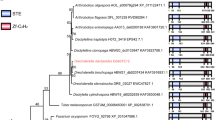
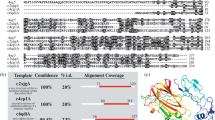
Abstract
The methylation of lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4), catalyzed by the histone methyltransferase KMT2/SET1, has been functionally identified in many pathogenic fungi but remains unexplored in nematode-trapping fungi (NTFs). Here, we report a regulatory mechanism of an H3K4-specific SET1 orthologue, AoSET1, in the typical nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. When the fungus is induced by the nematode, the expression of AoSET1 is up-regulated. Disruption of AoSet1 led to the abolishment of H3K4me. Consequently, the yield of traps and conidia of ΔAoSet1 was significantly lower than that of the WT strain, and the growth rate and pathogenicity were also compromised. Moreover, H3K4 trimethylation was enriched mainly in the promoter of two bZip transcription factor genes (AobZip129 and AobZip350) and ultimately up-regulated the expression level of these two transcription factor genes. In the ΔAoSet1 and AoH3K4A strains, the H3K4me modification level was significantly decreased at the promoter of transcription factor genes AobZip129 and AobZip350. These results suggest that AoSET1-mediated H3KEme serves as an epigenetic marker of the promoter region of the targeted transcription factor genes. Furthermore, we found that AobZip129 negatively regulates the formation of adhesive networks and the pathogenicity of downstream AoPABP1 and AoCPR1. Our findings confirm that the epigenetic regulatory mechanism plays a pivotal role in regulating trap formation and pathogenesis in NTFs, and provide novel insights into the mechanisms of interaction between NTFs and nematodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, P., Gouzy, J., Aury, J.M., Castagnone-Sereno, P., Danchin, E.G.J., Deleury, E., Perfus-Barbeoch, L., Anthouard, V., Artiguenave, F., Blok, V.C., et al. (2008). Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat Biotechnol 26, 909–915.
Adhvaryu, K.K., Morris, S.A., Strahl, B.D., and Selker, E.U. (2005). Methylation of histone H3 lysine 36 is required for normal development in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot Cell 4, 1455–1464.
Afonina, E., Stauber, R., and Pavlakis, G.N. (1998). The human poly(A)-binding protein 1 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 273, 13015–13021.
Allshire, R.C., and Madhani, H.D. (2018). Ten principles of heterochromatin formation and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19, 229–244.
Bailey, T.L., Boden, M., Buske, F.A., Frith, M., Grant, C.E., Clementi, L., Ren, J., Li, W.W., and Noble, W.S. (2009). MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37, W202–W208.
Briggs, S.D., Bryk, M., Strahl, B.D., Cheung, W.L., Davie, J.K., Dent, S.Y.R., Winston, F., and Allis, C.D. (2001). Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation is mediated by Set1 and required for cell growth and rDNA silencing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 15, 3286–3295.
Cheon, S.A., Jung, K.W., Chen, Y.L., Heitman, J., Bahn, Y.S., and Kang, H. A. (2011). Unique evolution of the UPR pathway with a novel bZIP transcription factor, Hxl1, for controlling pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans. PloS Pathog 7, e1002177.
Choudhury, R., Singh, S., Arumugam, S., Roguev, A., and Stewart, A.F. (2019). The Set1 complex is dimeric and acts with Jhd2 demethylation to convey symmetrical H3K4 trimethylation. Genes Dev 33, 550–564.
Cottier, F., Raymond, M., Kurzai, O., Bolstad, M., Leewattanapasuk, W., Jimenez-Lopez, C., Lorenz, M.C., Sanglard, D., Vachova, L., Pavelka, N., et al., (2012). The bZIP transcription factor Rca1p is a central regulator of a novel CO2 sensing pathway in yeast. PLoS Pathog 8, e1002485.
Du, W., Shi, G., Shan, C.M., Li, Z., Zhu, B., Jia, S., Li, Q., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Mechanisms of chromatin-based epigenetic inheritance. Sci China Life Sci 65, 2162–2190.
Etzerodt, T., Wetterhorn, K., Dionisio, G., and Rayment, I. (2017). Functional characterization of a soluble NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase from Fusarium graminearum. Protein Expr Purif 138, 69–75.
Feng, Q., Wang, H., Ng, H.H., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., Struhl, K., and Zhang, Y. (2002). Methylation of H3-lysine 79 is mediated by a new family of HMTases without a SET domain. Curr Biol 12, 1052–1058.
Fingerman, I.M., Wu, C.L., Wilson, B.D., and Briggs, S.D. (2005). Global loss of Set1-mediated H3 Lys4 trimethylation is associated with silencing defects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 280, 28761–28765.
Freitag, M. (2017). Histone methylation by SET domain proteins in fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol 71, 413–439.
Gorgoni, B., and Gray, N.K. (2004). The roles of cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins in regulating gene expression: a developmental perspective. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 3, 125–141.
Gray, N.K., Hrabálková, L., Scanlon, J.P., and Smith, R.W.P. (2015). Poly (A)-binding proteins and mRNA localization: who rules the roost? Biochem Soc Trans 43, 1277–1284.
Gu, Q., Tahir, H., Zhang, H., Huang, H., Ji, T., Sun, X., Wu, L., Wu, H., and Gao, X. (2017). Involvement of FvSet1 in Fumonisin B1 biosynthesis, vegetative growth, fungal virulence, and environmental stress responses in Fusarium verticillioides. Toxins 9, 43.
Guenther, M.G., Levine, S.S., Boyer, L.A., Jaenisch, R., and Young, R.A. (2007). A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells. Cell 130, 77–88.
He, D., Feng, Z., Gao, S., Wei, Y., Han, S., and Wang, L. (2021). Contribution of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase to azole resistance in Fusarium oxysporum. Front Microbiol 12.
He, F., Umehara, T., Saito, K., Harada, T., Watanabe, S., Yabuki, T., Kigawa, T., Takahashi, M., Kuwasako, K., Tsuda, K., et al. (2010). Structural insight into the zinc finger CW domain as a histone modification reader. Structure 18, 1127–1139.
Hohn, T.M., and Desjardins, A.E. (1992). Isolation and gene disruption of the Tox5 gene encoding trichodiene synthase in Gibberella pulicaris. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 5, 249.
Hsueh, Y.P., Mahanti, P., Schroeder, F.C., and Sternberg, P.W. (2013). Nematode-trapping fungi eavesdrop on nematode pheromones. Curr Biol 23, 83–86.
Huang, W., Shang, Y., Chen, P., Cen, K., and Wang, C. (2015). Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain transcription factor MBZ1 regulates cell wall integrity, spore adherence, and virulence in Metarhizium robertsii. J Biol Chem 290, 8218–8231.
Huang, Y., Bai, X., Cheng, N., Xiao, J., Li, X., and Xing, Y. (2020). Wide Grain 7 increases grain width by enhancing H3K4me3 enrichment in the OsMADS1 promoter in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J 102, 517–528.
Hyde, K., Swe, A., and Zhang, K.Q. (2014). Nematode-trapping fungi. In: Zhang, K.Q., and Hyde, K., eds. Nematode-Trapping Fungi. Fungal Diversity Research Series. Dordrecht: Springer. 1–12.
Jenuwein, T., Laible, G., Dorn, R., and Reuter, G. (1998). SET domain proteins modulate chromatin domains in eu- and heterochromatin. Cell Mol Life Sci 54, 80–93.
Ji, X., Li, H., Zhang, W., Wang, J., Liang, L., Zou, C., Yu, Z., Liu, S., and Zhang, K.Q. (2020a). The lifestyle transition of Arthrobotrys oligospora is mediated by microRNA-like RNAs. Sci China Life Sci 63, 543–551.
Ji, X., Yu, Z., Yang, J., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Zou, C., Li, J., Liang, L., and Zhang, K.Q. (2020b). Expansion of adhesion genes drives pathogenic adaptation of nematode-trapping fungi. iScience 23, 101057.
Kaczmarek Michaels, K., Mohd Mostafa, S., Ruiz Capella, J., and Moore, C.L. (2020). Regulation of alternative polyadenylation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by histone H3K4 and H3K36 methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 48, 5407–5425.
Keller, N.P., and Hohn, T.M. (1997). Metabolic pathway gene clusters in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 21, 17–29.
Kouzarides, T. (2007). Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128, 693–705.
Krogan, N.J., Dover, J., Khorrami, S., Greenblatt, J.F., Schneider, J., Johnston, M., and Shilatifard, A. (2002). COMPASS, a histone H3 (Lysine 4) methyltransferase required for telomeric silencing of gene expression. J Biol Chem 277, 10753–10755.
Kühn, U., and Wahle, E. (2004). Structure and function of poly(A) binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1678, 67–84.
Kumar, G.R., and Glaunsinger, B.A. (2010). Nuclear import of cytoplasmic poly(A) binding protein restricts gene expression via hyperadenylation and nuclear retention of mRNA. Mol Cell Biol 30, 4996–5008.
Kumar, G.R., Shum, L., and Glaunsinger, B.A. (2011). Importin α-mediated nuclear import of cytoplasmic poly(A) binding protein occurs as a direct consequence of cytoplasmic mRNA depletion. Mol Cell Biol 31, 3113–3125.
Lai, Y., Cao, X., Chen, J., Wang, L., Wei, G., and Wang, S. (2020). Coordinated regulation of infection-related morphogenesis by the KMT2-Cre1-Hyd4 regulatory pathway to facilitate fungal infection. Sci Adv 6, eaaz1659.
Lemay, J.F., Lemieux, C., St-André, O., and Bachand, F. (2010). Crossing the borders: poly(A)-binding proteins working on both sides of the fence. RNA Biol 7, 291–295.
Li, J., Wu, R., Wang, M., Borneman, J., Yang, J., and Zhang, K.Q. (2019). The pH sensing receptor AopalH plays important roles in the nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Fungal Biol 123, 547–554.
Li, J., Zou, C., Xu, J., Ji, X., Niu, X., Yang, J., Huang, X., and Zhang, K.Q. (2015). Molecular mechanisms of nematode-nematophagous microbe interactions: basis for biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53, 67–95.
Li, X., Foley, E.A., Molloy, K.R., Li, Y., Chait, B.T., and Kapoor, T.M. (2012). Quantitative chemical proteomics approach to identify post-translational modification-mediated protein-protein interactions. J Am Chem Soc 134, 1982–1985.
Liang, L., Shen, R., Mo, Y., Yang, J., Ji, X., and Zhang, K.Q. (2015). A proposed adhesin AoMad1 helps nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora recognizing host signals for life-style switching. Fungal Genet Biol 81, 172–181.
Liu, Q., Guo, X., Jiang, G., Wu, G., Miao, H., Liu, K., Chen, S., Sakamoto, N., Kuno, T., Yao, F., et al. (2020). NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase Ccr1 is a target of tamoxifen and participates in its antifungal activity via regulating cell wall integrity in fission yeast. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64.
Liu, Q., Li, D., Jiang, K., Zhang, K.Q., and Yang, J. (2022a). AoPEX1 and AoPEX6 are required for mycelial growth, conidiation, stress response, fatty acid utilization, and trap formation in Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiol Spectr 10, e0027522.
Liu, X., Miao, Q., Zhou, Z., Lu, S., and Li, J. (2022b). Identification of three novel conidiogenesis-related genes in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Pathogens 11, 717.
Liu, X.H., Lu, J.P., Zhang, L., Dong, B., Min, H., and Lin, F.C. (2007). Involvement of a Magnaporthe grisea serine/threonine kinase gene, MgATG1, in appressorium turgor and pathogenesis. Eukaryot Cell 6, 997–1005.
Miller, T., Krogan, N.J., Dover, J., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., Johnston, M., Greenblatt, J.F., and Shilatifard, A. (2001). COMPASS: a complex of proteins associated with a trithorax-related SET domain protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 12902–12907.
Moosavi, M.R., and Zare, R. (2012). Fungi as biological control agents of plant-parasitic nematodes. In: Mérillon, J.M., and Ramawat, K.G., eds. Plant Defence: Biological Control. Progress in Biological Control. Cham: Springer. 67–107.
Nakayama, J., Rice, J.C., Strahl, B.D., Allis, C.D., and Grewal, S.I.S. (2001). Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 292, 110–113.
Ng, H.H., Feng, Q., Wang, H., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., Zhang, Y., and Struhl, K. (2002). Lysine methylation within the globular domain of histone H3 by Dot1 is important for telomeric silencing and Sir protein association. Genes Dev 16, 1518–1527.
Noma, K., Allis, C.D., and Grewal, S.I.S. (2001). Transitions in distinct histone H3 methylation patterns at the heterochromatin domain boundaries. Science 293, 1150–1155.
Park, H.G., Lim, Y.R., Eun, C.Y., Han, S., Han, J.S., Cho, K.S., Chun, Y.J., and Kim, D. (2010). Candida albicans NADPH-P450 reductase: expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396, 534–538.
Peters, A.H.F.M., O’Carroll, D., Scherthan, H., Mechtler, K., Sauer, S., Schöfer, C., Weipoltshammer, K., Pagani, M., Lachner, M., Kohlmaier, A., et al. (2001). Loss of the Suv39h histone methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome stability. Cell 107, 323–337.
Pham, K.T., Inoue, Y., Vu, B.V., Nguyen, H.H., Nakayashiki, T., Ikeda, K., and Nakayashiki, H. (2015). MoSET1 (histone H3K4 methyltransferase in Magnaporthe oryzae) regulates global gene expression during infection-related morphogenesis. PLoS Genet 11, e1005385.
Ramakrishnan, S., Pokhrel, S., Palani, S., Pflueger, C., Parnell, T.J., Cairns, B.R., Bhaskara, S., and Chandrasekharan, M.B. (2016). Counteracting H3K4 methylation modulators Set1 and Jhd2 co-regulate chromatin dynamics and gene transcription. Nat Commun 7, 11949.
Ren, K., Mou, Y.N., Tong, S.M., Ying, S.H., and Feng, M.G. (2021). SET1/KMT2-governed histone H3K4 methylation coordinates the lifecycle in vivo and in vitro of the fungal insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana. Environ Microbiol 23, 5541–5554.
Roguev, A., Schaft, D., Shevchenko, A., Pijnappel, W.W., Wilm, M., Aasland, R., and Stewart, A.F. (2001). The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Set1 complex includes an Ash2 homologue and methylates histone 3 lysine 4. EMBO J 20, 7137–7148.
Schneider, J., Wood, A., Lee, J.S., Schuster, R., Dueker, J., Maguire, C., Swanson, S.K., Florens, L., Washburn, M.P., and Shilatifard, A. (2005). Molecular regulation of histone H3 trimethylation by COMPASS and the regulation of gene expression. Mol Cell 19, 849–856.
Seo, J.A., Proctor, R.H., and Plattner, R.D. (2001). Characterization of four clustered and coregulated genes associated with fumonisin biosynthesis in Fusarium verticillioides. Fungal Genet Biol 34, 155–165.
Shan, P., Fan, G., Sun, L., Liu, J., Wang, W., Hu, C., Zhang, X., Zhai, Q., Song, X., Cao, L., et al. (2017). SIRT1 functions as a negative regulator of eukaryotic Poly(A)RNA transport. Curr Biol 27, 2271–2284.e5.
Shilatifard, A. (2008). Molecular implementation and physiological roles for histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20, 341–348.
Shilatifard, A. (2012). The COMPASS family of histone H3K4 methylases: mechanisms of regulation in development and disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem 81, 65–95.
Sims, R.J., and Reinberg, D. (2006). Histone H3 Lys 4 methylation: caught in a bind? Genes Dev 20, 2779–2786.
Smith, R.W.P., Blee, T.K.P., and Gray, N.K. (2014). Poly(A)-binding proteins are required for diverse biological processes in metazoans. Biochem Soc Trans 42, 1229–1237.
Strahl, B.D., Grant, P.A., Briggs, S.D., Sun, Z.W., Bone, J.R., Caldwell, J. A., Mollah, S., Cook, R.G., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D.F., et al. (2002). Set2 is a nucleosomal histone H3-selective methyltransferase that mediates transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 22, 1298–1306.
Takahashi, Y.H., and Shilatifard, A. (2010). Structural basis for H3K4 trimethylation by yeast Set1/COMPASS. Adv Enzyme Regulation 50, 104–110.
Tamaru, H., and Selker, E.U. (2001). A histone H3 methyltransferase controls DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. Nature 414, 277–283.
Tang, W., Ru, Y., Hong, L., Zhu, Q., Zuo, R., Guo, X., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Zheng, X., Wang, P., et al. (2015). System-wide characterization of bZIP transcription factor proteins involved in infection-related morphogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae. Environ Microbiol 17, 1377–1396.
Xie, M., Ma, N., Bai, N., Yang, L., Yang, X., Zhang, K.Q., and Yang, J. (2022). PKC-SWI6 signaling regulates asexual development, cell wall integrity, stress response, and lifestyle transition in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Sci China Life Sci 65, 2455–2471.
Yang, J., Wang, L., Ji, X., Feng, Y., Li, X., Zou, C., Xu, J., Ren, Y., Mi, Q., Wu, J., et al., (2011). Genomic and proteomic analyses of the fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora provide insights into nematode-trap formation. PLoS Pathog 7, e1002179.
Young, C., McMillan, L., Telfer, E., and Scott, B. (2001). Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of an indole-diterpene gene cluster from Penicillium paxilli. Mol Microbiol 39, 754–764.
Zhen, Z., Xing, X., Xie, M., Yang, L., Yang, X., Zheng, Y., Chen, Y., Ma, N., Li, Q., Zhang, K.Q., et al. (2018). MAP kinase Slt2 orthologs play similar roles in conidiation, trap formation, and pathogenicity in two nematode-trapping fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 116, 42–50.
Zhen, Z., Zhang, G., Yang, L., Ma, N., Li, Q., Ma, Y., Niu, X., Zhang, K.Q., and Yang, J. (2019). Characterization and functional analysis of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs) in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 819–832.
Zhou, D., Zhu, Y., Bai, N., Yang, L., Xie, M., Yang, J., Zhu, M., Zhang, K. Q., and Yang, J. (2022). AoATG5 plays pleiotropic roles in vegetative growth, cell nucleus development, conidiation, and virulence in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Sci China Life Sci 65, 412–425.
Zhu, M.C., Zhao, N., Liu, Y.K., Li, X.M., Zhen, Z.Y., Zheng, Y.Q., Zhang, K.Q., and Yang, J.K. (2022). The cAMP-PKA signalling pathway regulates hyphal growth, conidiation, trap morphogenesis, stress tolerance, and autophagy in Arthrobotrys oligospora. Environ Microbiol 24, 6524–6538.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Materials
11427_2022_2300_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Nematode-induced trap formation regulated by the histone H3K4 methyltransferase AoSET1 in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Q., Wang, Z., Yin, Z. et al. Nematode-induced trap formation regulated by the histone H3K4 methyltransferase AoSET1 in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2663–2679 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2300-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2300-2