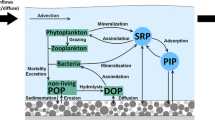
Abstract
Substantial particulates and phosphorus (P) loads are carried into the reservoir by flood runoff and the P exchange between water and settling particulates under variable water conditions in the reservoir after flooding is critical to the removal of active P from water. To investigate the impact of particulate sedimentation on P changes in reservoir water, runoff samples were collected at four locations in the upstream channels of two reservoirs after a rainstorm. Two batches of particulate sedimentation simulations were conducted separately in four plexiglass columns to analyze the changes of water P and environmental factors during particulate sedimentation. The results showed that the contents of total P (TP), total particulates P (TPP), and phosphate (PO43−) decreased with the settlement of particulates. The correlation between the environmental factors and the amount of PO43− in water changed from uncorrelated to correlated with particulate settlement, implying that the rapid settling of particulates might weaken the effect of environmental factors on P exchange between water and particulates. Particulates firstly release PO43− rapidly in river or reservoir and then adsorb PO43− slowly during settlement in reservoirs. Coarse particulates release more and adsorb less PO43− during settlement, and fine particulates play an important role in the removal of water PO43− due to the slow sedimentation rates. Therefore, to mitigate the reactive P content of reservoir water, the loss of coarse particulates from the watershed should be controlled, and the discharge of water with particulates downstream should also be avoided during the flood season.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The grant numbered 51879031 funded the sample collection, experimental devices, data analysis, and paper writing, while another grant numbered 51327004 funded the sample analysis.
References
Ahlgren J, Reitzel K, De Brabandere H, Gogoll A, Rydin E (2011) Release of organic P forms from lake sediments. Water Res 45(2):565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.020
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American public health association, America
Azadi F, Ashofteh PS, Loaiciga HA (2019) Reservoir water-quality projections under climate-change conditions. Water Resour Manag 33(1):401–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2109-z
Bao LL, Li XY, Cheng P (2018) Phosphorus retention along a typical urban landscape river with a series of rubber dams. J Environ Manag 228:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.019
Barrow NJ (1979) The effects of temperature on the reactions between inorganic-phosphate and soil. J Soil Sci 30(2):271–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1979.tb00984.x
Bilotta GS, Brazier RE (2008) Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res 42(12):2849–2861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.03.018
Boers PCM (1991) The influence of pH on phosphate release from lake sediments. Water Res 25(3):309–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90010-N
Brookes PC, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14(4):319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(82)90001-3
Cao CJ, Qin YW, Zheng BH, Huang MS (2008) Analysis of phosphorus distribution characters and their sources of the major input rivers of Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Sci 29(2):310–315 In Chinese
Christophoridis C, Fytianos K (2006) Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. J Environ Qual 35(4):1181–1192. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2005.0213
Currie DJ, Kalff J (1984) A comparison of the abilities of fresh-water algae and bacteria to acquire and retain phosphorus. Limnol Oceanogr 29(2):298–310. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1984.29.2.0298
Danz ME, Corsi SR, Graczyk DJ, Bannerman RT (2010) Characterization of suspended solids and total phosphorus loadings from small watersheds in Wisconsin, Southeastern Wisconsin Till Plains Ecoregion. US Geol Surv Sci Investig Rep 2010–5039, p 15
Devault DA, Gerino M, Laplanche C, Julien F, Winterton P, Merlina G et al (2009) Herbicide accumulation and evolution in reservoir sediments. Sci Total Environ 407(8):2659–2665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.064
Elci S (2008) Effects of thermal stratification and mixing on reservoir water quality. Limnology 9(2):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-008-0240-x
Furumai H, Ohgaki S (1989) Adsorption desorption of phosphorus by lake sediments under anaerobic conditions. Water Res 23(6):677–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(89)90199-1
Han CN, Zheng BH, Qin YW, Ma YQ, Yang CC, Liu ZC, Cao W, Chi M (2018) Impact of upstream river inputs and reservoir operation on phosphorus fractions in water-particulate phases in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci Total Environ 610:1546–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.109
Haygarth PM, Bilotta GS, Bol R, Brazier RE, Butler PJ, Freer J, Gimbert LJ, Granger SJ, Krueger T, Macleod CJA, Naden P, Old G, Quinton JN, Smith B, Worsfold P (2006) Processes affecting transfer of sediment and colloids, with associated phosphorus, from intensively farmed grasslands: an overview of key issues. Hydrol Process 20(20):4407–4413. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6598
Huang BQ, Hong HS (1999) Alkaline phosphatase activity and utilization of dissolved organic phosphorus by algae in subtropical coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 39(1–12):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(99)00006-5
Huang LD, Fu LL, Jin CW, Gielen G, Lin XY, Wang HL, Zhang YS (2011) Effect of temperature on phosphorus sorption to sediments from shallow eutrophic lakes. Ecol Eng 37(10):1515–1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.05.006
Huang TL, Li X, Rijnaarts H, Grotenhuis T, Ma WX, Sun X, Xu JL (2014) Effects of storm runoff on the thermal regime and water quality of a deep, stratified reservoir in a temperate monsoon zone, in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 485:820–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.008
Hupfer M, Lewandowski J (2008) Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments-a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. Int Rev Hydrobiol 93(4–5):415–432. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.200711054, 415
Istvanovics V (1994) Fractional composition, adsorption and release of sediment phosphorus in the Kis-Balaton reservoir. Water Res 28(3):717–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90152-X
James WF, Best EP, Barko JW (2004) Sediment resuspension and light attenuation in Peoria Lake: can macrophytes improve water quality in this shallow system? Hydrobiologia 515(1–3):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000027328.00153.b2
Jin XC, Wang SR, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006a) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 139(2):288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.05.010
Jin XC, Jiang X, Yao Y, Li LH, Wu FC (2006b) Effects of light and oxygen on the uptake and distribution of phosphorus at the sediment-water interface. Sci Total Environ 357(1–3):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.027
Kalff K (2002) Limnology. In: Inland water ecosystems. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, N.J.
Kang MX, Peng S, Tian YM, Zhang HY (2018) Effects of dissolved oxygen and nutrient loading on phosphorus fluxes at the sediment–water interface in the Hai River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 130:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.03.029
Kiedrzynska E, Kiedrzynski M, Zalewski M (2008) Flood sediment deposition and phosphorus retention in a lowland river floodplain: impact on water quality of a reservoir, Sulejow, Poland. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 8(2–4):281–289. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10104-009-0022-z
Kim LH, Choi E, Stenstrom MK (2003) Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere 50(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00310-7
Lai DYF, Lam KC (2009) Phosphorus sorption by sediments in a subtropical constructed wetland receiving stormwater runoff. Ecol Eng 35(5):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.11.009
Li X, Huang TL, Ma WX, Sun X, Zhang HH (2015) Effects of rainfall patterns on water quality in a stratified reservoir subject to eutrophication: implications for management. Sci Total Environ 521:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.062
Liu M, Zhang YL, Shi K, Zhu GW, Wu ZX, Liu ML, Zhang YB (2019) Thermal stratification dynamics in a large and deep subtropical reservoir revealed by high-frequency buoy data. Sci Total Environ 651:614–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.215
Llebot C, Spitz YH, Sole J, Estrada M (2010) The role of inorganic nutrients and dissolved organic phosphorus in the phytoplankton dynamics of a Mediterranean bay A modeling study. J Mar Syst 83(3–4):192–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.06.009
Lopez P, Lluch X, Vidal M, Morgui JA (1996) Adsorption of phosphorus on sediments of the Balearic Islands (Spain) related to their composition. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42(2):185–196. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.1996.0014
Ma WX, Huang TL, Li X, Zhang HH, Ju T (2015) Impact of short-term climate variation and hydrology change on thermal structure and water quality of a canyon-shaped, stratified reservoir. Environ Sci Pollut R 22(23):18372–18380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4764-4
Maavara T, Parsons CT, Ridenour C, Stojanovic S, Durr HH, Powley HR, Van Cappellen P (2015) Global phosphorus retention by river damming. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(51):15603–15608. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511797112
Miller MP (2012) The influence of reservoirs, climate, land use and hydrologic conditions on loads and chemical quality of dissolved organic carbon in the Colorado River. Water Resour Res 48(12):810–830. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR012312
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 26(1):31–36
Naoml ED, Patrick LB (1991) Phosphorus sorption by sediments from a soft-water seepage lake. 1. An evaluation of kinetic and equilibrium models. Environ Sci Technol 25(3):395–403. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00015a003
Oglesby RT, Schaffner WR (1978) Phosphorus loadings to lakes and some of their responses. 2. Regression-models of summer phytoplankton standing crops, winter total P, and transparency of New-York lakes with known phosphorus loadings. Limnol Oceanogr 23(1):135–145. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1978.23.1.0135
Owens PN, Batalla RJ, Collins AJ, Gomez B, Hicks DM, Horowitz AJ, Kondolf GM, Marden M, Page MJ, Peacock DH, Petticrew EL, Salomons W, Trustrum NA (2005) Fine-grained sediment in river systems: environmental significance and management issues. River Res Appl 21(7):693–717. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.878
Peterson BJ (1971) The role of zooplankton in the phosphorus cycle of Cayuga Lake. Dissertation, Cornell University
Qian B, Liu L, Xiao X, Chen LY (2013) The effect of environmental micro-interface on internal phosphorus release of the lake. J Hydraul Eng 44(3):295–301 In Chinese
Romero JR, Imberger J (2003) Effect of a flood underflow on reservoir water quality: Data and three-dimensional modeling. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 157(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2003/0157-0001
Sah RN, Mikkelsen DS (1986) Effects of temperature and prior flooding on intensity and sorption of phosphorus in soil. II Effects P Sorption Plant Soil 95(2):173–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375069
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (2003) Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506-509(1–3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008611.12704.dd
Urbaniak M, Kiedrzynska E, Zielinski M, Toloczko W, Zalewski M (2014) Spatial distribution and reduction of PCDD/PCDF Toxic Equivalents along three shallow lowland reservoirs. Environ Sci Pollut R 21(6):4441–4452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2401-7
Wang SR, Jin XC, Bu QY, Zhou XN, Wu FC (2006) Effects of particle size, organic matter and ionic strength on the phosphate sorption in different trophic lake sediments. J Hazard Mater 128(2-3):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.07.048
Wang SR, Jin XC, Bu QY, Hao LX, Wu FC (2008) Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloid Surf A 316(1–3):245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.09.007
Wang QJ, Wang SH, Jin XC, Li YF (2010) Characteristic analysis of the adsorption/desorption of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediments of Taihu Lake. Environ Sci 32(05):1285–1291. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.05.027
Wang TX, Liu JW, Xu SG, Qin GS, Sun Y, Wang FQ (2017) Spatial distribution, adsorption/release characteristics, and environment influence of phosphorus on sediment in reservoir. Water 9(9):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090724
Wu YH, Wang XX, Zhou J, Bing HJ, Sun HY, Wang JP (2016) The fate of phosphorus in sediments after the full operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Pollut 214:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.029
Yajima H, Choi JK (2013) Changes in phytoplankton biomass due to diversion of an inflow into the Urayama Reservoir. Ecol Eng 58:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.06.030
Yamamoto T, Oh SJ, Kataoka Y (2004) Growth and uptake kinetics for nitrate, ammonium and phosphate by the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum isolated from Hiroshima Bay, Japan. Fish Sci 70(1):108–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2003.00778.x
Yao QZ, Du JT, Chen HT, Yu ZG (2016) Particle-size distribution and phosphorus forms as a function of hydrological forcing in the Yellow River. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(4):3385–3398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5567-3
Yao LA, Zhao XM, Ma QL, Liang RC, Xia BC, Gou T (2018a) Simulation of the impact of Typhoon-induced suspended solids precipitation on water quality in a reservoir for drinking water. Ecol Environ Sci 27(10):1900–1907 In Chinese
Yao LA, Zhao XM, Ma QL, Liang RC, Xia BC, Zhou QF (2018b) Nitrogen and phosphorus adsorption characteristics of suspended solids input into a drinking water reservoir via typhoon Heavy rainfall. Environ Sci 39(8):3622–3630 In Chinese
Yu HJ, Xu SG, Tian W, Zhu L, Sun Y (2019) Impact of long-term water level fluctuation on the distribution, transport, and fate of phosphorus in reservoir sediment. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(32):33146–33156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06415-0
Yu HJ, Xu SG, Tian W, Zhu TX, Chen XQ (2021) Flood impact on the transport, transition, and accumulation of phosphorus in a reservoir: a case study of the Biliuhe Reservoir of Northeast. Environ Pollut 268(Pt B):115725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115725
Zhang Z, Wang LL, Zeng XL, Lu PY (2006) Influence of the suspended sediment on the related factors of Yangtze river’s eutrophication. Ecol Environ 15(3):457–460 In Chinese
Zhang Z, Zeng XL, Wang LL, Lu PY (2007) The influence of sediment subsiding on the index of the reservoir eutrophication. China Environ Sci 27(2):213–216 In Chinese
Zhang B, Fang F, Guo JS, Chen YP, Li Z, Guo SS (2012) Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics relevant to the soil composition of water-level-fluctuating zone of Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol Eng 40:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.12.024
Zhou XY (2020) Study on the effect of soil composition, sterilization and inoculation on soil organic carbon mineralization and their mechanisms. Zhejiang University. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Gao G, Zhang L, Luo LC, Zhang YL (2007) Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 581:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0519-z
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51879031, 51327004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Huijuan Yu, Shiguo Xu, and Weijia Li. The supervision was performed by Shiguo Xu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Huijuan Yu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2.67 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Xu, S., Li, W. et al. Removal process of phosphorus during the settlement of particulates with runoff and its implication for reservoir management. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 49588–49601 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14137-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14137-5