Abstract
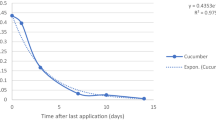
Residue field trials in cucumber were conducted for the safe use of a commercial formulation of cyproconazole·azoxystrobin 28% suspension concentrate (SC 294 g a.i. ha−1, three applications at a 7-day interval) in the year 2018, in China. To determine the residues of cyproconazole and azoxystrobin in cucumber, a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) method was developed using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. This validated method was applied to analyze cucumber samples collected from 12 specified regions. At the 3-day interval to harvest, the highest residue (HR) of azoxystrobin was 0.150 mg kg−1, which was lower than the maximum residue limit (MRL; 0.5 mg kg−1) permitted in China, and the HR of cyproconazole was 0.084 mg kg−1, for which no MRL value has been set in China. The chronic risk quotient values of cyproconazole and azoxystrobin for Chinese adults at a 3-day interval to harvest were 2.56% and 13.72%, respectively. The acute risk quotient values of cyproconazole in cucumber were specified as 5.52% for children (1–6 years old) and 2.83% for the adults (> 18 years old) in China. These results indicate that cyproconazole·azoxystrobin 28% SC sprayed on cucumber at the pre-harvest interval of 3 days has no significant potential risk for Chinese consumers.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Bakırcı GT, Hısßıl Y (2012) Fast and simple extraction of pesticide residues in selected fruits and vegetables using tetrafluoroethane and toluene followed by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 135(3):1901–1913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.051
Bartlett DW, Clough JM, Godwin JR, Hall AA, Hamer M, Parr-Dobrzanski B (2002) The strobilurin fungicides. Pest Manag Sci 8(7):649–662. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.520
Cao F II, CLS, Li P, Pang S, Qiu L, Martyniuk CJ (2019) Developmental toxicity of the triazole fungicide cyproconazole in embryo-larval stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut R 6(5):913–4923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3957-z
Cao F, Zhu L, Li H, Yu S, Wang C, Qiu L (2016) Reproductive toxicity of azoxystrobin to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 219:1109–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.015
Cui K, Wu X, Wei D, Zhang Y, Cao J, Xu J, Zheng Y (2021) Health risks to dietary neonicotinoids are low for Chinese residents based on an analysis of 13 daily-consumed foods. Environ Int 49:106385
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and RIVM (the Dutch National Institute for Public health and the Environment) (2015) Revisiting the International Estimate of Short‐Term Intake (IESTI equations) used to estimate the acute exposure to pesticide residues via food. Efsa Supporting Publications 12(12):1–81. https://doi.org/10.2903/sp.efsa.2015.EN-907
Fan X, Zhao S, Hu J (2019) Dissipation behavior and dietary risk assessment of lambda-cyhalothrin, thiamethoxam and its metabolite clothianidin in apple after open field application. Regul Toxicol Pharm 101:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.11.003
Feng J, Zhang H, Chen N, Wang Y (2008) Genetics and molecular markers of resistance to five diseases in cucumber China. Zhongguo Nong Xue Tong Bao 24(8):368–372
GB 2763-2019 National food safety standard–maximum residue limits for pesticides in food. China agriculture press, Beijing
Geng Y, Jiang L, Zhang Y, He Z, Wang L, Peng Y, Xu Y (2018) Assessment of the dissipation, pre-harvest interval and dietary risk of carbosulfan, dimethoate, and their relevant metabolites in greenhouse cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Pest Manag Sci 74(7):1654–1663. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4857
Golge O, Hepsag F, Kabak B (2018) Health risk assessment of selected pesticide residues in green pepper and cucumber. Food Chem Toxicol 121:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.08.027
Hou Z, Wang X, Zhao X, Wang X, Yuan X, Lu Z (2016) Dissipation rates and residues of fungicide azoxystrobin in ginseng and soil at two different cultivated regions in China. Environ Monit Assess 188(7):440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5449-2
JMPR(2008)http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Report08/Azoxystrobin.pdf. Accessed 2 June 2018
JMPR(2010)http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Report10/Cyproconazole. pdf. Accessed 2 June 2018
Kmellár B, Fodor P, Pareja L, Ferrer C, Martínez-Uroz MA, Valverde A, Fernandez-Alba AR (2008) Validation and uncertainty study of a comprehensive list of 160 pesticide residues in multi-class vegetables by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1215(1–2):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.10.121
Li R, He L, Wei W, Hao L, Ji X, Zhou Y, Wang Q (2015) Chlorpyrifos residue levels on field crops (rice, maize and soybean) in China and their dietary risks to consumers. Food Control 51:212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.11.023
Ma D, Jiang J, He L, Cui K, Mu W, Liu F (2018) Detection and characterization of QoI-resistant Phytophthora capsici causing pepper Phytophthora blight in China. Plant Dis 102(9):1725–1732. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-18-0197-RE
Machera K (1995) Developmental toxicity of cyproconazole, an inhibitor of fungal ergosterol biosynthesis, in the rat. B Environ Contam Tox 54(3):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195106
Matthews G (1998) The pesticide manual: By C. Tomlin. ISBN 1–901396118. 1606 pp. British Crop Protection Council EU (11th Edition), 1997. Crop Prot 17(7): 613. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(97)00118-X
NY/T788-2018 Guideline on pesticide residue trials. China agriculture press, Beijing
Olsvik PA, Kroglund F, Finstad B, Kristensen T (2010) Effects of the fungicide azoxystrobin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) smolt. Ecotox Environ Safe 73(8):1852–1861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.07.017
Organisation for Economic Co–operation and Development (OECD) 2011 OECD MRL calculator: spreadsheet for single data set and spreadsheet for multiple data set. http://www.epa.gov/pesticide-tolerances/oecd-maximum-residue-limit-calculator/. Accessed 12 Dec 2020
Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E, Kotopoulou A (1995) Dissipation of cyproconazole and quinalphos on/in grapes. Pest Manag Sci 45(2):111–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2780450204
Peffer RC, Moggs JG, Pastoor T, Currie RA, Wright J, Milburn G, Rusyn I (2007) Mouse liver effects of cyproconazole, a triazole fungicide: role of the constitutive androstane receptor. Toxicol Sci 99(1):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm154
Zhang Z, Tang T, Xu H, Li Z, Yang G, Wang Q (2012) Dietary intake risk assessment of Forchlorfenuron residue in fruits and vegetables. Zhongguo Nong Ye Ke Xue 45(10):1982–1991. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.10.011
Zhao F, She Y, Zhang C, Cao X, Wang S, Zheng L, Wang J (2017) Selective solid-phase extraction based on molecularly imprinted technology for the simultaneous determination of 20 triazole pesticides in cucumber samples using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 1064:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.08.022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Method validation and original draft: Chuanying Cheng
Writing—review and editing: Yiran Liang.
Oversight and leadership responsibility: Jiye Hu
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Liang, Y. & Hu, J. Estimation of residue levels and dietary risk assessment of cyproconazole and azoxystrobin in cucumber after field application in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 34186–34193 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17981-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17981-7