Abstract
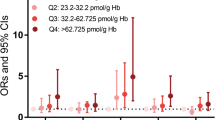
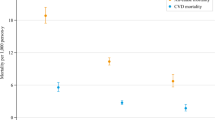
Ethylene oxide (EtO) is a widely used industrial chemical with recognized health risks. While its carcinogenic properties have been extensively studied, emerging evidence suggests potential associations with cardiovascular diseases. Using the recently introduced Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) score as a comprehensive cardiovascular health (CVH) measure, this study aimed to elucidate the relationship between EtO exposure and CVH. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) encompassing 3748 adults was analyzed. CVH was assessed using the LE8 score, which incorporates diet, physical activity, tobacco/nicotine exposure, sleep duration, BMI, non-HDL cholesterol, blood glucose, and blood pressure. The association between EtO exposure, gauged by Hemoglobin adduct (HbEtO) levels, and CVH was examined using linear regression and Cox regression models. An inverse relationship between EtO exposure and the overall CVH score was identified. Specifically, for every 1-unit increase in ln-transformed HbEtO, a 3.69-point decrease in the total CVH score was observed. An inverted J-shaped association between ln-transformed HbEtO and CVH score emerged, with an inflection point at 3.15 pmol/g Hb. Elevated EtO exposure was not significantly linked to all-cause mortality but was robustly associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. Elevated EtO exposure is negatively associated with CVH, as outlined by the LE8 metrics. Beyond a certain threshold, this association underscores the cardiovascular risks of EtO exposure and highlights the importance of further research to determine underlying mechanisms and recommend preventive strategies.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The survey data are publicly available on the internet for data users and researchers throughout the world (www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/).
Abbreviations
- EtO:
-
Ethylene oxide
- HbEtO:
-
Hemoglobin adducts of ethylene oxide
- LE8:
-
Life’s Essential 8
- CVH:
-
Cardiovascular health
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- LS7:
-
Life’s Simple 7
- NHANES:
-
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- non-HDL:
-
Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- NCHS:
-
National Center for Health Statistics
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DASH:
-
Dietary approaches to stop hypertension
- HPLC-MS/MS:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- ICD-10:
-
International Classification of Diseases
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- RCS:
-
Restricted cubic spline
References
Adedara IA, Farombi EO (2010) Induction of oxidative damage in the testes and spermatozoa and hematotoxicity in rats exposed to multiple doses of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether. Hum Exp Toxicol 29:801–812
Brockmann WG, Kostoryz EL, Eick JD (2006) Correlation of apoptotic potential of simple oxiranes with cytotoxicity. Toxicol In Vitro 20:729–735
Cheang I, Zhu X, Zhu Q, Li M, Liao S, Zuo Z, Yao W, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Li X (2022) Inverse association between blood ethylene oxide levels and obesity in the general population: NHANES 2013-2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13:926971
Chen K, Thomas SR, Keaney JF Jr (2003) Beyond LDL oxidation: ROS in vascular signal transduction. Free Radic Biol Med 35:117–132
Dehghani S, Vali M, Jafarian A, Oskoei V, Maleki Z, Hoseini M (2022) Ecological study of ambient air pollution exposure and mortality of cardiovascular diseases in elderly. Sci Rep 12:21295
Dehghani S, Yousefi S, Oskoei V, Tazik M, Moradi MS, Shaabani M, Vali M (2023) Ecological study on household air pollution exposure and prevalent chronic disease in the elderly. Sci Rep 13:11763
Ferrucci L, Fabbri E (2018) Inflammageing: chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat Rev Cardiol 15:505–522
Gardner MJ, Coggon D, Pannett B, Harris EC (1989) Workers exposed to ethylene oxide: a follow up study. Br J Ind Med 46:860–865
Guo J, Wan Z, Cui G, Pan A, Liu G (2021) Association of exposure to ethylene oxide with risk of diabetes mellitus: results from NHANES 2013-2016. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:68551–68559
Huang Q, Li S, Wan J, Nan W, He B (2023) Association between ethylene oxide exposure and prevalence of COPD: evidence from NHANES 2013-2016. Sci Total Environ 885:163871
Isiozor NM, Kunutsor SK, Voutilainen A, Laukkanen JA (2023) Life’s Essential 8 and the risk of cardiovascular disease death and all-cause mortality in Finnish men. Eur J Prev Cardiol 30:658–667
Jain RB (2020) Associations between observed concentrations of ethylene oxide in whole blood and smoking, exposure to environmental tobacco smoke, and cancers including breast cancer: data for US children, adolescents, and adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:20912–20919
Jinot J, Fritz JM, Vulimiri SV, Keshava N (2018) Carcinogenicity of ethylene oxide: key findings and scientific issues. Toxicol Mech Methods 28:386–396
Jones RR, Fisher JA, Medgyesi DN, Buller ID, Liao LM, Gierach G, Ward MH, Silverman DT (2023) Ethylene oxide emissions and incident breast cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a US cohort. J Natl Cancer Inst 115:405–412
Kaneko H, Suzuki Y, Ueno K, Okada A, Fujiu K, Matsuoka S, Michihata N, Jo T, Takeda N, Morita H, Kamiya K, Node K, Yasunaga H, Komuro I (2022) Association of Life’s Simple 7 with incident cardiovascular disease in 53 974 patients with cancer. Eur J Prev Cardiol 29:2324–2332
Kirman CR, Li AA, Sheehan PJ, Bus JS, Lewis RC, Hays SM (2021) Ethylene oxide review: characterization of total exposure via endogenous and exogenous pathways and their implications to risk assessment and risk management. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 24:1–29
Kostoryz EL, Wetmore LA, Brockmann WG, Yourtee DM, Eick JD (2004) Genotoxicity assessment of oxirane-based dental monomers in mammalian cells. J Biomed Mater Res A 68:660–667
Kostoryz EL, Zhu Q, Zhao H, Glaros AG, Eick JD (2007) Assessment of cytotoxicity and DNA damage exhibited by siloranes and oxiranes in cultured mammalian cells. Mutat Res 634:156–162
Kuiper HC, Miranda CL, Sowell JD, Stevens JF (2008) Mercapturic acid conjugates of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and 4-oxo-2-nonenal metabolites are in vivo markers of oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 283:17131–17138
Li Z, Shi P, Chen Z, Zhang W, Lin S, Zheng T, Li M, Fan L (2023) The association between ethylene oxide exposure and asthma risk: a population-based study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:24154–24167
Lloyd-Jones DM, Allen NB, Anderson CAM, Black T, Brewer LC, Foraker RE, Grandner MA, Lavretsky H, Perak AM, Sharma G, Rosamond W (2022) Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct of Cardiovascular Health: a Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association’. Circulation 146:e18–e43
Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, Greenlund K, Daniels S, Nichol G, Tomaselli GF, Arnett DK, Fonarow GC, Ho PM, Lauer MS, Masoudi FA, Robertson RM, Roger V, Schwamm LH, Sorlie P et al (2010) Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association’s strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 121:586–613
Lynch DW, Lewis TR, Moorman WJ, Burg JR, Groth DH, Khan A, Ackerman LJ, Cockrell BY (1984) Carcinogenic and toxicologic effects of inhaled ethylene oxide and propylene oxide in F344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 76:69–84
Lynch HN, Kozal JS, Russell AJ, Thompson WJ, Divis HR, Freid RD, Calabrese EJ, Mundt KA (2022) Systematic review of the scientific evidence on ethylene oxide as a human carcinogen. Chem Biol Interact 364:110031
Ma H, Wang X, Xue Q, Li X, Liang Z, Heianza Y, Franco OH, Qi L (2023) Cardiovascular Health and Life Expectancy Among Adults in the United States. Circulation 147:1137–1146
Marsh GM, Keeton KA, Riordan AS, Best EA, Benson SM (2019) Ethylene oxide and risk of lympho-hematopoietic cancer and breast cancer: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 92:919–939
Rasool M, Malik A, Ashraf MAB, Mubbin R, Ayyaz U, Waquar S, Asif M, Umar M, Hua GS, Iqbal Z, Alam H, Achakzai NM (2021) Phytochemical analysis and protective effects of Vaccinium macrocarpon (cranberry) in rats (Rattus norvegicus) following ethylene oxide-induced oxidative insult. Bioengineered 12:4593–4604
Shintani H (2017) Ethylene oxide gas sterilization of medical devices. Biocontrol Sci 22:1–16
Song W, Hu H, Ni J, Zhang H, Zhang H, Yang G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Peng B (2023) The relationship between ethylene oxide levels in hemoglobin and the prevalence of kidney stones in US adults: an exposure-response analysis from NHANES 2013-2016. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:26357–26366
Steenland K, Stayner L, Deddens J (2004) Mortality analyses in a cohort of 18 235 ethylene oxide exposed workers: follow up extended from 1987 to 1998. Occup Environ Med 61:2–7
Steenland K, Whelan E, Deddens J, Stayner L, Ward E (2003) Ethylene oxide and breast cancer incidence in a cohort study of 7576 women (United States). Cancer Causes Control 14:531–539
Sun J, Li Y, Zhao M, Yu X, Zhang C, Magnussen CG, Xi B (2023) Association of the American Heart Association’s new “Life’s Essential 8” with all-cause and cardiovascular disease-specific mortality: prospective cohort study. BMC Med 21:116
Tangvarasittichai S (2015) Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 6:456–480
Tzeng IS (2021) To handle the inflation of odds ratios in a retrospective study with a profile penalized log-likelihood approach. J Clin Lab Anal 35:e23849
Wang X, Ma H, Li X, Heianza Y, Manson JE, Franco OH, Qi L (2023) Association of cardiovascular health with life expectancy free of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and dementia in UK adults. JAMA Intern Med 183:340–349
Weiderpass E, Meo M, Vainio H (2011) Risk factors for breast cancer, including occupational exposures. Saf Health Work 2:1–8
Wu N, Cao W, Wang Y, Liu X (2022) Association between blood ethylene oxide levels and the prevalence of hypertension. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:76937–76943
Xia X, Chen S, Tian X, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang P, Wu S, Lin L, Wang A (2023) Association of cardiovascular health assessed by the new Life’s Essential 8 metrics with years lived without cardiovascular disease. J Am Heart Assoc 12:e029241
Xie R, Liu X, Wu H, Liu M, Zhang Y (2023) Associations between systemic immune-inflammation index and abdominal aortic calcification: results of a nationwide survey. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 33:1437–1443
Xie R, Zhang Y (2023) Associations between dietary flavonoid intake with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis quantified by VCTE: evidence from NHANES and FNDDS. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 33:1179–1189
Xing A, Tian X, Wang Y, Chen S, Xu Q, Xia X, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang A, Wu S (2023) Life’s Essential 8’ cardiovascular health with premature cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in young adults: the Kailuan prospective cohort study. Eur J Prev Cardiol 30:593–600
Zeng G, Zhang Q, Wang X, Wu KH (2021) Association between blood ethylene oxide levels and the risk of cardiovascular diseases in the general population. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:64921–64928
Zhang J, Chen G, Habudele Z, Wang X, Cai M, Li H, Gao Y, Lip GYH, Lin H (2023) Relation of Life’s Essential 8 to the genetic predisposition for cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality: results from a national prospective cohort. Eur J Prev Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjpc/zwad179/7179827
Zhu X, Kong X, Chen M, Shi S, Cheang I, Zhu Q, Lu X, Yue X, Tang Y, Liao S, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Yao W, Li X (2022) Blood ethylene oxide, systemic inflammation, and serum lipid profiles: results from NHANES 2013-2016. Chemosphere 299:134336
Acknowledgements
Graphical abstract partially created by BioRender (https://biorender.com/).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing manuscript: Ruijie Xie, Linjian Liu, Changxiong Liu, and Ya Zhang; data extraction and statistical analysis: Ruijie Xie, Linjian Liu and Songlin Xie; reviewing and editing: Linjian Liu, Xiongjie Huang, and Ya Zhang. conceptualization, project administration, and supervision: Ruijie Xie and Ya Zhang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All human subjects involved in this study were treated by the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, and the study was approved by the Research Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Consent for publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ruijie Xie and Linjian Liu are the co-first authors of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, R., Liu, L., Liu, C. et al. Associations of ethylene oxide exposure and “Life’s Essential 8”. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 121150–121160 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30741-z