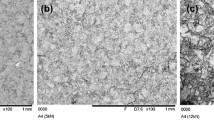
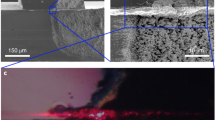
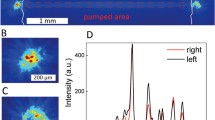
Abstract
The experimental results were compared with the different perovskite quantum dot–doped materials, which explicitly include losses, gain, lasing, and threshold. The random lasers emerge multiple emission peaks at different central wavelengths, due to the recurrent optical gain feedback and the localized field resonance effect in vicinity of particles. By the operation of the applied different devices, the perovskite quantum dots can be better materials for generating photons and can create stronger light scattering for transition from incoherent lasing to coherent lasing. Contrary to conventional random lasers, we found that the nature of the random lasing is dictated by the perovskite quantum dots, and the quantum dots with a high refractive index can be advantageous for random lasing in mediums. The experiments also reveal a regime including the fundamental aspects of surface plasmon resonance light scattering for facile active lasing mode switching. These results will guide future design of different quantum dot random lasers with controlled lasing wavelength output.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are not publicly available.
References
Cao H, Zhao YG, Ho ST, Seelig EW, Wang QH, Chang RPH (1999) Random laser action in semiconductor powder. Phys Rev Lett 82:2278–2281
Mujumdar S, Ricci M, Torre R, Wiersma DS (2004) Quasi-two-dimensional diffusive random laser action. Phys Rev Lett 93:053903
Cao H, JYX, Zhang DZ (2000) Spatial confinement of laser light in active random media. Phys Rev Lett 84:24
Consoli A, Soria E, Caselli N, López C (2019) López. Random lasing emission tailored by femtosecond and picosecond pulsed polymer ablation. Opt Lett 44(3):518C521
Liu Z, Zhiping Hu, Zhang Z, Juan Du, Yang J, Tang X, Liu W, Leng Y (2019) Two-photon pumped amplified spontaneous emission and lasing from formamidinium lead bromine nanocrystals. ACS Photonics 6(12):3150–3158
Ting F, Jiantao L, Yihong C, Wenxiong Y, Yongfa H (2019) Random lasing in cesium lead bromine perovskite quantum dots film. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:1084C1088
Kumar A, Prakash J, Deshmukh AD, Haranath D, Silotia P, Biradar AM (2012) Enhancing the photoluminescence of ferroelectric liquid crystal by doping with ZnS quantum dots. Appl Phys Lett 100:134101
Park YS, Bae WK, Baker T, Lim J, Klimov VI (2015) Klimov. Effect of Auger recombination on lasing in heterostructured quantum dots with engineered core/shell interfaces. Nano Lett 15:7319–7328
Li X, Wang Y, Sun H, Zeng H (2017) Amino-mediated anchoring perovskite quantum dots for stable and low-threshold random lasing. Adv Mater 29:1701185
Murzin AO, Stroganov BV, Gnnemann C, Hammouda SB, Shurukhina AV, Lozhkin MS, Emeline AV, Kapitonov YV (2020) Amplified spontaneous emission and random lasing in MAPbBr 3 halide perovskite single crystals. Adv Opt Mater 8(17):2000690
Liu Z, Zhiping Hu, Shi T, Juan Du, Yang J, Zhang Z, Tang X, Leng Y (2019) Stable and enhanced frequency up-converted lasing from CsPbBr 3 quantum dots embedded in silica sphere. Opt Express 27(7):9459–9466
Zhengzheng L, Jie Y, Juan D, Zhiping H, Shi ZZ, Yanqi L, Xiaosheng T, Yuxin L, Ruxin L (2018) Robust subwavelength single-mode perovskite nanocuboid laser. ACS Nano 12(6):5923–5931
Li L-W, Deng L-G (2013) Random lasing from dye-doped chiral nematic liquid crystals in oriented and non-oriented cells. Eur Phys J B 86:112
Longwu L, Luogen D (2013) Low threshold and coherent random lasing from dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystals using oriented cells. Laser Phys 23:085001-6
Li L (2016) Random lasing from PM597-DCM solutions containing Pt nanoparticles. Optics Communications 364:24–28
Carvalho PM, Felício MR, Santos NC, Gonçalves S, Domingues MM (2018) Application of light scattering techniques to nanoparticle characterization and development. Front Chem 6
Wang Z, Meng X, Choi SH, Knitter S, Kim YL, Cao H, Shalaev VM, Boltasseva A (2016) Controlling random lasing with three-dimensional plasmonic nanorod metamaterials. Nano Lett 16(4):2471C2477
Li Y, Li L (2022) A coherence random lasing for gain media based on lnP/ZnS quantum dots. Optics Communications 517:128350
Son DI et al (2012) Emissive ZnO–graphene quantum dots for white-light-emitting diodes. Nat Nanotechnol 7:465C471
Gryczynski I, Malicka J, Jiang W, Fischer H, Chan WC, Gryczynski Z, Grudzinski W, Lakowicz JR (2005) Surface-plasmon-coupled emission of quantum dots J Phys Chem B 109:1088–1093
Wang Z, Cao M, Shao G, Zhang Z, Huiwen Yu, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Baiping Xu, Wang Y, Yao J (2020) Coherent random lasing in colloidal quantum dots doped polymer-dispersed liquid crystal with low threshold and high stability. J Phys Chem Lett 11:767–774
Cao M, Zhang Y, Song X, Che Y, Zhang H, Dai H, Zhang G, Yao J (2016) Random lasing in a colloidal quantum dot-doped disordered polymer. Opt Express 24:9325–9331
Mirzaei J, Reznikov M, Hegmann T (2012) Quantum dots as liquid crystal dopants. J Mater Chem 22:22350
Azmi AN, Wan Ismail WZ, Abu Hassan H, Halim MM, Zainal N, Muskens OL, Wan Ahmad Kamil WM (2022) Review of open cavity random lasers as laser-based sensors. ACS Sens 7:914–928
Luan F, Gu B, Gomes ASL, Yong KT, Wen S, Prasad PN (2015) Lasing in nanocomposite random media. Nano Today 10:168–192
Santos EP, Silva RF, Silva JF, Maciel CV, Luz DF, De Lima E, Maia LJ, Lima BC, Moura AL (2021) Gain clamping in random lasers. Laser Phys Lett 18:125002–8
Rocha EG, Paz ÍR, Santos BJ, Soares WC, de Lima E, Leão LM, Maia LJ, Moura AL (2019) Self-induced optical parametric amplification of random laser emission. Laser Phys 29:045402
Xie R-C, Tsay S-Y, Jin-Jei Wu, Kuo C-C, Zhang H, Lin J-H (2022) Manipulation of plasmonic random laser from dye-doped liquid crystals inside photonic crystal fiber by the electric field. Opt Laser Technol 151:108013
Li Y, Li L (2022) Random lasing of the active organic nanocrystals of SFX-2-7-DDPA solution. Opt Mater 132:112723
Funding
This work was supported by the Science Research Start-up Funding of Langfang Normal University (Nos. XBQ202019, XPY202129, and XPT202105) and by the Guizhou Province Science Foundation (Grant [2016]1105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributed to the preparation, creation, and/or presentation of the published work from the original research author, specifically critical review, commentary, or revision, including pre- or post-publication stages.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
There is no relevant ethical issue involving human tissue in the experiments.
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L. Realization of Lasing Emission from the Different Perovskite Quantum Dot–Doped Materials. Plasmonics 18, 607–615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01794-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01794-0