Abstract
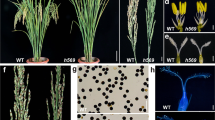
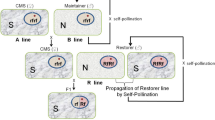
Hybrid seed production technology (SPT) using genic recessive male sterility is of great importance in maize breeding. Here, we report a novel SPT based on a maize unilateral cross-incompatibility gene ZmGa1F with an extremely low transgene transmission rate (TTR). Proper pollen-specific ZmGa1F expression severely inhibits pollen tube growth leading to no fertilization. The maintainer line harbors a transgene cassette in an ipe1 male sterile background containing IPE1 to restore ipe1 male fertility, ZmGa1F to prevent transgenic pollen escape, the red fluorescence protein encoding gene DsRed2 for the separation of male sterile and fertile seeds, and the herbicide-resistant gene Bar for transgenic plant selection. When the maintainer line is selfed, gametes of ipe1/transgene and ipe1/- genotypes are produced, and pollen of the ipe1/transgene genotype is not able to fertilize female gametes due to pollen tube growth inhibition by ZmGa1F. Subsequently, seeds of ipe1/ipe1 and ipe1/transgene genotypes are produced at a 1:1 ratio and could be separated easily by fluorescence-based seed sorting. Not a single seed emitting fluorescence is detected in more than 200,000 seeds examined demonstrating that the pollen-tube-inhibition (PTI)-based TTR is lower than what has been reported for similar technologies to date. This PTI-based SPT shows promising potential for future maize hybrid seed production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.L., and Lonsdale, D.M. (1993). Molecular characterization of one of the maize polygalacturonase gene family members which are expressed during late pollen development. Plant J 3, 261–271.
An, X., Ma, B., Duan, M., Dong, Z., Liu, R., Yuan, D., Hou, Q., Wu, S., Zhang, D., Liu, D., et al. (2020). Molecular regulation of ZmMs7 required for maize male fertility and development of a dominant male-sterility system in multiple species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 23499–23509.
Chang, Z., Chen, Z., Wang, N., Xie, G., Lu, J., Yan, W., Zhou, J., Tang, X., and Deng, X.W. (2016). Construction of a male sterility system for hybrid rice breeding and seed production using a nuclear male sterility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 14145–14150.
Chen, L., and Liu, Y.G. (2014). Male sterility and fertility restoration in crops. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65, 579–606.
Chen, R., Deng, Y., Ding, Y., Guo, J., Qiu, J., Wang, B., Wang, C., Xie, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2022). Rice functional genomics: decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci China Life Sci 65, 33–92.
Chen, X., Zhang, H., Sun, H., Luo, H., Zhao, L., Dong, Z., Yan, S., Zhao, C., Liu, R., Xu, C., et al. (2017). Irregular pollen exine1 is a novel factor in anther cuticle and pollen exine formation. Plant Physiol 173, 307–325.
Dobnik, D., Spilsberg, B., Bogožalec Košir, A., Štebih, D., Morisset, D., Holst-Jensen, A., and Šel, J. (2018). Multiplex droplet digital PCR protocols for quantification of GM maize events. In Digital PCR: Methods and Protocols, G. Karlin-Neumann and F. Bizouarn, ed. (New York: Springer), pp. 69–98.
Duvick, D.N. (2001). Biotechnology in the 1930s: the development of hybrid maize. Nat Rev Genet 2, 69–74.
Fang, X., Sun, X., Yang, X., Li, Q., Lin, C., Xu, J., Gong, W., Wang, Y., Liu, L., Zhao, L., et al. (2021). MS1 is essential for male fertility by regulating the microsporocyte cell plate expansion in soybean. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1533–1545.
Fox, T., DeBruin, J., Haug Collet, K., Trimnell, M., Clapp, J., Leonard, A., Li, B., Scolaro, E., Collinson, S., Glassman, K., et al. (2017). A single point mutation in Ms44 results in dominant male sterility and improves nitrogen use efficiency in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 942–952.
Hanson, D.D., Hamilton, D.A., Travis, J.L., Bashe, D.M., and Mascarenhas, J.P. (1989). Characterization of a pollen-specific cDNA clone from Zea mays and its expression.. Plant Cell 1, 173–179.
Huo, Y., Pei, Y., Tian, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, K., Liu, J., Xiao, S., Chen, H., and Liu, J. (2020). IRREGULAR POLLENEXINE2 encodes a GDSL lipase essential for male fertility in maize. Plant Physiol 184, 1438–1454.
Kalla, R., Shimamoto, K., Potter, R., Nielsen, P.S., Linnestad, C., and Olsen, O.A. (1994). The promoter of the barley aleurone-specific gene encoding a putative 7 kDa lipid transfer protein confers aleurone cell-specific expression in transgenic rice. Plant J 6, 849–860.
Kim, Y.J., and Zhang, D. (2018). Molecular control of male fertility for crop hybrid breeding. Trends Plant Sci 23, 53–65.
Lauter, A.N.M., Muszynski, M.G., Huffman, R.D., and Scott, M.P. (2017). A pectin methylesterase ZmPme3 is expressed in Gametophyte factor1-s (Ga1-s) silks and maps to that locus in maize (Zea mays L.). Front Plant Sci 8, 1926.
Matz, M.V., Fradkov, A.F., Labas, Y.A., Savitsky, A.P., Zaraisky, A.G., Markelov, M.L., and Lukyanov, S.A. (1999). Fluorescent proteins from nonbioluminescent Anthozoa species. Nat Biotechnol 17, 969–973.
Qi, X., Zhang, C., Zhu, J., Liu, C., Huang, C., Li, X., and Xie, C. (2020). Genome editing enables next-generation hybrid seed production technology. Mol Plant 13, 1262–1269.
Song, S., Wang, T., Li, Y., Hu, J., Kan, R., Qiu, M., Deng, Y., Liu, P., Zhang, L., Dong, H., et al. (2021). A novel strategy for creating a new system of third-generation hybrid rice technology using a cytoplasmic sterility gene and a genic male-sterile gene. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 251–260.
Tian, Y., Xiao, S., Liu, J., Somaratne, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, M., Zhang, H., Zhao, L., and Chen, H. (2017). Male sterile6021 (ms6021) is required for the development of anther cuticle and pollen exine in maize. Sci Rep 7, 16736.
Timofejeva, L., Skibbe, D.S., Lee, S., Golubovskaya, I., Wang, R., Harper, L., Walbot, V., and Cande, W.Z. (2013). Cytological characterization and allelism testing of anther developmental mutants identified in a screen of maize male sterile lines. G3: Genes-Genomes-Genet 3, 231–249.
Wan, X., Wu, S., Li, Z., Dong, Z., An, X., Ma, B., Tian, Y., and Li, J. (2019). Maize genic male-sterility genes and their applications in hybrid breeding: progress and perspectives. Mol Plant 12, 321–342.
Williams, M.E. (1995). Genetic engineering for pollination control. Trends Biotechnol 13, 344–349.
Wu, Y., Fox, T.W., Trimnell, M.R., Wang, L., Xu, R.J., Cigan, A.M., Huffman, G.A., Garnaat, C.W., Hershey, H., and Albertsen, M.C. (2016). Development of a novel recessive genetic male sterility system for hybrid seed production in maize and other cross-pollinating crops. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 1046–1054.
Yuan, L. (1994). Purification and production of foundation seed of rice PGMS and TGMS lines. Hybrid Rice 6, 1–3.
Zhang, D., Wu, S., An, X., Xie, K., Dong, Z., Zhou, Y., Xu, L., Fang, W., Liu, S., Liu, S., et al. (2018a). Construction of a multicontrol sterility system for a maize male-sterile line and hybrid seed production based on the ZmMs7 gene encoding a PHD-finger transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 459–471.
Zhang, Z., Zhang, B., Chen, Z., Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Wang, H., Zhang, Y.’., Cai, D., Liu, J., Xiao, S., et al. (2018b). A Pectin methylesterase gene at the maize Ga1 locus confers male function in unilateral cross-incompatibility. Nat Commun 9, 3678.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32101725, 32172058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Zhang, Z., Zhao, L. et al. A novel hybrid seed production technology based on a unilateral cross-incompatibility gene in maize. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 595–601 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2191-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2191-7