Reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia: pathophysiology, MR imaging, and potential therapies. Neuroradiology 49:93–102
Percie du Sert N et al (2017) The IMPROVE Guidelines (Ischaemia Models: Procedural Refinements Of in Vivo Experiments). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37:3488–3517
Percie du Sert N et al (2020) Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol 18:e3000411
Polletta L, Vernucci E, Carnevale I, Arcangeli T, Rotili D, Palmerio S, Steegborn C, Nowak T, Schutkowski M, Pellegrini L, Sansone L, Villanova L, Runci A, Pucci B, Morgante E, Fini M, Mai A, Russo MA, Tafani M (2015) SIRT5 regulation of ammonia-induced autophagy and mitophagy. Autophagy 11:253–270
Sandalio LM, Gotor C, Romero LC, Romero-Puertas MC (2019) Multilevel Regulation of Peroxisomal Proteome by Post-Translational Modifications. Int J Mol Sci 20:4881
Sauve AA, Wolberger C, Schramm VL, Boeke JD (2006) The biochemistry of sirtuins. Annu Rev Biochem 75:435–465
Shang B, Xu T, Hu N, Mao Y, Du X (2021) Circ-Klhl8 overexpression increased the therapeutic effect of EPCs in diabetic wound healing via the miR-212-3p/SIRT5 axis. J Diabetes Complications 35:108020
Tsao CW et al (2023) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 147:e93–e621
Walter M, Chen IP, Vallejo-Gracia A, Kim IJ, Bielska O, Lam VL, Hayashi JM, Cruz A, Shah S, Soveg FW, Gross JD, Krogan NJ, Jerome KR, Schilling B, Ott M, Verdin E (2022) SIRT5 is a proviral factor that interacts with SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 protein. PLoS Pathog 18:e1010811
Wang YJ et al (2022) China Stroke Statistics: an update on the 2019 report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7:415–450
Wu QJ, Zhang TN, Chen HH, Yu XF, Lv JL, Liu YY, Liu YS, Zheng G, Zhao JQ, Wei YF, Guo JY, Liu FH, Chang Q, Zhang YX, Liu CG, Zhao YH (2022) The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:402
Xia Q, Li X, Zhou H, Zheng L, Shi J (2018) S100A11 protects against neuronal cell apoptosis induced by cerebral ischemia via inhibiting the nuclear translocation of annexin A1. Cell Death Dis 9:657
Xia Q, Zhang X, Zhan G, Zheng L, Mao M, Zhao Y, Zhao Y (2020) Li X (2023) A cell-penetrating peptide exerts therapeutic effects against ischemic stroke by mediating the lysosomal degradation of sirtuin 5. MedComm 4:e436
Xia Q, Mao M, Zeng Z, Luo Z, Zhao Y, Shi J, Li X (2021) Inhibition of SENP6 restrains cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating Annexin-A1 nuclear translocation-associated neuronal apoptosis. Theranostics 11:7450–7470
Xia Q, Zhan G, Mao M, Zhao Y, Li X (2022a) TRIM45 causes neuronal damage by aggravating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation upon cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Exp Mol Med 54:180–193
Xia Q, Gao S, Han T, Mao M, Zhan G, Wang Y, Li X (2022b) Sirtuin 5 aggravates microglia-induced neuroinflammation following ischaemic stroke by modulating the desuccinylation of Annexin-A1. J Neuroinflammation 19:301
Yang Y, Gao H, Liu W, Liu X, Jiang X, Li X, Wu Q, Xu Z, Zhao Q (2021) Arctium lappa L. roots ameliorates cerebral ischemia through inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and suppressing AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Phytomedicine 85:153526
Yu Y, Xia Q, Zhan G, Gao S, Han T, Mao M, Li X, Wang Y (2023) TRIM67 alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by protecting neurons and inhibiting neuroinflammation via targeting IkappaBalpha for K63-linked polyubiquitination. Cell Biosci 13:99
Zabel MD, Mollnow L, Bender H (2019) Lipopeptide Delivery of siRNA to the Central Nervous System. Methods Mol Biol 1943:389–403
Zhai Q, Li F, Chen X, Jia J, Sun S, Zhou D, Ma L, Jiang T, Bai F, Xiong L, Wang Q (2017) Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 2, a Novel Regulator of Immunocyte Phenotypes, Confers Neuroprotection by Relieving Neuroinflammation. Anesthesiology 127:98–110
Zhao Y, Wang J, Jiang H, Yu Z, Li X, Shi J (2015) Following OGD/R, annexin 1 nuclear translocation and subsequent induction of apoptosis in neurons are assisted by myosin IIA in a TRPM7 kinase-dependent manner. Mol Neurobiol 51:729–742
Zhao B, Wang J, Liu L, Li X, Liu S, Xia Q, Shi J (2016) Annexin A1 translocates to nucleus and promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in a PKC-dependent manner after OGD/R. Sci Rep 6:27028
Zhao Y, Li X, Gong J, Li L, Chen L, Zheng L, Chen Z, Shi J, Zhang H (2017) Annexin A1 nuclear translocation induces retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury through the p65/IL-1beta pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863:1350–1358
Zhu Y, Chen X, Lu Y, Xia L, Fan S, Huang Q, Liu X, Peng X (2022) Glutamine mitigates murine burn sepsis by supporting macrophage M2 polarization through repressing the SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Burns Trauma 10:tkac041
Funding
This study was supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32271037 to XL, 82201472 to QX), Tongji Hospital (HUST) Foundation for Excellent Young Scientist (No. 2020YQ17 to XL), Shanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology General projects in natural science research (No. 202203021221241 to YHW) and Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Tongji Hospital (No. 2021hgry011 to YLZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qian Xia and Yongbo Yu conceived the ideas and designed and conducted the experiments; Gaofeng Zhan, Xue Zhang, Shuai Gao and Tangrui Han conducted the data analysis; Yilin Zhao, Xing Li and Yonghong Wang conceived the ideas, designed the experiments, supervised the entire project, and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Q., Yu, Y., Zhan, G. et al. The Sirtuin 5 Inhibitor MC3482 Ameliorates Microglia‑induced Neuroinflammation Following Ischaemic Stroke by Upregulating the Succinylation Level of Annexin-A1. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 19, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-024-10117-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-024-10117-x