Abstract
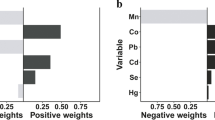
Metals exposure has gained increasing attention in the hypertension prevention. However, previous studies have focused on the impacts of single or separated metals on hypertension, and the critical metals contributing to the prevalence of hypertension are still under discussion. We collected data from 5092 participants across three consecutive National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) circles (2011–2016). Weighted logistic regression, weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression, quantile-based g-computation (QGC), and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) analyses were conducted to evaluate the combined and individual effects of 15 urinary metals, as well as to identify the critical metals on the development of hypertension. In our study, the weighted prevalence of hypertension was 37.9%, and the average age was 47.42 years. Manganese, uranium and tin were found as the independent risk factors for hypertension, while barium, lead, and thallium were found to have protective effects against hypertension. Lead, barium, tungsten, uranium, and tin were determined as critical elements for the prediction of hypertension. No significant interaction relationship was detected between multiple metals. There might be potential positive combined effects of urinary metal mixture on hypertension. Tungsten, uranium, and tin were positively associated with hypertension while lead and barium were negatively associated with hypertension. The underlying mechanisms of urinary metal exposure on the risk of hypertension deserve further investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm
References
Abadin H, Ashizawa A, Stevens Y-W, Llados F, Diamond G, Sage G, Citra M, Quinones A, Bosch SJ, Swarts SG (2007) Toxicological profile for lead, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) toxicological profiles. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US), Atlanta, GA
Ansoborlo E, Lebaron-Jacobs L, Prat O (2015) Uranium in drinking-water: a unique case of guideline value increases and discrepancies between chemical and radiochemical guidelines. Environ Int 77:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.12.011
Barr DB, Wilder LC, Caudill SP, Gonzalez AJ, Needham LL, Pirkle JL (2005) Urinary Creatinine Concentrations in the U.S. Population: Implications for Urinary Biologic Monitoring Measurements. Environ Health Perspect 113:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7337
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus Henn B, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Godleski JJ, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16:493–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxu058
Bolt AM, Mann KK (2016) Tungsten: an Emerging Toxicant, Alone or in Combination. Curr Environ Health Rep 3:405–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-016-0106-z
Buser MC, Ingber SZ, Raines N, Fowler DA, Scinicariello F (2016) Urinary and Blood Cadmium and Lead and Kidney Function: NHANES 2007–2012. Int J Hyg Environ Health 219:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2016.01.005
Carrico C, Gennings C, Wheeler DC, Factor-Litvak P (2015) Characterization of weighted quantile sum regression for highly correlated data in a risk analysis setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 20:100–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0180-3
Chen L, Sun Q, Peng S, Tan T, Mei G, Chen H, Zhao Y, Yao P, Tang Y (2022) Associations of blood and urinary metals with rheumatoid arthritis risk among adults in NHANES, 1999–2018. Chemosphere 289:133147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133147
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Roccella EJ, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee (2003) The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.19.2560
da Cunha Martins A, Carneiro MFH, Grotto D, Adeyemi JA, Barbosa F (2018) Arsenic, cadmium, and mercury-induced hypertension: mechanisms and epidemiological findings. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 21:61–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2018.1432025
Desai G, Niu Z, Luo W, Frndak S, Shaver AL, Kordas K (2021) Low-level exposure to lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium, and blood pressure among 8–17-year-old participants of the 2009–2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Res 197:111086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111086
Everson TM, Niedzwiecki MM, Toth D, Tellez-Plaza M, Liu H, Barr DB, Gribble MO (2021) Metal biomarker mixtures and blood pressure in the United States: cross-sectional findings from the 1999–2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Environ Health 20:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-021-00695-1
Fernández-Mariño AI, Porras-González C, González-Rodríguez P, Selent J, Pastor M, Ureña J, Castellano A, Valverde MA, Fernández-Fernández JM (2012) Tungstate activates BK channels in a β subunit- and Mg2+-dependent manner: relevance for arterial vasodilatation. Cardiovasc Res 95. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvs139
Fu Z, Xi S (2020) The effects of metals on human metabolism. Toxicol Mech Methods 30:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2019.1701594
GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators (2018) Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392:1923–1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6
Guo X, Li N, Wang H, Su W, Song Q, Liang Q, Liang M, Sun C, Li Y, Lowe S, Bentley R, Song EJ, Zhou Q, Ding X, Sun Y (2022) Combined exposure to multiple metals on cardiovascular disease in NHANES under five statistical models. Environ Res 215:114435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114435
Jenny-Burri J, Blanc A, Aubert R, Haldimann M, Zürcher U, Burnier M, Paccaud F, Bochud M, Dudler V (2020) Uranium exposure of the Swiss population based on 24-hour urinary excretion. Swiss Med Wkly 150:w20207. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2020.20207
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J (2005) Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 365:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17741-1
Keil AP, Buckley JP, O’Brien KM, Ferguson KK, Zhao S, White AJ (2020) A Quantile-Based g-Computation Approach to Addressing the Effects of Exposure Mixtures. Environ Health Perspect 128:47004. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP5838
Ma Y, Hu Q, Yang D, Zhao Y, Bai J, Mubarik S, Yu C (2022) Combined exposure to multiple metals on serum uric acid in NHANES under three statistical models. Chemosphere 301:134416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134416
MEC Laboratory Procedures Manual (n.d.) 683
Miao H, Liu Y, Tsai TC, Schwartz J, Ji JS (2020) Association Between Blood Lead Level and Uncontrolled Hypertension in the US Population (NHANES 1999–2016). J Am Heart Assoc 9:e015533. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.015533
Mills KT, Bundy JD, Kelly TN, Reed JE, Kearney PM, Reynolds K, Chen J, He J (2016) Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A Systematic Analysis of Population-Based Studies From 90 Countries. Circulation 134:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018912
Muntner P, Hardy ST, Fine LJ, Jaeger BC, Wozniak G, Levitan EB, Colantonio LD (2020a) Trends in Blood Pressure Control Among US Adults With Hypertension, 1999–2000 to 2017–2018. JAMA 324:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.14545
Muntner P, Hardy ST, Fine LJ, Jaeger BC, Wozniak G, Levitan EB, Colantonio LD (2020b) Trends in Blood Pressure Control Among US Adults With Hypertension, 1999–2000 to 2017–2018. JAMA 324:1190–1200. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.14545
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (2021) Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 398:957–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1
Paithankar JG, Saini S, Dwivedi S, Sharma A, Chowdhuri DK (2021) Metal associated health hazards: An interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 262:128350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128350
Peng M, Chen G, Kaplan GG, Lix LM, Drummond N, Lucyk K, Garies S, Lowerison M, Weibe S, Quan H (2016) Methods of defining hypertension in electronic medical records: validation against national survey data. J Public Health (oxf) 38:e392–e399. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdv155
Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D, Caulfield M (2015) Hypertension. The Lancet 386:801–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61468-9
Qu Y, Lv Y, Ji S, Ding L, Zhao F, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Hu X, Lu Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Zhang M, Yang Y, Li C, Zhang M, Li Z, Chen C, Zheng L, Gu H, Zhu H, Sun Q, Cai J, Song S, Ying B, Lin S, Cao Z, Liang D, Ji JS, Ryan PB, Barr DB, Shi X (2022) Effect of exposures to mixtures of lead and various metals on hypertension, pre-hypertension, and blood pressure: A cross-sectional study from the China National Human Biomonitoring. Environ Pollut 299:118864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118864
Rahman HH, Niemann D, Munson-McGee SH (2022) Environmental exposure to metals and the risk of high blood pressure: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2015–2016. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:531–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15726-0
Scinicariello F, Abadin HG, Murray HE (2011) Association of low-level blood lead and blood pressure in NHANES 1999–2006. Environ Res 111:1249–1257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2011.08.011
Shi P, Jing H, Xi S (2019) Urinary metal/metalloid levels in relation to hypertension among occupationally exposed workers. Chemosphere 234:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.099
Shiue I (2014) Higher urinary metal, arsenic, and phthalate concentrations in people with high blood pressure: US NHANES, 2009–2010. Blood Press 23:363–369. https://doi.org/10.3109/08037051.2014.925228
Shiue I, Hristova K (2014) Higher urinary metal, phthalate and arsenic concentrations accounted for 3–19% of the population attributable risk for high blood pressure: US NHANES, 2009–2012. Hypertens Res 37:1075–1081. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2014.121
Swayze S, Rotondi M, Kuk JL (2021) The Associations between Blood and Urinary Concentrations of Metal Metabolites, Obesity, Hypertension, Type 2 Diabetes, and Dyslipidemia among US Adults: NHANES 1999–2016. J Environ Public Health 2021:2358060. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2358060
Uranium | Toxicological Profile | ATSDR [WWW Document] (n.d) URL https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=440&tid=77 (accessed 10.30.22)
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, Initiative STROBE (2007) The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 370:1453–1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X
Wagner SE, Burch JB, Bottai M, Pinney SM, Puett R, Porter D, Vena JE, Hébert JR (2010) Uranium Exposures in a Community near a Uranium Processing Facility: Relationship with Hypertension and Hematologic Markers. Environ Res 110:786–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2010.09.004
Wang Q, Wei S (2018) Cadmium affects blood pressure and negatively interacts with obesity: Findings from NHANES 1999–2014. Sci Total Environ 643:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.105
Weaver VM, Kim N-S, Jaar BG, Schwartz BS, Parsons PJ, Steuerwald AJ, Todd AC, Simon D, Lee B-K (2011) Associations of low-level urine cadmium with kidney function in lead workers. Occup Environ Med 68:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2010.056077
Zeng H, Wang Q, Wang H, Guo L, Fang B, Zhang L, Wang X, Wang Q, Yang W, Wang M (2022) Exposure to barium and blood pressure in children and adolescents: results from the 2003–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:68476–68487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20507-4
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge all staffs and participants of NHANES survey. The authors acknowledge Dr. Jing Zhang and Dr. Ni Yin for their generous help on the statistical analyses.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China(81771233, 82171290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Songfeng Zhao: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Liqiaona Fan: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Yutong Wang: Conceptualization, Writing—review &editing.
Siyuan Dong: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Mingyang Han: Formal analysis, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Yongkai Qin: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing—review &editing.
Jigang Chen: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing-review &editing.
Aihua Liu: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing-review &editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All scholarly contributions by other authors, tables, graphs, data sources, etc. are cited properly. No unethical content is added.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Fan, L., Wang, Y. et al. Combined exposure to multiple metals on hypertension in NHANES under four statistical models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 92937–92949 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28902-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28902-1