Abstract
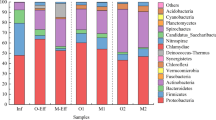
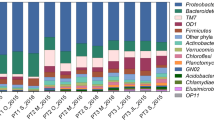
Bacterial community structure of activated sludge directly affects the stable operation of WWTPS, and these bacterial communities may carry a variety of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which is a threat to the public health. This study employed 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenomic sequencing to investigate the bacterial community composition and the ARGs in a sludge bulking oxidation ditch-denitrification filter WWTP in a cold region. The results showed that Trichococcus (20.34%), Blautia (7.72%), and Faecalibacterium (3.64%) were the main bacterial genera in the influent. The relative abundances of norank_f_Saprospiraceae and Candidatus_Microthrix reached 10.24% and 8.40%, respectively, in bulking sludge, and those of norank_f_Saprospiraceae and Candidatus_Microthrix decreased to 6.56 and 7.10% after the anaerobic tank, indicating that the anaerobic tank had an inhibitory effect on filamentous bacteria. After 20 mJ/cm2 UV disinfection, about 540 bacterial genera, such as Romboutsia (7.99%), Rhodoferax (7.98%), and Thermomonas (4.13%), could still be detected in the effluent. The ARGs were 345.11 ppm in the influent and 11.20 ppm in the effluent; 17 subtypes, such as sul1, msrE, aadA5, ErmF, and tet(A), could be detected throughout the entire process. These ARG subtypes were persistent ARGs with a high health risk. Network analysis indicated that the changes in filamentous bacteria norank_f_Saprospiraceae abundance mainly contributed to the abundance shift of MexB, and Acinetobacter mainly increased the abundance of drfA1. These results above will provide theoretical support for the sludge bulking and ARGs controls of WWTPs in cold regions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
16S rRNA gene and metagenomic sequences were deposited in NCBI under the accession number PRJNA736217 and PRJNA736202 respectively.
References
An WX, Guo F, Song YL, Gao N, Bai SJ, Dai JC, Wei HH, Zhang LP, Yu DZ, Xia M, Yu Y, Qi M, Tian CY, Chen HF, Wu ZB, Zhang T, Qiu DR (2016) Comparative genomics analyses on EPS biosynthesis genes required for floc formation of Zoogloea resiniphila and other activated sludge bacteria. Water Res 102:494–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.058
An XL, Su JQ, Li B, Ouyang WY, Zhao Y, Chen QL, Cui L, Chen H, Gillings MR, Zhang T, Zhu YG (2018) Tracking antibiotic resistome during wastewater treatment using high throughput quantitative PCR. Environ Int 117:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.011
Aranda J, Lopez M, Leiva E, Magan A, Adler B, Bou G, Barbe J (2014) Role of Acinetobacter baumannii UmuD homologs in antibiotic resistance acquired through DNA damage-induced mutagenesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(3):1771–1773. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.02346-13
Becerra-Castro C, Macedo G, Silva AMT, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2016) Proteobacteria become predominant during regrowth after water disinfection. Sci Total Environ 573:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.054
Boettger BC, Cayo R, Streling AP, Nodari CS, Almeida LGP, Martins WMBS, Girardello R, Vasconcelos ATR, Gales AC, Pignatari AC (2021) Dynamic of high-risk Acinetobacter baumannii major clones in a brazilian tertiary hospital during a short time period. Microb Drug Resist 27(3):320–327. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2020.0195
Chen Y, Jiang YM, Huang HY, Mou LC, Ru JL, Zhao JH, Xiao S (2018) Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci Total Environ 637:1400–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.109
Chen HY, Li XK, Meng LW, Liu GG, Ma XC, Piao CY, Wang K (2022) The fate and behavior mechanism of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in anaerobic reactors treating oxytetracycline manufacturing wastewater. J Hazard Mater 424:127352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127352
Cheng XX, Xu JN, Smith G, Zhang YY (2021) Metagenomic insights into dissemination of antibiotic resistance across bacterial genera in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 271:129563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129563
Childress H, Sullivan B, Kaur J, Karthikeyan R (2014) Effects of ultraviolet light disinfection on tetracycline-resistant bacteria in wastewater effluents. J Water Health 12(3):404–409. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2013.257
Destiani R, Templeton MR, Kowalski W (2018) Relative ultraviolet sensitivity of selected antibiotic re-sistance genes in waterborne bacteria. Environ Eng Sci 35(7):770–774. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2017.0179
Ding HJ, Qiao M, Zhong JY, Zhu YG, Guo CJ, Zhang QQ, Yang P, Han L, Zhang WH, Wu YX, Liu JT, Zhang LT, Sun JH (2020) Characterization of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community in selected municipal and industrial sewage treatment plants beside Poyang Lake. Water Res 174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115603
Fan NS, Qi R, Rossetti S, Tandoi V, Gao YX, Yang M (2017) Factors affecting the growth of Microthrix parvicella: batch tests using bulking sludge as seed sludge. Sci Total Environ 609:1192–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.261
Gajewska M, Jozwiakowski K, Ghrabi A, Masi F (2015) Impact of influent wastewater quality on nitrogen removal rates in multistage treatment wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(17):12840–12848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3647-4
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC, Sutter JL, Koren O, Blekhman R, Beaumont M, Van Treuren W, Knight R, Bell JT, Spector TD, Clark AG, Ley RE (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159(4):789–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053
Guo F, Wang ZP, Yu K, Zhang T (2015) Detailed investigation of the microbial community in foaming activated sludge reveals novel foam formers. Sci Rep 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07637
Guo B, Liu CX, Gibson C, Frigon D (2019) Wastewater microbial community structure and functional traits change over short timescales. Sci Total Environ 662:779–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.207
Guo Y, Gao JF, Wang ZQ, Cui YC, Li ZQ, Wu ZJ, Yifan Z, Li DC, Dai HH (2022) The fate and behavior mechanism of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in flocs, aerobic granular and biofilm sludge under chloroxylenol pressure. J Hazard Mater 438:129465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129465
Hu Q, Zhang XX, Jia SY, Huang KL, Tang JY, Shi P, Ye L, Ren HQ (2016) Metagenomic insights into ultraviolet disinfection effects on antibiotic resistome in biologically treated wastewater. Water Res 101:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.092
Hülsen T, Barry EM, Lu Y, Puyol D, Batstone DJ (2016) Low temperature treatment of domestic wastewater by purple phototrophic bacteria: performance, activity, and community. Water Res 100:537–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.054
Joly-Guillou ML (2005) Clinical impact and pathogenicity of Acinetobacter. Clin Microbiol Infect 11(11):868–873. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01227.x
Ju F, Li B, Ma LP, Wang YB, Huang DP, Zhang T (2016) Antibiotic resistance genes and human bacterial pathogens: Co-occurrence, removal, and enrichment in municipal sewage sludge digesters. Water Res 91:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.071
Lee J, Jeon JH, Shin J, Jang HM, Kim S, Song MS, Kim YM (2017) Quantitative and qualitative changes in antibiotic resistance genes after passing through treatment processes in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 605:906–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.250
Li B, Yang Y, Ma LP, Ju F, Guo F, Tiedje JM, Zhang T (2015) Metagenomic and network analysis reveal wide distribution and co-occurrence of environmental antibiotic resistance genes. ISME J 9(11):2490–2502. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.59
Li B, Qiu Y, Li J, Liang P, Huang X (2019) Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in four full-scale me-mbrane bioreactors. Sci Total Environ 653:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.305
Li C, He W, Liang D, Tian Y, Yadav RS, Li D, Liu J, Feng Y (2021) The anaerobic and starving treatment eliminates filamentous bulking and recovers biocathode biocatalytic activity with residual organic loading in microbial electrochemical system. Chem Eng J 404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127072
Lin ZJ, Zhou ZC, Zhu L, Meng LX, Shuai XY, Sun YJ, Chen H (2021) Behavior of antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater treatment plant with different upgrading processes. Sci Total Environ 771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144814
Liu GQ, Wang JM (2013) Long-term low DO enriches and shifts nitrifier community in activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 47(10):5109–5117. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304647y
Liu LZ, Xing XC, Hu C, Wang HB, Lyu L (2019) Effect of sequential UV/free chlorine disinfection on opportunistic pathogens and microbial community structure in simulated drinking water distribution systems. Chemosphere 219:971–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.067
Luo YS, Yao JQ, Wang XY, Zheng MY, Guo DY, Chen YG (2020) Efficient municipal wastewater treatment by oxidation ditch process at low temperature: bacterial community structure in activated sludge. Sci Total Environ 703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135031
Maritz JM, Ten Eyck TA, Elizabeth Alter S, Carlton JM (2019) Patterns of protist diversity associated with raw sewage in New York City. ISME J 13(11):2750–2763. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0467-z
Martins AMP, Pagilla K, Heijnen JJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Filamentous bulking sludge - a critical review. Water Res 38(4):793–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.005
McConnell MM, Hansen LT, Jamieson RC, Neudorf KD, Yost CK, Tong A (2018) Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in two tertiary level municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 643:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.212
McIlroy SJ, Starnawska A, Starnawski P, Saunders AM, Nierychlo M, Nielsen PH, Nielsen JL (2016) Identification of active denitrifiers in full-scale nutrient removal wastewater treatment systems. Environ Microbiol 18(1):50–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12614
McKinney CW, Pruden A (2012) Ultraviolet disinfection of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their antibiotic resistance genes in water and wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 46(24):13393–13400. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303652q
Metch JW, Wang H, Ma Y, Miller JH, Vikesland PJ, Bott C, Higgins M, Murthy S, Pruden A (2019) Insights gained into activated sludge nitrification through structural and functional profiling of microbial community response to starvation stress. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 5(5):884–896. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ew00001a
Miller JH, Novak JT, Knocke WR, Pruden A (2014) Elevation of antibiotic resistance genes at cold temperatures: implications for winter storage of sludge and biosolids. Lett Appl Microbiol 59(6):587–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12325
Pan KL, Gao JF, Fan XY, Li DC, Dai HH (2018) The more important role of archaea than bacteria in nitrification of wastewater treatment plants in cold season despite their numerical relationships. Water Res 145:552–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.066
Park HD, Noguera DR (2004) Evaluating the effect of dissolved oxygen on ammonia-oxidizing bacteri-al communities in activated sludge. Water Res 38(14–15):3275–3286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.047
Pazda M, Kumirska J, Stepnowski P, Mulkiewicz E (2019) Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wa-stewater treatment plant systems - a review. Sci Total Environ 697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134023
PereiraDias J, Nguyen Ngoc Minh C, Tran Thi Hong C, Nguyen Thi Nguyen T, Ha Thanh T, Zellmer C, Chung The H, Pike L, Higginson EE, Baker S (2021) The gut microbiome of healthy Vietnamese adults and children is a major reservoir for resistance genes against critical antimicrobials. J Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab398
Qin H, Ji B, Zhang SF, Kong ZH (2018) Study on the bacterial and archaeal community structure and diversity of activated sludge from three wastewater treatment plants. Mar Pollut Bull 135:801–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.08.010
Rafraf ID, Lekunberri I, Sànchez-Melsió A, Aouni M, Borrego CM, Balcázar JL (2016) Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in five municipal wastewater treatment plants in the Monastir Governorate, Tunisia. Environ Pollut 219:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.062
Rossetti S, Tomei MC, Nielsen PH, Tandoi V (2005) "Microthrix parvicella", a filamentous bacterium causing bulking and foaming in activated sludge systems: a review of current knowledge. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(1):49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2004.09.005
Sabri NA, Holst S, Schmitt H, Zaan BM, Gerritsen HW, Rijnaarts HHM, Langenhoff AAM (2020) Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during conventional and additional treatment technologies in wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140199
Serwecińska L (2020) Antimicrobials and antibiotic-resistant bacteria: a risk to the environment and to public health. Water 12(12):3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123313
Sharma VK, Johnson N, Cizmas L, McDonald TJ, Kim H (2016) A review of the influence of treatment strategies on antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes. Chemosphere 150:702–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.084
Stange C, Sidhu JPS, Toze S, Tiehm A (2019) Comparative removal of antibiotic resistance genes during chlorination, ozonation, and UV treatment. Int J Hyg Environ Health 222(3):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.02.002
Sunde M, Simonsen GS, Slettemeas JS, Bockerman I, Norstrom M (2015) Integron, plasmid and host strain characteristics of Escherichia coli from humans and food included in the Norwegian antimicrobial resistance monitoring programs. Plos One 10(6). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128797
Tong J, Tang AP, Wang HY, Liu XX, Huang ZH, Wang ZY, Zhang JY, Wei YS, Su YY, Zhang YF (2019) Microbial community evolution and fate of antibiotic resistance genes along six different full-scale municipal wastewater treatment processes. Bioresour Technol 272:489–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.079
Wang P, Yu ZS, Qi R, Zhang HX (2016) Detailed comparison of bacterial communities during seasonal sludge bulking in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 105:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.050
Wang HC, Wang J, Li SM, Ding GY, Wang K, Zhuang T, Huang X, Wang XY (2020a) Synergistic effect of UV/chlorine in bacterial inactivation, resistance gene removal, and gene conjugative transfer blocking. Water Res 185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116290
Wang J, Chu L, Wojnárovits L, Takács E (2020b) Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) in municipal wastewater treatment plant: An overview. Sci Total Environ 744:140997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140997
Wang WG, Xie HC, Wang H, Xue H, Wang JJ, Zhou MD, Dai XH, Wang YY (2020c) Organic compounds evolution and sludge properties variation along partial nitritation and subsequent anammox processes treating reject water. Water Res 184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116197
Welander U, Mattiasson B (2003) Denitrification at low temperatures using a suspended carrier biofilm process. Water Res 37(10):2394–2398. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(03)00019-8
Wen QX, Yang L, Duan R, Chen ZQ (2016) Monitoring and evaluation of antibiotic resistance genes in four municipal wastewater treatment plants in Harbin, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 212:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.043
Xu S, Yao JQ, Ainiwaer M, Hong Y, Zhang YJ (2018) Analysis of bacterial community structure of activated sludge from wastewater treatment plants in winter. BioMed Res Int 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8278970
Yang M, Sun PD, Wang RY, Han JY, Wang JQ, Song YQ, Cai J, Tang XD (2013a) Simulation and optimization of ammonia removal at low temperature for a double channel oxidation ditch based on fully coupled activated sludge model (FCASM): A full-scale study. Bioresour Technol 143:538–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.029
Yang Y, Li B, Ju F, Zhang T (2013b) Exploring variation of antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge over a four-year period through a metagenomic approach. Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10197–10205. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4017365
Yang Y, Li B, Zou SC, Fang HH, Zhang T (2014) Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sewage treatment plant revealed by metagenomic approach. Water Res 62:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.05.019
Yang QX, Zhao HL, Du BB (2017) Bacteria and bacteriophage communities in bulking and non-bulking activated sludge in full-scale municipal wastewater treatment systems. Biochem Eng J 119:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.12.017
Yang YY, Liu GH, Song WJ, Ye C, Lin H, Li Z, Liu WZ (2019) Plastics in the marine environment are reservoirs for antibiotic and metal resistance genes. Environ Int 123:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.061
Zhang QH, Yang WN, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Jin PK, Dzakpasu M, Yang SJ, Wang Q, Wang XC, Ao D (2016) Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ Int 92:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.03.024
Zhang M, Yao JQ, Wang XY, Hong Y, Chen YG (2019a) The microbial community in filamentous bulking sludge with the ultra-low sludge loading and long sludge retention time in oxidation ditch. Sci Rep 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50086-3
Zhang ZG, Li BX, Li N, Sardar MF, Song TT, Zhu CX, Lv XW, Li HN (2019b) Effects of UV disinfection on phenotypes and genotypes of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in secondary effluent from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 157:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.079
Zhang L, Cheng YN, Qian C, Lu WX (2020) Bacterial community evolution along full-scale municipal wastewater treatment processes. J Water Health 18(5):665–680. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2020.092
Zhao RX, Feng J, Liu J, Fu WJ, Li XY, Li B (2019) Deciphering of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge reactors under high selective pressure of different antibiotics. Water Res 151:388–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.034
Zheng J, Su C, Zhou JW, Xu LK, Qian YY, Chen H (2017) Effects and mechanisms of ultraviolet, chlorination, and ozone disinfection on antibiotic resistance genes in secondary effluents of municipal wastewater treatment plants. Chem Eng J 317:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.076
Zheng XW, Zhang SY, Huang DY, Zhang L, Zhang JB (2019) A pilot-scale deep bed denitrification filter for secondary effluent treatment using sodium acetate as external carbon. Water Environ Res 91(6):491–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1035
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52160005) and the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang of China (No. 2021D01C047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zenghui Liang is assigned to the writing and statistical analysis. Junqin Yao designed the study and provided financial resources. Huiying Ma did the investigation. Wei Peng is involved in the statistical analysis. Xueliang Xia performed sample collection. Yinguang Chen designed the study and reviewed and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The manuscript was reviewed and consents to participate by all authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerald Thouand
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Z., Yao, J., Ma, H. et al. A sludge bulking wastewater treatment plant with an oxidation ditch-denitrification filter in a cold region: bacterial community composition and antibiotic resistance genes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 33767–33779 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24591-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24591-4