Abstract
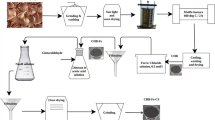
This paper presents a new material easily synthesized and with low cost, with the possibility of remove arsenic and the potential capability for the remediate water bodies. In this work, the efficiency in removing arsenic of the chitosan, supported onto modified polypropylene membrane, was studied using an aqueous As(V) solution of 0.4 mg/L, achieving a removal efficiency of 75%, which corresponds to an adsorption capacity of 0.031 mg/g. The As(V) adsorption depends on pH and the degree of chitosan grafting on the polypropylene membrane. A pseudo-second-order equation describes the adsorption of the membrane, classifying it as a chemisorption process. The chitosan supported on the membrane was characterized by the analysis of wettability, FT-IR-ATR, SEM-EDS, XRD powder, and surface charge. The As ions coordinate to the chitosan polar groups, allowing their removal from the aqueous solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- K L :
-
pseudo-first-order constant or sorption rate (L/min)
- q e :
-
amount of solute adsorbed at equilibrium (mg/g)
- q t :
-
Amount of solute adsorbed at time t (mg/g)
- t :
-
time (min)
- K 2 :
-
pseudo-second-order constant (g/mg min)
- h :
-
constant in the initial range (mg/g h)
- a :
-
initial adsorption rate (g/mg min)
- b :
-
desorption constant (mg/g)
- q:
-
adsorption capacity (mg/g)
- v:
-
volume (L)
- ci:
-
initial concentration
- cf :
-
equilibrium concentration of As(V) in the solution
- m:
-
mass of the dry membrane
References
Argos M, Kalra T, Rathouz PJ, Chen Y, Pierce B, Parvez F, Ahsan H (2010) Arsenic exposure from drinking water, and all-cause and chronic-disease mortalities in Bangladesh (HEALS): a prospective cohort study. Lancet 376(9737):252–258
Asere TG, Mincke S, De Clercq J, Verbeken K, Tessema DA, Fufa F, Du Laing G (2017) Removal of arsenic (V) from aqueous solutions using chitosan–red scoria and chitosan–pumice blends. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(8):895
Bhowmick S, Chakraborty S, Mondal P, Van Renterghem W, Van den Berghe S, Roman-Ross G, Iglesias M (2014) Montmorillonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of arsenic from aqueous solution: kinetics and mechanism. Chem Eng J 243:14–23
Elwakeel KZ, Guibal E (2015) Arsenic (V) sorption using chitosan/Cu(OH)2 and chitosan/CuO composite sorbents. Carbohydr Polym 134:190–204
Hernández OA, Nunez A, Tapia M, Gomez RM (2016) Surface modification of polypropylene membrane using biopolymers with potential applications for metal ion removal. J Chem, vol. 2016.
Hughes MF (2002) Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett 133(1):1–16
Kanmani P, Aravind J, Kamaraj M, Sureshbabu P y, Karthikeyan S (2017) Aplicaciones ambientales de quitosano y biopolímeros celulósicos: una perspectiva integral. Tecnología de fuentes biológicas 242:295–303
Kwok KC, Koong LF, Chen G, McKay G (2014) Mechanism of arsenic removal using chitosan and nanochitosan. J Colloid Interface Sci 416:1–10
Kwok KC, Koong LF, Al Ansari T, McKay G (2018) Adsorption/desorption of arsenite and arsenate on chitosan and nanochitosan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(15):14734–14742
Lee CG, Alvarez PJ, Nam A, Park SJ, Do T, Choi US, Lee SH (2017) Arsenic (V) removal using an amine-doped acrylic ion exchange fiber: kinetic, equilibrium, and regeneration studies. J Hazard Mater 325:223–229
Malwal D, Gopinath P (2017) Silica stabilized magnetic-chitosan beads for removal of arsenic from water. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 19:14–19
Miller SM, Zimmerman JB (2010) Novel, bio-based, photoactive arsenic sorbent: TiO2-impregnated chitosan bead. Water Res 44(19):5722–5729
Naujokas MF, Anderson B, Ahsan H, Aposhian HV, Graziano JH, Thompson C, Suk WA (2013) The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ Health Perspect 121(3):295–302
Qi J, Zhang G, Li H (2015) Efficient removal of arsenic from water using a granular adsorbent: Fe–Mn binary oxide impregnated chitosan bead. Bioresour Technol 193:243–249
Sherlala AIA, Raman AAA, Bello MM, Buthiyappan A (2019) Adsorption of arsenic using chitosan magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite. J Environ Manag 246:547–556
Singh R, Singh S, Parihar P, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2015) Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:247–270
Teixeira MC, Santos AC, Fernandes CS, Ng JC (2020) Arsenic contamination assessment in Brazil–Past, present and future concerns: a historical and critical review. Sci Total Environ 730:138217
Thepmanee O, Prapainop K, Noppha O, Rattanawimanwong N, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O, Songsrirote K (2020) A simple paper-based approach for arsenic determination in water using hydride generation coupled with mercaptosuccinic-acid capped CdTe quantum dots. Anal Methods :2718–2726 https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY00273A
Wang X, Liu Y, Zheng J (2016) Removal of As (III) and As (V) from water by chitosan and chitosan derivatives: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(14):13789–13801
Wang YY, Chai LY, Yang WC (2019) Arsenic distribution and pollution characteristics. In: En Arsenic Pollution Control in Nonferrous Metallurgy. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–15
Zeng H, Yu Y, Wang F, Zhang J, Li D (2020) Arsenic (V) removal by granular adsorbents made from water treatment residuals materials and chitosan. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 585:124036
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Dr. Uvaldo Hernández Balderas and María Citlalit Martínez Soto for technical assistance.
Funding
Financial support of CONACYT No. 935960 to conduct postgraduate studies through scholarship. Financial support of SIyEA UAEMex Project 6161/2020CIB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
José Juan. García-García: experimental development of the research work.
Rosa María Gómez-Espinosa: author of correspondence, development, and coordination of the research.
Reyna Natividad Rangel: in charge of the kinetic study.
Rubí Romero Romero: in charge of the adsorption mechanism.
Gabriela Roa Morales: in charge of speciation studies.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable (there was no need for ethical approval due to the type of study).
Consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent to publish.
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-García, .J., Gómez-Espinosa, R.M., Rangel, R.N. et al. New material for arsenic (V) removal based on chitosan supported onto modified polypropylene membrane. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 1909–1916 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15725-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15725-1