Abstract
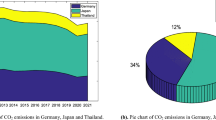
Objective and accurate prediction of carbon emissions can provide a basis for the country to achieve carbon emission reduction targets and can also comprehensively and scientifically predict the peak of carbon emissions effectively, providing valuable reference information for the implementation of specific emission reduction policies and measures at each stage. In this paper, a novel fractional-order grey multivariate forecasting model is established to analyze and forecast China’s carbon emissions, reflecting the principle of new information priority. The model adds fractional-order cumulative sequences to the traditional integer-order cumulative sequences, uses the Gamma function to represent the fractional-order sequences and the time-response equation, and uses the particle swarm algorithm to find the optimal order of the cumulative sequence. Finally, the modeling steps of the model are given. Then, the new model is analyzed for its effectiveness from three different perspectives using 21 years of Chinese carbon emission data. The results of the first and second cases show that the newly established particle swarm optimization fractional-order model is superior to the grey multivariate comparison model. The results of the third case show that the new model is superior to the three classical grey prediction comparison models. It has stable characteristics for both simulation and prediction and also shows high accuracy, and all three cases fully illustrate the effectiveness of the new model. Finally, this new model is applied to forecast China’s carbon emissions from 2022–2026, analyze the forecast results, and make relevant recommendations.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Alkheder S, Almusalam A, Kalogirou SA et al (2022) Forecasting of carbon dioxide emissions from power plants in Kuwait using United States Environmental Protection Agency, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, and machine learning methods. RenewEnerg 191:819–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.04.023
Chu JJ, Xiao XP (2023) Benefits evaluation of the Northeast Passage based on grey relational degree of discrete Z-numbers. Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.02.085
Deng JL (1982) Control problems of grey systems. Syst Control Lett 1:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6911(82)80025-X
Ding S, Xu N, Ye J et al (2020) Estimating Chinese energy-related CO2 emissions by employing a novel discrete grey prediction model. J Clean Prod 259:120793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120793
Duan HM, Liu YM (2021) Research on a grey prediction model based on energy prices and its applications. Comput Ind Eng 162:107729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107729
Duan HM, Luo XL (2022) A novel multivariable grey prediction model and its application in forecasting coal consumption. ISA Trans 120:110–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2021.03.024
Duan HM, Pang XY (2023) A novel grey prediction model with system structure based on energy background: a case study of Chinese electricity. J Clean Prod 390:136099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136099
Duan HM, Wang G (2023) Partial differential grey model based on control matrix and its application in short-term traffic flow prediction. Appl Math Model 116:763–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2022.12.012
Eberhart RC, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. Proc Sixth Int Symp Micromach Human Sci 95:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/mhs.1995.494215
Gao MY, Yang HL, Xiao QZ et al (2021) A novel fractional grey Riccati model for carbon emission prediction. J Clean Prod 282:124471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124471
Gao MY, Yang HL, Xiao QZ et al (2022) A novel method for carbon emission forecasting based on Gompertz’s law and fractional grey model: evidence from American industrial sector. Renew Energ 181:803–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.09.07
He J, Mao SH, Kang YX (2023) Augmented fractional accumulation grey model and its application: class ratio and restore error perspectives. Math Comput Simul 209:220–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2023.02.008
Hien NsLH, Kor AL (2022) Analysis and prediction model of fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of light-duty vehicles. Appl Sci 12:803–831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020803
Hou W, Li RYM, Sittihi K (2022) Management Optimization of electricity system with sustainability enhancement. Sustainability 14:6650. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116650
Jeong YS, Cho S (2020) Post-2020 greenhouse gas emission projection in building sector. J Archit Inst Korea 36(10):117–125. https://doi.org/10.5659/JAIK.2020.36.10.639.117
Kumar S, Kumar H, Bhatia M (2022) Linking carbon emission and economic growth: case from developing economies of the Asian region. Environ Qual Manage 31(4):449–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.21830
Li H, Wu ZX, Yuan X et al (2022) The research on modeling and application of dynamic grey forecasting model based on energy price-energy consumption-economic growth. Energy 257:124801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124801
Li RYM, Wang QQ, Zeng LY et al (2023) A study on public perceptions of carbon neutrality in China: has the idea of ESG been encompassed. Front Env Sci-switz 10:949959. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.949959
Liu C, Lao TF, Wu WZ et al (2021) Application of optimized fractional grey model-based variable background value to predict electricity consumption. Fractals 29:2150038. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X21500389
Liu BL, Wang JX, Li RYM et al (2022) Achieving carbon neutrality-the role of heterogeneous environmental regulations on urban green innovation. Front Ecol Evol 10:923354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2022.923354
Lu HF, Ma X, Huang K et al (2020) Carbon trading volume and price forecasting in China using multiple machine learning models. J Clean Prod 249:119386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119386
Ma X, Wu WQ, Zeng B et al (2020) The conformable fractional grey system model. ISA Trans 96:255–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2019.07.009
Ofosu-Adarkwa J, Xie NM, Javed SA (2020) Forecasting CO2 emissions of China’s cement industry using a hybrid Verhulst-GM(1, N) model and emissions’ technical conversion. Renew Sust Energ Rev 130:109945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109945
Rao CJ, Zhang Y, Wen JH et al (2023) Energy demand forecasting in China: a support vector regression-compositional data second exponential smoothing model. Energy 263:125955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.125955
Ren F, Long D (2021) Carbon emission forecasting and scenario analysis in Guangdong Province based on optimized Fast Learning Network. J Cleaner Prod 317(6):128408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128408
Shaheen A, Sheng JY, Arshad S et al (2020) Forecasting the determinants of environmental degradation: a gray modeling approach. Energ Source Part A 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1827090
Shan S, Ahmad M, Tan ZX et al (2021) The role of energy prices and non-linear fiscal decentralization in limiting carbon emissions: tracking environmental sustainability. Energy 234:121243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121243
Sun Y, Liu S, Li L (2022) Grey correlation analysis of transportation carbon emissionsunder the background of carbon peak and carbon neutrality. Energies 15(9):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093064
Tu LP, Chen Y (2021) An unequal adjacent grey forecasting air pollution urban model. Appl Math Model 99:260–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.06.025
Vijayakumar V, Jenn A, Fulton L (2021) Low carbon scenario analysis of a hydrogen-based energy transition for on-road transportation in California. Energies 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14217163
Wang ZX, Wang ZW, Li Q (2020) Forecasting the industrial solar energy consumption using a novel seasonal GM(1, 1) model with dynamic seasonal adjustment factors. Energy 200:117460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117460
Wen JH, Hong LJ, Dai M et al (2023) A stochastic model for stop-and-go phenomenon in traffic oscillation: on the prospective of macro and micro traffic flow. Appl Math Comput 440:127637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2022.127637
Wu LF, Liu SF, Yao LY et al (2013) Grey system model with the fractional order accumulation. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18:1775–1785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2012.11.017
Wu WQ, Ma X, Zhang YY et al (2020) A novel conformable fractional non-homogeneous grey model for forecasting carbon dioxide emissions of BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 707:135447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135447
Xie DR, Li XW, Duan HM (2023) A novel nonlinear grey multivariate prediction model based on energy structure and its application to energy consumption. Chaos Soliton Fract 173:113767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113767
Yan C, Wu LF, Liu LY et al (2020) Fractional Hausdorff grey model and its properties. Chaos Soliton Fract 138:109915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109915
Yao XT, Mao SH (2023) Electric supply and demand forecasting using seasonal grey model based on PSO-SVR. Grey Syst 13:141–171. https://doi.org/10.1108/GS-10-2021-0159
Zeng B, Luo CM, Liu SF et al (2016) A novel multi-variable grey forecasting model and its application in forecasting the amount of motor vehicles in Beijing. Comput Ind Eng 101:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.10.009
Zeng B, Ma X, Zhou M (2020) A new-structure grey Verhulst model for China’s tight gas production forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 96:106600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106600
Zeng B, Li H, Mao CW et al (2023) Modeling, prediction and analysis of new energy vehicle sales in China using a variable-structure grey model. Expert Syst Appl 213:118879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118879
Zhang YH, Li JX, Che JP (2021) Grey prediction model based on carbon emission optimization. Clausius Sci Press (3). https://doi.org/10.23977/EREJ.2021.050302
Zhao YJ, Liu Q, Duan YY et al (2022) Hydrogen energy deployment in decarbonizing transportation sector using multi-supply-demand integrated scenario analysis with nonlinear programming-a Shanxi case study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:19338–19352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.04.102
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editors and the reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work is supported by the Basic Research Project of Science and Technology Plan of Guizhou of China under Grants Qian Ke He Foundation ZK [2023] General 022 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62241301,72171031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was reviewed and approved for publication by all authors. Hui Li performed the experiments. Zixuan Wu analyzed the data. Hui Li and Huiming Duan wrote the paper. Shuqu Qian, Hui Li, and Huiming Duan reviewed and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The manuscript was reviewed and ethically approved for publication by all authors.
Consent to participate
The manuscript was reviewed and consented to participate by all authors.
Consent for publication
The manuscript was reviewed and consented to be published by all authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wu, Z., Qian, S. et al. A novel fractional-order grey prediction model: a case study of Chinese carbon emissions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110377–110394 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29919-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29919-2