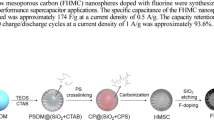
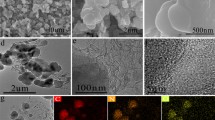
Abstract
Here we report a new approach referred as “soft-to-hard templating” strategy via the copolymerization of carbon source (dopamine) and silica source (tetraethyl orthosilicate) for the synthesis of well dispersed N-doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres (MCNs), which exhibit high performance for electrochemical supercapacitor. This method overcomes the shortcoming of uncontrolled dispersity and complicated procedures of soft- or hard-templating methods, respectively. Moreover, the synthesized MCNs feature enriched heteroatom N-doping and easy functionalization by noble-metal nanoparticles during the one-pot synthesis. All the above characters make the as-prepared MCNs a promising platform in a variety of applications. To demonstrate the applicability of the synthesized nitrogen-doped MCNs, this material has been employed as an electrode for high-performance electrochemical supercapacitor, which shows a capacitance of 223 and 140 F/g at current densities of 0.5 and 10 A/g in 1 mol/L KOH electrolyte, respectively.
摘要
本文报道了一种新的“由软到硬的模板”策略,通过碳源(多巴胺)和硅源(正硅酸乙酯)的共聚合合成了分散性良好的N掺杂介孔碳纳米球(MCNs)。该方法克服了复杂软模板和硬模板法难以控制MCNs分散性的问题。获得的MCNs含有丰富的N掺杂物种,且易于实现贵金属纳米颗粒的负载。该MCNs可应用于多领域。本文研究了其超电容特性:在1 mol/L NaOH溶液中,当电流密度为0.4和10 A/g时,该MCNs电极电容可分别达到223和140 F/g。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Wickramaratne N, Qiao S et al (2015) Molecular-based design and emerging applications of nanoporous carbon spheres. Nat Mater 14:763–774
Zhou W, Wang C, Zhang Q et al (2015) Tailoring pore size of nitrogen-doped hollow carbon nanospheres for confining sulfur in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Energy Mater 5:1401752
Zhai Y, Dou Y, Zhao D et al (2011) Carbon materials for chemical capacitive energy storage. Adv Mater 23:4828–4850
Yang T, Zhou R, Wang D et al (2015) Hierarchical mesoporous yolk–shell structured carbonaceous nanospheres for high performance electrochemical capacitive energy storage. Chem Commun 51:2518–2521
Yang T, Liu J, Zhou R et al (2014) N-doped mesoporous carbon spheres as the oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. J Mater Chem A 2:18139–18146
Wei J, Liang Y, Zhang X et al (2015) Controllable synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanospheres and Fe–N/carbon nanospheres as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Nanoscale 7:6247–6254
Wang S, Li W, Hao G et al (2011) Temperature-programmed precise control over the sizes of carbon nanospheres based on benzoxazine chemistry. J Am Chem Soc 133:15304–15307
Schuster J, He G, Mandlmeier B et al (2012) Spherical ordered mesoporous carbon nanoparticles with high porosity for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:3591–3595
Ma C, Shao X, Cao D (2012) Nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets as anode materials for lithium ion batteries: a first-principles study. J Mater Chem 22:8911–8915
Liu L, Deng Q, Agula B et al (2011) Ordered mesoporous carbon catalyst for dehydrogenation of propane to propylene. Chem Commun 47:8334–8336
Li C, Meng Y, Wang S et al (2015) Mesoporous carbon nanospheres featured fluorescent aptasensor for multiple diagnosis of cancer in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 9:12096–12103
Kong Q, Zhang L, Liu J et al (2014) Facile synthesis of hydrophilic multi-colour and upconversion photoluminescent mesoporous carbon nanoparticles for bioapplications. Chem Commun 50:15772–15775
Jeong H, Lee J, Shin W et al (2011) Nitrogen-doped graphene for high-performance ultracapacitors and the importance of nitrogen-doped sites at basal planes. Nano Lett 11:2472–2477
Gu J, Su S, Li Y et al (2011) Hydrophilic mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as carriers for sustained release of hydrophobic anti-cancer drugs. Chem Commun 47:2101–2103
Li Z, Xu Z, Tan X et al (2013) Mesoporous nitrogen-rich carbons derived from protein for ultra-high capacity battery anodes and supercapacitors. Energy Environ Sci 6:871–878
Konicki W, Cendrowski K, Chen X et al (2013) Application of hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres as an high effective adsorbent for the fast removal of acid dyes from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 228:824–833
Goettmann F, Fischer A, Antonietti M et al (2006) Chemical synthesis of mesoporous carbon nitrides using hard templates and their use as a metal-free catalyst for Friedel–Crafts reaction of benzene. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:4467–4471
Chen A, Yu Y, Zhang Y et al (2014) Aqueous-phase synthesis of nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres as an efficient adsorbent for acidic gases. Carbon 80:19–27
Wan Y, Shi Y, Zhao D (2007) Supramolecular aggregates as templates: ordered mesoporous polymers and carbons. Chem Mater 20:932–945
Tang J, Liu J, Li C et al (2015) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres with extra-large pores through assembly of diblock copolymer micelles. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:588–593
Ren J, Ding J, Chan K et al (2007) Dual-porosity carbon templated from monosize mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Mater 19:2786–2795
Lu A, Li W, Hao G et al (2010) Easy synthesis of hollow polymer, carbon, and graphitized microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:1615–1618
Liu J, Yang T, Wang D et al (2013) A facile soft-template synthesis of mesoporous polymeric and carbonaceous nanospheres. Nat Commun 4:2798
Fang Y, Gu D, Zou Y et al (2010) A low-concentration hydrothermal synthesis of biocompatible ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres with tunable and uniform size. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:7987–7991
Liu J, Qiao S, Liu H et al (2011) Extension of the Stöber method to the preparation of monodisperse resorcinol–formaldehyde resin polymer and carbon spheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5947–5951
Liang C, Li Z, Dai S (2008) Mesoporöse Kohlenstoffmaterialien: synthese und modifizierung. Angew Chem 120:3754–3776
Tian H, Saunders M, Dodd A et al (2016) Triconstituent co-assembly synthesis of N, S-doped carbon–silica nanospheres with smooth and rough surfaces. J Mater Chem A 4:3721–3727
Ai K, Liu Y, Ruan C et al (2013) sp2 C-dominant N-doped carbon sub-micrometer spheres with a tunable size: a versatile platform for highly efficient oxygen-reduction catalysts. Adv Mater 25:998–1003
Teranishi T, Hosoe M, Tanaka T et al (1999) Size control of monodispersed Pt nanoparticles and their 2D organization by electrophoretic deposition. J Phys Chem B 103:3818–3827
Lim S, Li R, Ji W et al (2007) Effects of nitrogenation on single-walled carbon nanotubes within density functional theory. Phys Rev B 76:195406
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB933200), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA062703), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21177137) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2012200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Q., Zhang, L., Wang, M. et al. Soft-to-hard templating to well-dispersed N-doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres via one-pot carbon/silica source copolymerization. Sci. Bull. 61, 1195–1201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1119-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1119-6