Abstract
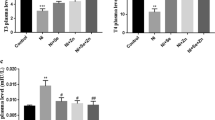
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) are one of the various nanoparticles that have been increasingly commonly used in vital sectors. This study was aimed at evaluating the effects of prenatal exposure to the chemical TiO2 NPs (CHTiO2 NPs) and green-synthesized TiO2 NPs (GTiO2 NPs) on immunological and oxidative status as well as lungs and spleen. Fifty pregnant female albino rats were divided into five groups of ten rats each: control, CHTiO2 NPs-treated groups orally received 100 and 300 mg/kg CHTiO2 NPs, and GTiO2 NPs-treated groups received 100 and 300 mg/kg GTiO2 NPs, respectively, daily for 14 days. The serum level of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, oxidative stress markers (MDA and NO), and antioxidant biomarkers (SOD and GSH-PX) were assayed. Spleen and lungs were collected from pregnant rats and fetuses for histopathological examinations. The results showed a significant increase in IL-6 levels in treated groups. In the CHTiO2 NPs-treated groups, there was a significant increase in MDA activity and a significant decrease in GSH-Px and SOD activities, revealing its oxidative effect, while GSH-Px and SOD activities significantly increased in the 300 GTiO2 NPs-treated group, confirming the antioxidant effect of green-synthesized TiO2 NPs. Histopathological findings of the spleen and lungs of the CHTiO2 NPs-treated group revealed severe congestion and thickening of the blood vessels, while those of the GTiO2 NPs-treated group revealed mild tissue alterations. It could be deduced that green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles have immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects on pregnant female albino rats and their fetuses, with an ameliorated impact on the spleen and lung compared to chemical titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data for this study is available inside the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- TiO2 NPs:
-
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles
- CHTiO2 NPs:
-
Chemical titanium dioxide nanoparticles
- GTiO2 NPs:
-
Green titanium dioxide nanoparticles
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GST:
-
Glutathione-S-transferase
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor- α
- TTIP:
-
Titanium isopropoxide
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- GD:
-
Gestational day
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res 7:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Ammendolia MG, Iosi F, Maranghi F et al (2017) Short-term oral exposure to low doses of nano-sized TiO2 and potential modulatory effects on intestinal cells. Food Chem Toxicol 102:63–75
Awaad A (2015) Histopathological and immunological changes induced by magnetite nanoparticles in the spleen, liver and genital tract of mice following intravaginal instillation. J Basic Appl Zool 71:32–47
Block E (1992) The organosulfur chemistry of the genus allium–implications for the organic chemistry of sulfur. Angew Chemie Int Ed English 31:1135–1178
Borenstein M, Rothstein H, Cohen J (1997) Sample power statistics 10. SPSS Inc, Chicago
Chandra H, Kumari P, Bontempi E, Yadav S (2020) Medicinal plants: treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 24:101518
Chen J, Dong X, Zhao J, Tang G (2009) In vivo acute toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to mice after intraperitioneal injection. J Appl Toxicol 29:330–337
Coelho SG, Patri AK, Wokovich AM et al (2016) Repetitive application of sunscreen containing titanium dioxide nanoparticles on human skin. JAMA Dermatol 152:470–472
Dodd NJF, Jha AN (2009) Titanium dioxide induced cell damage: a proposed role of the carboxyl radical. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 660:79–82
Drobiova H, Thomson M, Al-Qattan K, et al (2011) Garlic increases antioxidant levels in diabetic and hypertensive rats determined by a modified peroxidase method. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2011
Duan Y, Liu J, Ma L et al (2010) Toxicological characteristics of nanoparticulate anatase titanium dioxide in mice. Biomaterials 31:894–899
El-Saber M (2021) Effect of biosynthesized Zn and Se nanoparticles on the productivity and active constituents of garlic subjected to saline stress. Egypt J Desert Res 71:99–128
Fabian E, Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L et al (2008) Tissue distribution and toxicity of intravenously administered titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rats. Arch Toxicol 82:151–157
Ferreira ME, de Lourdes Pereira M, e Costa FG et al (2003) Comparative study of metallic biomaterials toxicity: a histochemical and immunohistochemical demonstration in mouse spleen. J trace Elem Med Biol 17:45–49
Fruijtier-Pölloth C (2012) The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica—a nanostructured material. Toxicology 294:61–79
Fukuda Y, Mochimaru H, Terasaki Y et al (2001) Mechanism of structural remodeling in pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 120:S41–S43
Gao G, Ze Y, Li B et al (2012) Ovarian dysfunction and gene-expressed characteristics of female mice caused by long-term exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 243:19–27
Ghareeb DA, Khalil AA, Elbassoumy AM et al (2010) Ameliorated effects of garlic (Allium sativum) on biomarkers of subchronic acrylamide hepatotoxicity and brain toxicity in rats. Toxicol Environ Chem 92:1357–1372
Gnach A, Lipinski T, Bednarkiewicz A et al (2015) Upconverting nanoparticles: assessing the toxicity. Chem Soc Rev 44:1561–1584
Goutam SP, Saxena G, Singh V et al (2018) Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using leaf extract of Jatropha curcas L. for photocatalytic degradation of tannery wastewater. Chem Eng J 336:386–396
Grassian VH, O’Shaughnessy PT, Adamcakova-Dodd A et al (2007) Inhalation exposure study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environ Health Perspect 115:397–402
Gui S, Zhang Z, Zheng L et al (2011) Molecular mechanism of kidney injury of mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 195:365–370
Hodge G, Hodge S, Han P (2002) Allium sativum (garlic) suppresses leukocyte inflammatory cytokine production in vitro: potential therapeutic use in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Cytom J Int Soc Anal Cytol 48:209–215
Hong F, Yu X, Wu N, Zhang Y-Q (2017) Progress of in vivo studies on the systemic toxicities induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Res (camb) 6:115–133
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB et al (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Ibrahim R, Elkady M, Hassanein A (2019) Effect of some antioxidants on rats treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Egypt J Food Sci 47:91–103
Kamal Z, Ebnalwaled AA, Al-Amgad Z et al (2022) Ameliorative effect of biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using garlic extract on the body weight and developmental toxicity of liver in albino rats compared with chemically synthesized nanoparticles. Front Vet Sci 9:1049817. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.1049817
Kang SJ, Kim BM, Lee YJ et al (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis through the JNK/p38-caspase-8-Bid pathway in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:682–687
Karimipour M, Javanmard MZ, Ahmadi A, Jafari A (2018) Oral administration of titanium dioxide nanoparticle through ovarian tissue alterations impairs mice embryonic development. Int J Reprod Biomed 16:397
Katayama S, Xu X, Fan MZ, Mine Y (2006) Antioxidative stress activity of oligophosphopeptides derived from hen egg yolk phosvitin in Caco-2 cells. J Agric Food Chem 54:773–778
Khayal E, Amin D, Shabana M (2019) The possible protective role of N-acetyl cysteine against titanium dioxide nanoparticles intestinal toxicity in adult male albino rats. Ain Shams J Forensic Med Clin Toxicol 33:59–69
Kim J, Lee J, Lyoo YS et al (2013) The effects of topical mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in canine experimental cutaneous wounds. Vet Dermatol 24:242-e53
Kopeć A, Skoczylas J, Jędrszczyk E et al (2020) Chemical composition and concentration of bioactive compounds in garlic cultivated from air bulbils. Agriculture 10:40
Larson K, Ho HH, Anumolu PL, Chen TM (2011) Hematoxylin and eosin tissue stain in Mohs micrographic surgery: a review. Dermatologic Surg 37:1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02051.x
Lawson LD, Wang ZJ (2005) Allicin and allicin-derived garlic compounds increase breath acetone through allyl methyl sulfide: use in measuring allicin bioavailability. J Agric Food Chem 53:1974–1983
Li N, Duan Y, Hong M et al (2010) Spleen injury and apoptotic pathway in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticules. Toxicol Lett 195:161–168
Li B, Ze Y, Sun Q et al (2013) Molecular mechanisms of nanosized titanium dioxide–induced pulmonary injury in mice. PLoS One 8:e55563
Lowe JS, Anderson PG (2015) Blood and lymphatic circulatory systems and heart. Stevens Lowe’s Hum Histol 143–165
Mahesh S, Narasaiah BP, Balaji GL (2022) Fabrication of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using sunflower leaf extract and their applications towards the synthesis and biological evaluation of some novel phenanthro imidazole derivatives. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 12:3372–3389
Maldonado PD, Barrera D, Medina-Campos ON et al (2003) Aged garlic extract attenuates gentamicin induced renal damage and oxidative stress in rats. Life Sci 73:2543–2556
Mantovani A, Bussolino F, Introna M (1997) Endothelial cell activation by cytokines: from molecular level to the bed side. Immunol Today 18:231–240
Meena R, Paulraj R (2012) Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of TiO2 nano anatase in liver and kidney of Wistar rat. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:146–163
Mohammadi F, Sadeghi L, Mohammadi A et al (2015) The effects of nano titanium dioxide (TiO2NPs) on lung tissue. Bratisl Lek Listy 116:363–367
Nadeem M, Abbasi BH, Younas M et al (2017) A review of the green syntheses and anti-microbial applications of gold nanoparticles. Green Chem Lett Rev 10:216–227
Nakamura M, Miyamoto K, Hayashi K et al (2013) Time-lapse fluorescence imaging and quantitative single cell and endosomal analysis of peritoneal macrophages using fluorescent organosilica nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol, Biol Med 9:274–283
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Park E-J, Yi J, Chung K-H et al (2008) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett 180:222–229
Pawlina W, Ross MH (2018) Histology: a text and atlas: with correlated cell and molecular biology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
RajaniKanth V, Uma Maheswara Reddy P, Raju TN (2008) Attenuation of streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress in hepatic and intestinal tissues of Wistar rat by methanolic-garlic extract. Acta Diabetol 45:243–251
Rattanapinyopituk K, Shimada A, Morita T et al (2014) Demonstration of the clathrin-and caveolin-mediated endocytosis at the maternal–fetal barrier in mouse placenta after intravenous administration of gold nanoparticles. J Vet Med Sci 76:377–387
Renwick LC, Brown D, Clouter A, Donaldson K (2004) Increased inflammation and altered macrophage chemotactic responses caused by two ultrafine particle types. Occup Environ Med 61:442–447
Rider BF, Mellon MG (1946) Colorimetric determination of nitrites. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 18:96–99
Sang X, Zheng L, Sun Q et al (2012) The chronic spleen injury of mice following long-term exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 100:894–902. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34024
Schanen BC, Karakoti AS, Seal S et al (2009) Exposure to titanium dioxide nanomaterials provokes inflammation of an in vitro human immune construct. ACS Nano 3:2523–2532
Shakeel M, Jabeen F, Shabbir S et al (2016) Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) through various routes of exposure: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res 172:1–36
Shi H, Magaye R, Castranova V, Zhao J (2013) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: A review of current toxicological data. Part Fibre Toxicol 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-10-15
Shimizu M, Tainaka H, Oba T et al (2009) Maternal exposure to nanoparticulate titanium dioxide during the prenatal period alters gene expression related to brain development in the mouse. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:1–8
Singh V, Kumar R (2017) Study of phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of Allium sativum of Bundelkhand region. Int J Life-Sciences Sci Res 3:1451–1458
Singh P, Kim Y-J, Zhang D, Yang D-C (2016) Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 34:588–599
Smith AJP, Humphries SE (2009) Cytokine and cytokine receptor gene polymorphisms and their functionality. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:43–59
Standring S (2021) Gray’s anatomy e-book: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier Health Sciences
Suleria HAR, Butt MS, Khalid N et al (2015) Garlic (Allium sativum): diet based therapy of 21st century–a review. Asian Pacific J Trop Dis 5:271–278
Sun J, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Yan B (2013) Effects of nanotoxicity on female reproductivity and fetal development in animal models. Int J Mol Sci 14:9319–9337
Sund J, Palomäki J, Ahonen N et al (2014) Phagocytosis of nano-sized titanium dioxide triggers changes in protein acetylation. J Proteomics 108:469–483
Tepe B, Daferera D, Sökmen M et al (2004) In vitro antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oils and various extracts of Thymus eigii M. Zohary et PH Davis. J Agric Food Chem 52:1132–1137
Tsuchiya T, Oguri I, Yamakoshi YN, Miyata N (1996) Novel harmful effects of [60] fullerene on mouse embryos in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett 393:139–145
Umbreit TH, Francke-Carroll S, Weaver JL et al (2012) Tissue distribution and histopathological effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles after intravenous or subcutaneous injection in mice. J Appl Toxicol 32:350–357
Vazquez-Prieto MA, González RE, Renna NF et al (2010) Aqueous garlic extracts prevent oxidative stress and vascular remodeling in an experimental model of metabolic syndrome. J Agric Food Chem 58:6630–6635
Wang J-X, Fan Y-B, Gao Y et al (2009) TiO2 nanoparticles translocation and potential toxicological effect in rats after intraarticular injection. Biomaterials 30:4590–4600
Wang J, Li N, Zheng L et al (2011) P38-Nrf-2 signaling pathway of oxidative stress in mice caused by nanoparticulate TiO2. Biol Trace Elem Res 140:186–197
Warheit DB, Hoke RA, Finlay C et al (2007) Development of a base set of toxicity tests using ultrafine TiO2 particles as a component of nanoparticle risk management. Toxicol Lett 171:99–110
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L et al (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ Sci Technol 46:2242–2250. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES204168D
Wick P, Malek A, Manser P et al (2010) Barrier capacity of human placenta for nanosized materials. Environ Health Perspect 118:432–436
Zhao L, Zhu Y, Chen Z et al (2018) Cardiopulmonary effects induced by occupational exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 12:169–184
Funding
This research was funded by South Valley University, Qena, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZK and AAE jointly developed the hypothesis and concept of the study and contributed to the chemical and material preparation, and the techniques performed. ZA-A, AAM, and AHS were involved in the experimental procedures and analyses. AAS developed the graphical abstract. AAS and AAM reviewed, revised, and edited the final version of the paper. All authors revised, edited, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The rats and all the procedures in this study were used in compliance with the guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Science, South Valley University, Qena, Egypt (approval no. 002/9/22).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, Z., Ebnalwaled, A.A., Al-Amgad, Z. et al. Immunomodulatory and antioxidant effect of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles on pregnant female albino rats and their fetuses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 55455–55470 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26264-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26264-2