Abstract
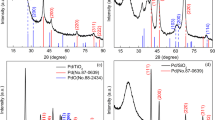
In this paper, Pd/C catalysts are synthesized via Ar glow-discharge plasma reduction using activated carbon as the support and Pd(acac)2, Pd(NO3)2, K2PdCl4, and H2PdCl4 as the Pd precursors, and their catalytic performances are investigated by hydrogen production from dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole (H12-NEC). Pd/C-A, prepared from Pd(acac)2, which has the smallest palladium nanoparticles (1.7 nm), the highest dispersion (34%) and no residue of inorganic ions, exhibits the best catalytic activity with a hydrogen release of 5.28 wt.%, which is 2.2 times that of Pd/C-H. The order of the apparent activation energies of the prepared Pd/C catalysts, according to the kinetics of the H12-NEC dehydrogenation reaction, is as follows: Pd/C-A ≈ Pd/C-N < Pd/C-K < Pd/C-H. When Pd(acac)2 with a large ligand acts as a cation Pd precursor, the effect of coulombic attraction to Pd2+ during the plasma reduction process makes it difficult for Pd nanoparticles (NPs) to migrate, which leads to the formation of ultrafine Pd NPs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aakko-Saksa PT, Cook C, Kiviaho J, Repo T (2018) Liquid organic hydrogen carriers for transportation and storing of renewable energy—review and discussion. J Power Sources 396:803–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.011
Amende M, Gleichweit C, Schernich S, Höfert O, Lorenz MPA, Zhao W, Koch M, Obesser K, Papp C, Wasserscheid P, Steinrück HP, Libuda J (2014a) Size and Structure Effects Controlling the Stability of the Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier Dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole during Dehydrogenation over Pt Model Catalysts. J Phys Chem Lett 5:1498–1504. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz500157r
Amende M, Gleichweit C, Werner K, Schernich S, Zhao W, Lorenz MPA, Höfert O, Papp C, Koch M, Wasserscheid P, Laurin M, Steinrück HP, Libuda J (2014b) Model Catalytic Studies of Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers: Dehydrogenation and Decomposition Mechanisms of Dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole on Pt(111). ACS Catal 4:657–665. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400946x
Brigljević B, Byun M, Lim H (2020) Design, economic evaluation, and market uncertainty analysis of LOHC-based, CO2 free, hydrogen delivery systems. Appl Energy 274:115314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115314
Chen S-Q, Li M, Ma XY, Zhou MJ, Wang D, Yan MY, Li Z, Yao KF (2021) Influence of inorganic ions on degradation capability of Fe-based metallic glass towards dyeing wastewater remediation. Chemosphere 264:128392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128392
Liu C et al (2006) Plasma application for more environmentally friendly catalyst preparation. Pure Appl Chem 78:1227–1238. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200678061227
Claudio-Piedras A, Ramírez-Zamora RM, Alcántar-Vázquez BC, Gutiérrez-Martínez A, Mondragón-Galicia G, Morales-Anzures F, Pérez-Hernández R (2021) One dimensional Pt/CeO2-NR catalysts for hydrogen production by steam reforming of methanol: effect of Pt precursor. Catal Today 360:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.08.013
Davies D, Donald S, Macgregor S (2005) Computational Study of the Mechanism of Cyclometalation by Palladium Acetate. J Am Chem Soc 127:13754–13755. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja052047w
de Graaf S, Momand J, Mitterbauer C, Lazar S, Kooi BJ (2020) Resolving hydrogen atoms at metal-metal hydride interfaces. Sci Adv 6:eaay4312. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay4312
Di L, Zhang J, Zhang X (2018) A review on the recent progress, challenges, and perspectives of atmospheric-pressure cold plasma for preparation of supported metal catalysts. Plasma Process Polym 15:1700234. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201700234
Di L, Zhang J, Ma C, Tu X, Zhang X (2019) Atmospheric-pressure dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma for synthesizing high performance Pd/C formic acid dehydrogenation catalyst. Catal Today 337:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.02.062
Eblagon KM, Tam K, Yu KMK, Tsang SCE (2012) Comparative Study of Catalytic Hydrogenation of 9-Ethylcarbazole for Hydrogen Storage over Noble Metal Surfaces. J Phys Chem C 116:7421–7429. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp212249g
Feng Z, Chen X, Bai X (2020) Catalytic dehydrogenation of liquid organic hydrogen carrier dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole over palladium catalysts supported on different supports. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36172–36185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09698-w
Hodoshima S, Arai H, Takaiwa S, Saito Y (2003) Catalytic decalin dehydrogenation/naphthalene hydrogenation pair as a hydrogen source for fuel-cell vehicle. Int J Hydrog Energy 28:1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00250-1
Iglauer S, Abid H, Al-Yaseri A, Keshavarz A (2021) Hydrogen Adsorption on Sub-Bituminous Coal: Implications for Hydrogen Geo-Storage. Geophys Res Lett 48:e2021GL092976. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL092976
Jin M-H, Park J-H, Oh D, Park J-S, Lee K-Y, Lee D-W (2019) Effect of the amine group content on catalytic activity and stability of mesoporous silica supported Pd catalysts for additive-free formic acid dehydrogenation at room temperature. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:4737–4744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.208
Khaledian HR, Zolfaghari P, Nezhad PDK, Niaei A, Khorram S, Salari D (2021) Surface modification of LaMnO3 perovskite supported on CeO2 using argon plasma for high-performance reduction of NO. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 9:104581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104581
Kim Y, Song Y, Choi Y, Jeong K, Park JH, Ko KC, Na K (2021) Catalytic Consequences of Supported Pd Catalysts on Dehydrogenative H2 Evolution from 2-[(n-Methylcyclohexyl)methyl]piperidine as the Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:809–821. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07338
Kinnunen NM, Suvanto M, Moreno MA, Savimäki A, Kallinen K, Kinnunen TJJ, Pakkanen TA (2009) Methane oxidation on alumina supported palladium catalysts: effect of Pd precursor and solvent. Appl Catal A Gen 370:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.09.018
Kong L, Li L, Cai G, Liu C, Ma P, Bian Y, Ma T (2021) Techno-economic analysis of hydrogen energy for renewable energy power smoothing. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:2847–2861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.231
Lee H-S, Lee J, Seo H, Kang H, Kim DH, Lee Y-W (2021a) Evaluation of Pd/ZSM-5 catalyst for simultaneous reaction of transesterification and partial catalytic transfer hydrogenation of soybean oil under supercritical methanol. Fuel Process Technol 218:106870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106870
Lee J, Williams TS, Hicks RF (2021b) Atmospheric pressure plasma reduction of copper oxide to copper metal. J Vac Sci Technol A 39:023001. https://doi.org/10.1116/6.0000704
Li B, Li H, Weng W-Z, Zhang Q, Huang C-J, Wan H-L (2013) Synthesis gas production from partial oxidation of methane over highly dispersed Pd/SiO2 catalyst. Fuel 103:1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.09.059
Li Y, Liu H, Ma L, He D (2016) Influence of Pd precursors and Cl addition on performance of Pd-Re catalysts in glycerol hydrogenolysis to propanediols. Appl Catal A Gen 522:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2016.04.029
Liu Y, Bai X (2016) Preparation of Pd Nanoparticles Supported on Activated Carbon via Glow Discharge Plasma and Their Catalytic Properties for Suzuki Coupling Reactions. Chem Lett 45:705–707. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.160219
Liu Y, Yang J, Yang J, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhan W, Guo Y, Zhao Y, Guo Y (2021) Understanding the three-way catalytic reaction on Pd/CeO2 by tuning the chemical state of Pd. Appl Surf Sci 556:149766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149766
Makowski P, Thomas A, Kuhn P, Goettmann F (2009) Organic materials for hydrogen storage applications: from physisorption on organic solids to chemisorption in organic molecules. Energy & Environmental Science - ENERGY ENVIRON SCI 2:480. https://doi.org/10.1039/b822279g
Mallick K, Witcomb MJ, Scurrell MS (2004) Supported gold catalysts prepared by in situ reduction technique: preparation, characterization and catalytic activity measurements. Appl Catal A Gen 259:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2003.09.043
Merlano AS, Hoyos LM, Gutiérrez GJ, Valenzuela MA, Salazar Á (2020) Effect of Zn precursor concentration in the synthesis of rGO/ZnO composites and their photocatalytic activity. New J Chem 44:19858–19867. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ03683H
Modisha PM, Ouma CNM, Garidzirai R, Wasserscheid P, Bessarabov D (2019) The Prospect of Hydrogen Storage Using Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers. Energy Fuel 33:2778–2796. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00296
Moradi R, Groth KM (2019) Hydrogen storage and delivery: review of the state of the art technologies and risk and reliability analysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:12254–12269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.041
Mrusek S, Preuster P, Müller K, Bösmann A, Wasserscheid P (2021) Pressurized hydrogen from charged liquid organic hydrogen carrier systems by electrochemical hydrogen compression. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:15624–15634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.02.021
Panpranot J, Tangjitwattakorn O, Praserthdam P, Goodwin JG (2005) Effects of Pd precursors on the catalytic activity and deactivation of silica-supported Pd catalysts in liquid phase hydrogenation. Appl Catal A Gen 292:322–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2005.06.008
Paragian K, Li B, Massino M, Rangarajan S (2020) A computational workflow to discover novel liquid organic hydrogen carriers and their dehydrogenation routes. Molecular Systems Design & Engineering 5:1658–1670. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0ME00105H
Putluru SSR, Schill L, Jensen AD, Siret B, Tabaries F, Fehrmann R (2021) Precursor Effect on Mn-Fe-Ce/TiO2 Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperatures. Catalysts 11:259. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020259
Ramos SV, Cisquini P, Nascimento RC Jr, Franco AR Jr, Vieira EA (2021) Morphological changes and kinetic assessment of Cu2O powder reduction by non-thermal hydrogen plasma. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 11:328–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.038
Rizal MY, Saleh R, Taufik A, Yin S (2021) Photocatalytic decomposition of methylene blue by persulfate-assisted Ag/Mn3O4 and Ag/Mn3O4/graphene composites and the inhibition effect of inorganic ions. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management 15:100408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100408
Satyapal S, Petrovic J, Read C, Thomas G, Ordaz G (2007) The U.S. Department of Energy's National Hydrogen Storage Project: progress towards meeting hydrogen-powered vehicle requirements. Catal Today 120:246–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2006.09.022
Schmidt F (2001) New catalyst preparation technologies—observed from an industrial viewpoint. Appl Catal A Gen 221:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(01)00802-X
Shimbayashi T, K-i F (2020) Metal-catalyzed hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions for efficient hydrogen storage. Tetrahedron 76:130946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2020.130946
Sotoodeh F, Smith KJ (2013) An overview of the kinetics and catalysis of hydrogen storage on organic liquids. Can J Chem Eng 91:1477–1490. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.21871
Sotoodeh F, Zhao L, Smith KJ (2009) Kinetics of H2 recovery from dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole over a supported Pd catalyst. Appl Catal A Gen 362:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.04.039
Stark K, Emel’yanenko VN, Zhabina AA, Varfolomeev MA, Verevkin SP, Müller K, Arlt W (2015) Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers: Thermophysical and Thermochemical Studies of Carbazole Partly and Fully Hydrogenated Derivatives. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:7953–7966. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b01841
Toebes ML, van Dillen JA, de Jong KP (2001) Synthesis of supported palladium catalysts. J Mol Catal A Chem 173:75–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(01)00146-7
Verevkin SP, Siewert R, Pimerzin AA (2020) Furfuryl alcohol as a potential liquid organic hydrogen carrier (LOHC): Thermochemical and computational study. Fuel 266:117067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117067
Wang Y, Tao Z, Wu B, Xu J, Huo C, Li K, Chen H, Yang Y, Li Y (2015) Effect of metal precursors on the performance of Pt/ZSM-22 catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. J Catal 322:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2014.11.004
Wang B, Yan T, Chang T, Wei J, Zhou Q, Yang S, Fang T (2017) Palladium supported on reduced graphene oxide as a high-performance catalyst for the dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole. Carbon 122:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.06.021
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Neyts EC, Cao X, Zhang X, Jang BWL, C-j L (2018) Catalyst Preparation with Plasmas: How Does It Work? ACS Catal 8:2093–2110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b03723
Wang B, T-y C, Jiang Z, J-j W, Fang T (2019) Component controlled synthesis of bimetallic PdCu nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide for dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole. Appl Catal B Environ 251:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.071
Wang B, Chen YT, Chang TY, Jiang Z, Huang ZQ, Wang SY, Chang CR, Chen YS, Wei JJ, Yang S, Fang T (2020a) Facet-dependent catalytic activities of Pd/rGO: exploring dehydrogenation mechanism of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole. Appl Catal B Environ 266:118658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118658
Wang J, Liu H, Fan S, Li W, Li Z, Yun H, Xu X, Guo A, Wang Z (2020b) Size-Dependent Catalytic Cyclohexane Dehydrogenation with Platinum Nanoparticles on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon. Energy Fuel 34:16542–16551. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c03085
Wang Q, Tao H, Li Z, Wang G (2020c) Effect of iron precursor on the activity and stability of PtFe/C catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J Alloys Compd 814:152212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152212
Wu Y, Peng Y, Jiang X, Zeng H, Wang Z, Zheng J, Li X (2021) Reversible hydrogenation of AB2-type Zr–Mg–Ni–V based hydrogen storage alloys. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International 31:319–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2021.01.008
Wulf C, Zapp P (2018) Assessment of system variations for hydrogen transport by liquid organic hydrogen carriers. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:11884–11895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.198
Xia C, Liu Y, Zhou S, Yang C, Liu S, Guo S, Liu Q, Yu J, Chen J (2009) The influence of ion effects on the Pd-catalyzed hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solutions. Catal Commun 10:1443–1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2009.03.018
Xie Y, Milstein D (2019) Pd Catalyzed, Acid Accelerated, Rechargeable, Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier System Based on Methylpyridines/Methylpiperidines. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2:4302–4308. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b00523
Xie Y-h et al (2015) Mechanistic aspects of formation of sintering-resistant palladium nanoparticles over SiO2 prepared using Pd(acac)2 as precursor. Appl Catal A Gen 504:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.008
Xue W, Liu H, Mao B, Liu H, Qiu M, Yang C, Chen X, Sun Y (2020) Reversible hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of N-ethylcarbazole over bimetallic Pd-Rh catalyst for hydrogen storage. Chem Eng J 421:127781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127781
Yang M, Han C, Ni G, Wu J, Cheng H (2012) Temperature controlled three-stage catalytic dehydrogenation and cycle performance of perhydro-9-ethylcarbazole. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:12839–12845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.05.092
Yang M, Dong Y, Fei S, Ke H, Cheng H (2014) A comparative study of catalytic dehydrogenation of perhydro-N-ethylcarbazole over noble metal catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:18976–18983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.09.123
Yang X, Wu Y, Yu H, Sun M, Zheng J, Li X, Lin W, Wu Y (2020) A YH3 promoted palladium catalyst for reversible hydrogen storage of N-ethylcarbazole. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:33657–33662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.043
Yoshii K, Oshino Y, Tachikawa N, Toshima K, Katayama Y (2015) Electrodeposition of palladium from palladium(II) acetylacetonate in an amide-type ionic liquid. Electrochem Commun 52:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2015.01.003
Yu H, Yang X, Jiang X, Wu Y, Chen S, Lin W, Wu Y, Xie L, Li X, Zheng J (2021) LaNi5.5 particles for reversible hydrogen storage in N-ethylcarbazole. Nano Energy 80:105476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105476
Zhang X, Du Y, Jiang H, Liu Y, Chen R (2019) Matching Relationship Between Carbon Material and Pd Precursor. Catal Lett 149:813–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2630-y
Zhang J, Wang H, Zhao Q, Di L, Zhang X (2020) Facile synthesis of PdAu/C by cold plasma for efficient dehydrogenation of formic acid. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:9624–9634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.196
Zhu M, Xu L, Du L, An Y, Wan C (2018) Palladium Supported on Carbon Nanotubes as a High-Performance Catalyst for the Dehydrogenation of Dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole. Catalysts 8:638. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120638
Zore UK, Yedire SG, Pandi N, Manickam S, Sonawane SH (2021) A review on recent advances in hydrogen energy, fuel cell, biofuel and fuel refining via ultrasound process intensification. Ultrason Sonochem 73:105536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105536
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program (2018YFE0108800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21676074), and the Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Academy of Sciences (KY2020SH01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Zhaolu Feng, Xiaomin Chen, and Xuefeng Bai. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zhaolu Feng and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conceptualization: Xuefeng Bai and Zhaolu Feng; Methodology: Zhaolu Feng; Formal analysis and investigation: Zhaolu Feng; Writing - original draft preparation: Zhaolu Feng; Writing—review and editing: Xuefeng Bai; Funding acquisition: Xuefeng Bai; Resources: Xuefeng Bai; Supervision: Xuefeng Bai and Xiaomin Chen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 795 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Chen, X. & Bai, X. Hydrogen production from the catalytic dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole: effect of Pd precursor on the catalytic performance of Pd/C catalysts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 61623–61635 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15108-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15108-6