Abstract
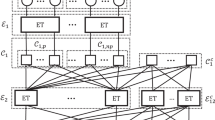
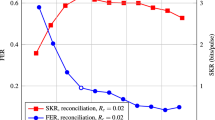
In the practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD) system, the postprocessing process, particularly the error correction part, significantly impacts the system performance. Multi-edge type low-density parity-check (MET-LDPC) codes are suitable for CV-QKD systems because of their Shannon-limit-approaching performance at a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). However, the process of designing a low-rate MET-LDPC code with good performance is extremely complicated. Thus, we introduce Raptor-like LDPC (RL-LDPC) codes into the CV-QKD system, exhibiting both the rate compatible property of the Raptor code and capacity-approaching performance of MET-LDPC codes. Moreover, this technique can significantly reduce the cost of constructing a new matrix. We design the RL-LDPC matrix with a code rate of 0.02 and easily and effectively adjust this rate from 0.016 to 0.034. Simulation results show that we can achieve more than 98% reconciliation efficiency in a range of code rate variation using only one RL-LDPC code that can support high-speed decoding with an SNR less than −16.45 dB. This code allows the system to maintain a high key extraction rate under various SNRs, paving the way for practical applications of CV-QKD systems with different transmission distances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Pirandola, U. L. Andersen, L. Banchi, M. Berta, D. Bunandar, R. Colbeck, D. Englund, T. Gehring, C. Lupo, C. Ottaviani, J. L. Pereira, M. Razavi, J. Shamsul Shaari, M. Tomamichel, V. C. Usenko, G. Vallone, P. Villoresi, and P. Wallden, Adv. Opt. Photon. 12, 1012 (2020), arXiv: 1906.01645.
F. Xu, X. Ma, Q. Zhang, H. K. Lo, and J. W. Pan, Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 025002 (2020), arXiv: 1903.09051.
E. Diamanti, H. K. Lo, B. Qi, and Z. Yuan, npj Quantum Inf. 2, 16025 (2016).
C. H. Bennett, and G. Brassard, in Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing (Bangalore, 1984), pp. 175–179.
N. Gisin, G. Ribordy, W. Tittel, and H. Zbinden, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145 (2002), arXiv: quant-ph/0101098.
V. Scarani, H. Bechmann-Pasquinucci, N. J. Cerf, M. Dušek, N. Lütkenhaus, and M. Peev, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301 (2009), arXiv: 0802.4155.
F. Grosshans, and P. Grangier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002), arXiv: quant-ph/0109084.
F. Grosshans, G. van Assche, J. Wenger, R. Brouri, N. J. Cerf, and P. Grangier, Nature 421, 238 (2003), arXiv: quant-ph/0312016.
S. L. Braunstein, and P. van Loock, Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 513 (2005), arXiv: quant-ph/0410100.
C. Weedbrook, S. Pirandola, R. García-Patrón, N. J. Cerf, T. C. Ralph, J. H. Shapiro, and S. Lloyd, Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621 (2012), arXiv: 1110.3234.
P. Jouguet, S. Kunz-Jacques, A. Leverrier, P. Grangier, and E. Diamanti, Nat. Photon. 7, 378 (2013), arXiv: 1210.6216.
Y. Zhang, Z. Li, Z. Chen, C. Weedbrook, Y. Zhao, X. Wang, Y. Huang, C. Xu, X. Zhang, Z. Wang, M. Li, X. Zhang, Z. Zheng, B. Chu, X. Gao, N. Meng, W. Cai, Z. Wang, G. Wang, S. Yu, and H. Guo, Quantum Sci. Technol. 4, 035006 (2019).
Y. Zhang, Z. Chen, S. Pirandola, X. Wang, C. Zhou, B. Chu, Y. Zhao, B. Xu, S. Yu, and H. Guo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 010502 (2020), arXiv: 2001.02555.
H. Guo, Z. Li, S. Yu, and Y. Zhang, Fundam. Res. 1, 96 (2021).
P. Jouguet, D. Elkouss, and S. Kunz-Jacques, Phys. Rev. A 90, 042329 (2014), arXiv: 1406.1050.
A. Leverrier, R. Alléaume, J. Boutros, G. Zémor, and P. Grangier, Phys. Rev. A 77, 042325 (2008), arXiv: 0712.3823.
P. Jouguet, S. Kunz-Jacques, and A. Leverrier, Phys. Rev. A 84, 062317 (2011), arXiv: 1110.0100.
S. M. Zhao, Z. G. Shen, H. Xiao, and L. Wang, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 090323 (2018).
Z. L. Bai, X. Y. Wang, S. S. Yang, and Y. M. Li, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 59, 614201 (2016).
M. Milicevic, C. Feng, L. M. Zhang, and P. G. Gulak, npj Quantum Inf. 4, 21 (2018), arXiv: 1702.07740.
C. Zhou, X. Wang, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, S. Yu, and H. Guo, Phys. Rev. Appl. 12, 054013 (2019), arXiv: 1908.04526.
T. Richardson, and R. Urbanke, in Workshop honoring Prof. Bob McEliece on his 60th birthday (California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, 2002), pp. 24–25.
A. Leverrier, and P. Grangier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 180504 (2009), arXiv: 0812.4246.
X. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Yu, B. Xu, Z. Li, and H. Guo, Quantum Inf. Comput. 17, 1123 (2017).
S. S. Yang, Z. G. Lu, and Y. M. Li, J. Lightwave Technol. 38, 3935 (2020).
A. Rakita, N. Nikolić, M. Mildner, J. Matiasek, and A. Elbe-Bürger, Sci. Rep. 10, 1 (2020).
S. I. Park, Y. Wu, H. M. Kim, N. Hur, and J. Kim, IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 60, 239 (2014).
T. Y. Chen, K. Vakilinia, D. Divsalar, and R. D. Wesel, IEEE Trans. Commun. 63, 1522 (2015).
J. Liu, and R. C. de Lamare, AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69, 1582 (2015).
A. Shokrollahi, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 52, 2551 (2006).
A. Leverrier, F. Grosshans, and P. Grangier, Phys. Rev. A 81, 062343 (2010), arXiv: 1005.0339.
P. Jouguet, S. Kunz-Jacques, E. Diamanti, and A. Leverrier, Phys. Rev. A 86, 032309 (2012), arXiv: 1206.6357.
F. Grosshans, N. J. Cerf, J. Wenger, R. Tualle-Brouri, and P. Grangier, Quantum Inf. Comput. 3, 535 (2003).
G. Van Assche, J. Cardinal, and N. J. Cerf, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 50, 394 (2004).
C. H. Bennett, G. Brassard, C. Crepeau, and U. M. Maurer, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 41, 1915 (1995).
X.-Y. Hu, E. Eleftheriou, and D. M. Arnold, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 51, 386 (2005).
X. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Yu, and H. Guo, Sci. Rep. 8, 10543 (2018), arXiv: 1711.01783.
X. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Yu, and H. Guo, Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 264 (2019), arXiv: 1806.00173.
C. Wang, D. Huang, P. Huang, D. Lin, J. Peng, and G. Zeng, Sci. Rep. 5, 14607 (2015).
D. Huang, P. Huang, D. Lin, and G. Zeng, Sci. Rep. 6, 19201 (2016).
S. Pirandola, R. Laurenza, C. Ottaviani, and L. Banchi, Nat. Commun. 8, 15043 (2017), arXiv: 1512.04945.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61531003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62001041), and the Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Wang, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Rate compatible reconciliation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution using Raptor-like LDPC codes. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 260311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1688-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1688-4