Abstract
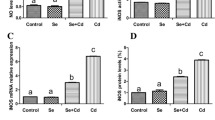
Cadmium (Cd) is a widely distributed environmental contaminant that is highly toxic to animals and humans. However, detailed reports on Cd-induced programmed necrosis have not been seen in chicken testicular Leydig cells. Selenium (Se) is a trace element in the human body that has cytoprotective effects in a variety of pathological damages caused by heavy metals. This study investigated the potential mechanisms of Cd-induced programmed cell necrosis and the antagonistic effect of Se on Cd toxicity. Chicken testis Leydig cells were divided into six groups, namely, control, Se (5 µmol/L Na2SeO3), Cd (20 µmol/L CdCl2), Se + Cd (5 µmol/L Na2SeO3 and 20 µmol/L CdCl2), 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) + Cd (10 mmol/L 4-phenylbutyric acid and 20 µmol/L CdCl2), and Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) + Cd (60 µmol/L Necrostatin-1 and 20 µmol/L CdCl2). The results showed that Cd exposure decreased the activity of CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD and the concentration of GSH, and increased the concentration of MDA and the content of ROS. Relative mRNA and protein expression of GRP78, PERK, ATF6, IRE1, CHOP, and JNK increased in the Cd group, and mRNA and protein expression of TNF-α, TNFR1, RIP1, RIP3, MLKL, and PARP1 significantly increased in the Cd group, while Caspase-8 mRNA and protein expression significantly decreased. The abnormal expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins was significantly reduced by 4-PBA pretreatment; the increased expression of TNF-α, TNFR1, RIP1, RIP3, MLKL, and PARP1 caused by Cd toxicity was alleviated; and the expression of caspase-8 was upregulated. Conversely, the increased mRNA and protein expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress marker genes (GRP78, ATF6, PERK, IRE1, CHOP, JNK) caused by Cd was not affected after pretreatment with Nec-1. We also found that these Cd-induced changes were significantly attenuated in the Se + Cd group. We clarified that Cd can cause programmed necrosis of chicken testicular Leydig cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress, and Se can antagonize Cd-induced programmed necrosis of chicken testicular Leydig cells.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adamkovicova M, Toman R, Martiniakova M, Omelka R, Babosova R, Krajcovicova V, Grosskopf B, Massanyi P (2016) Sperm motility and morphology changes in rats exposed to cadmium and diazinon. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 14:42
Agir MS, Eraslan G (2019) The effect of diosmin against liver damage caused by cadmium in rats. J Food Biochem 43:e12966
Branca JJV, C Fiorillo, D Carrino, F Paternostro, N Taddei, M Gulisano, A Pacini, M Becatti (2020) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress: focus on the central nervous system. Antioxidants (Basel) 9
Cao L, Mu W (2021) Necrostatin-1 and necroptosis inhibition: pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Res 163:105297
Chen H, Li P, Shen Z, Wang J, Diao L (2021) Protective effects of selenium yeast against cadmium-induced necroptosis through miR-26a-5p/PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in chicken kidney. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 220:112387
Chen X, Bi M, Yang J, Cai J, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Liu Q, Shi G, Zhang Z (2022) Cadmium exposure triggers oxidative stress, necroptosis, Th1/Th2 imbalance and promotes inflammation through the TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB pathway in swine small intestine. J Hazard Mater 421:126704
Dong Y, Zhao J, Zhu Q, Liu H, Wang J, Lu W (2020) Melatonin inhibits the apoptosis of rooster Leydig cells by suppressing oxidative stress via AKT-Nrf2 pathway activation. Free Radical Biol Med 160:1–12
Dong A, Huo J, Yan J, Dong A (2021) Oxidative stress in liver of turtle Mauremys reevesii caused by cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:6405–6410
Etemadi T, Momeni HR, Darbandi N, Abnosi MH (2022) Silymarin modulates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in human spermatozoa. Andrologia 54:e14475
Fedala A, Adjroud O, Abid-Essefi S, Timoumi R (2021) Protective effects of selenium and zinc against potassium dichromate-induced thyroid disruption, oxidative stress, and DNA damage in pregnant Wistar rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:22563–22576
Feyen D, Gaetani R, Liu J, Noort W, Martens A, den Ouden K, Doevendans PA, Sluijter JP (2013) Increasing short-term cardiomyocyte progenitor cell (CMPC) survival by necrostatin-1 did not further preserve cardiac function. Cardiovasc Res 99:83–91
Gong ZG, Zhao Y, Wang ZY, Fan RF, Liu ZP, Wang L (2022) Epigenetic regulator BRD4 is involved in cadmium-induced acute kidney injury via contributing to lysosomal dysfunction, autophagy blockade and oxidative stress. J Hazard Mater 423:127110
Ham J, Lim W, Whang KY, Song G (2020) Butylated hydroxytoluene induces dysregulation of calcium homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum stress resulting in mouse Leydig cell death. Environ Pollut 256:113421
He Z et al (2022) Cadmium induces liver dysfunction and ferroptosis through the endoplasmic stress-ferritinophagy axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 245:114123
Huang H, Wang M, Hou L, Lin X, Pan S, Zheng P, Zhao Q (2021) A potential mechanism associated with lead-induced spermatogonia and Leydig cell toxicity and mitigative effect of selenium in chicken. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 209:111671
Kaur B, Bhat A, Chakraborty R, Adlakha K, Sengupta S, Roy S, Chakraborty K (2018) Proteomic profile of 4-PBA treated human neuronal cells during ER stress. Molecular Omics 14:53–63
Khoury MK, Gupta K, Franco SR, Liu B (2020) Necroptosis in the pathophysiology of disease. Am J Pathol 190:272–285
Kim HJ, Jeong JS, Kim SR, Park SY, Chae HJ, Lee YC (2013) Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation through modulation of NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway. Sci Rep 3:1142
Kim EH, Wong SW, Martinez J (2019) Programmed necrosis and disease: we interrupt your regular programming to bring you necroinflammation. Cell Death Differ 26:25–40
Kishino A, K Hayashi, M Maeda, T Jike, C Hidai, Y Nomura, T Oshima (2019) Caspase-8 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced necroptosis independent of the apoptosis pathway in auditory cells, Int J Mol Sci 20
Lee HY, Lee GH, Kim HR, Lee YC, Chae HJ (2020) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-delta controls endoplasmic reticulum membrane fluidity and permeability in fungus-induced allergic inflammation in mice. Br J Pharmacol 177:1556–1567
Li M, Zhang Y, Li S (2020) Effects of selenium deficiency on testis development and autophagy in chicks. Ital J Anim Sci 19:753–761
Lian, Cai-Yu, Bing-Xin Chu, Wei-Hao Xia, Zhen-Yong Wang, Rui-Feng Fan, Lin Wang (2022) Persistent activation of Nrf2 in a p62-dependent non-canonical manner aggravates lead-induced kidney injury by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting autophagy. J Adv Res
Liu X, Tian G, Jiang D, Zhang C, Kong L (2016) Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:17941–17952
Liu H et al (2021) Exposure to copper oxide nanoparticles triggers oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-stress induced toxicology and apoptosis in male rat liver and BRL-3A cell. J Hazard Mater 401:123349
Liu, Jing-Bo, Zi-Fa Li, Lu Lu, Zhen-Yong Wang, Lin Wang (2022) Glyphosate damages blood-testis barrier via NOX1-triggered oxidative stress in rats: long-term exposure as a potential risk for male reproductive health. Environ Int 159
Luo B, Lin Y, Jiang S, Huang L, Yao H, Zhuang Q, Zhao R, Liu H, He C, Lin Z (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2alpha-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney. Cell Death Dis 7:e2251
Mamdouh S, Mohamed AS, Mohamed HA, Fahmy WS (2022a) The effect of zinc concentration on physiological, immunological, and histological changes in crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) as bio-indicator for environment quality criteria. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:375–384
Mamdouh S, Mohamed AS, Mohamed HA, Fahmy WS (2022b) Zn contamination stimulate agonistic behavior and oxidative stress of crayfishes (Procambarus clarkii). J Trace Elem Med Biol 69:126895
Mandal R, Barron JC, Kostova I, Becker S, Strebhardt K (2020) Caspase-8: the double-edged sword. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1873:188357
Oghbaei H, Hosseini L, Farajdokht F, Rahigh Aghsan S, Majdi A, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Sandoghchian Shotorbani S, Mahmoudi J (2021) Heat stress aggravates oxidative stress, apoptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the cerebellum of male C57 mice. Mol Biol Rep 48:5881–5887
Ohba KI (2018) [Transport and toxicity of cadmium], Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. Jpn J Hyg 73:269–274
Ojekunle, Opeyemi Oluwadamilola, Ayodotun Sodipe (2020) Antioxidative effect of selenium in cadmium-exposed Tardigrade (H. exemplaris). Water Air Soil Pollution 231
Owumi SE, Aliyu-Banjo NO, Odunola OA (2020) Selenium attenuates diclofenac-induced testicular and epididymal toxicity in rats. Andrologia 52:e13669
Pao HP, Liao WI, Tang SE, Wu SY, Huang KL, Chu SJ (2021) Suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress by 4-PBA protects against hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury via up-regulating claudin-4 expression. Front Immunol 12:674316
Rafiee Z, Rezaee-Tazangi F, Zeidooni L, Alidadi H, Khorsandi L (2021) Protective effects of selenium on Bisphenol A-induced oxidative stress in mouse testicular mitochondria and sperm motility. JBRA Assist Reprod 25:459–465
Reddy SS, Shruthi K, Joy D, Reddy GB (2019) 4-PBA prevents diabetic muscle atrophy in rats by modulating ER stress response and ubiquitin-proteasome system. Chem Biol Interact 306:70–77
Ren X, Wang S, Zhang C, Hu X, Zhou L, Li Y, Xu L (2020) Selenium ameliorates cadmium-induced mouse Leydig TM3 cell apoptosis via inhibiting the ROS/JNK /c-jun signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 192:110266
Riaz M, Kamran M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Parveen A, Malik Z, Wang X (2021) Cadmium uptake and translocation: selenium and silicon roles in Cd detoxification for the production of low Cd crops: a critical review. Chemosphere 273:129690
Sepand MR, Aliomrani M, Hasani-Nourian Y, Khalhori MR, Farzaei MH, Sanadgol N (2020) Mechanisms and pathogenesis underlying environmental chemical-induced necroptosis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:37488–37501
Shan B, Pan H, Najafov A, Yuan J (2018) Necroptosis in development and diseases. Genes Dev 32:327–340
Shen B, Mei M, Pu Y, Zhang H, Liu H, Tang M, Pan Q, He Y, Wu X, Zhao H (2019) Necrostatin-1 attenuates renal ischemia and reperfusion injury via meditation of HIF-1alpha/mir-26a/TRPC6/PARP1 signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 17:701–713
Tian RD et al (2020) Phosphorylation of eIF2alpha mitigates endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatocyte necroptosis in acute liver injury. Ann Hepatol 19:79–87
Wang J, Zhang Y, Fang Z, Sun L, Wang Y, Liu Y, Xu D, Nie F, Gooneratne R (2019a) Oleic acid alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative damage in rat by its radicals scavenging activity. Biol Trace Elem Res 190:95–100
Wang S, Ren X, Hu X, Zhou L, Zhang C, Zhang M (2019b) Cadmium-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial oxidative stress and the JNK signaling pathway in TM3 cells, a model of mouse Leydig cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 368:37–48
Wang M, Wang XF, Li YM, Chen N, Fan Y, Huang WK, Hu SF, Rao M, Zhang YZ, Su P (2020) Cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis regulates testicular injury/recovery induced by cadmium via PI3K with mTOR-independent pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:46
Wu Z, Wang F, Hu L, Zhang J, Chen D, Zhao S (2021) Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related autophagy attenuates MCLR-induced apoptosis in zebrafish testis and mouse TM4 cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 221:112438
Xin C, Guangliang S, Qing Z, Qingqing L, Hang Y, Yiming Z, Shu L (2020) Astilbin protects chicken peripheral blood lymphocytes from cadmium-induced necroptosis via oxidative stress and the PI3K/Akt pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 190:110064
Xiong Y, Q Yin, E Jin, H Chen, S He (2020) Selenium attenuates chronic heat stress-induced apoptosis via the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse granulosa cells. Molecules 25
Yi S, Shi W, Zuo M, Wang S, Ma R, Bi H, Cong B, Li Y (2021) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Anal Cell Pathol (amst) 2021:5565671
Yu A, Ji Y, Ma G, Xu J, Hu Q (2023) Identification and preparation of selenium-containing peptides from selenium-enriched Pleurotus eryngii and their protective effect on lead-induced oxidative damage in NCTC1469 hepatocytes. J Sci Food Agric 103:4522–4534
Zeng L, Zhou J, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang M, Su P (2021) Cadmium attenuates testosterone synthesis by promoting ferroptosis and blocking autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Free Radical Biol Med 176:176–188
Zhang S, Che L, He C, Huang J, Guo N, Shi J, Lin Y, Lin Z (2019) Drp1 and RB interaction to mediate mitochondria-dependent necroptosis induced by cadmium in hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis 10:523
Zhang C, Ge J, Lv M, Zhang Q, Talukder M, Li JL (2020a) Selenium prevent cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity through modulation of endoplasmic reticulum-resident selenoproteins and attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Environ Pollut 260:113873
Zhang J, Hao X, Xu S (2020b) Selenium prevents lead-induced necroptosis by restoring antioxidant functions and blocking MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in chicken lymphocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 198:644–653
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zheng Z, Tang W, Song M, Wang J, Wang K (2021) ‘Lentinan inhibited colon cancer growth by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagic cell death and apoptosis. Carbohyd Polym 267:118154
Zhao C et al (2021a) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy activation is involved in cadmium-induced ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. Free Radical Biol Med 175:236–248
Zhao X, Wang S, Li X, Liu H, Xu S (2021b) Cadmium exposure induces TNF-alpha-mediated necroptosis via FPR2/TGF-beta/NF-kappaB pathway in swine myocardium. Toxicology 453:152733
Zhirong Z, Qiaojian Z, Chunjing X, Shengchen W, Jiahe L, Zhaoyi L, Shu L (2021) Methionine selenium antagonizes LPS-induced necroptosis in the chicken liver via the miR-155/TRAF3/MAPK axis. J Cell Physiol 236:4024–4035
Zhong W, Wang X, Rao Z, Pan X, Sun Y, Jiang T, Wang P, Zhou H, Wang X (2020) Aging aggravated liver ischemia and reperfusion injury by promoting hepatocyte necroptosis in an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent manner. Ann Transl Med 8:869
Zhou T, Huang WK, Xu QY, Zhou X, Shao LQ, Song B (2020) Nec-1 attenuates inflammation and cytotoxicity induced by high glucose on THP-1 derived macrophages through RIP1’. Arch Oral Biol 118:104858
Funding
This research was supported by the Heilongjiang Province on Natural Fund Project of China (Grant No. LH2019C026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lulu Hou designed and conducted the experiments and wrote the article. Size Wang, Yueyue Wang, and Min Wang conducted the experiments and wrote the article. Zilin Cui contributed to the conduction of the experiments. He Huang designed the experiments and wrote and revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures used in this experiment were approved by the Northeast Agricultural University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee under the approved protocol number SRM-06.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. They agreed with the publication and consented to submit. They obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the Northeast Agricultural University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, L., Wang, S., Wang, Y. et al. Antagonistic effect of selenium on programmed necrosis of testicular Leydig cells caused by cadmium through endoplasmic reticulum stress in chicken. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 112517–112535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29803-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29803-z