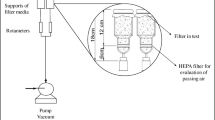
Abstract
Two polypropylene HVAC electret filters: a regular filter and an antimicrobial filter containing zinc pyrithione (ZPT), were compared for filtration performance. The study was conducted over 7 months in realistic conditions with semi-urban outdoor air. Several parameters were monitored over the study period: the average temperature was about 20 °C and relative humidity about 60%, the average inlet concentration of cultivable microorganisms was 50 CFU m−3, the average inlet concentration of particles was 10 μg m−3, the filter pressure drop increased moderately by about 30 Pa, and the particle collection efficiency of soda fluorescein (median diameter 0.35 μm) decreased in the first half of the study period by about 30% and then stabilized. The microbial concentration on the filters was quantified every 2 months using an innovative methodology based on media coupons in conjunction with microorganism quantification by CFU counting, with 5 culture media favorable to bacteria and/or fungi growth. The microbial concentrations on the filters were between 100 and 2000 CFU cm−2. The antimicrobial effect of zinc pyrithione was confirmed by the fungi cultivated with DRBC agar: no effects in the level of filter clogging were revealed in the range studied. The high statistical deviation in the results regarding the inhibiting effect of zinc pyrithione on bacteria prevents any conclusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balagna C, Perero S, Bosco F, Mollea C, Irfan M, Ferraris M (2020) Antipathogen nanostructured coating for air filters. Appl Surf Sci 508:145283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145283
Batterman SA, Burge H (1995) HVAC Systems. As emission sources affecting indoor air quality: A Critical Review. HVACR Res 1:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10789669.1995.10391309
Baxi SN, Portnoy JM, Larenas-Linnemann D, Phipatanakul W, Barnes C, Baxi S, Grimes C, Horner WE, Kennedy K, Larenas-Linnemann D, Levetin E, Miller JD, Phipatanakul W, Portnoy JM, Scott J, Williams PB (2016) Exposure and health effects of fungi on humans. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 4:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2016.01.008
Black WD (2020) A comparison of several media types and basic techniques used to assess outdoor airborne fungi in Melbourne, Australia. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.27.269704
Bluyssen PM, Cox C, Seppänen O, Oliveira Fernandes E, Clausen G, Müller B, Roulet CA (2003) Why, when and how do HVAC-systems pollute the indoor environment and what to do about it? The European AIRLESS project. Build Environ 38:209–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1323(02)00058-6
Chegini FM, Baghani AN, Hassanvand MS, Sorooshian A, Golbaz S, Bakhtiari R, Ashouri A, Joubani MN, Alimohammadi M (2020) Indoor and outdoor airborne bacterial and fungal air quality in kindergartens: Seasonal distribution, genera, levels, and factors influencing their concentration. Build Environ 175:106690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106690
Choi DY, Heo KJ, Kang J, An EJ, Jung SH, Lee BU, Lee HM, Jung JH (2018) Washable antimicrobial polyester/aluminum air filter with a high capture efficiency and low pressure drop. J Hazard Mater 351:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.043
Chow PK, Chan WY, Vrijmoed LLP (2005) An investigation on the occurrence of fungi and bacteria in the MVAC system in an office premise. Proceedings of indoor air 2005 – the 10th international conference on indoor air quality and climate, vol 1–5. Tsinghua University Press, pp. 1096–1100
European Council, Council of the European Union (2013) The clean air package: Improving Europe’s air quality. https://europa.eu/!Fp96YH. Accessed 20 Apr 2020
Forthomme A, Joubert A, Andres Y et al (2014) Microbial aerosol filtration: growth and release of a bacteria-fungi consortium collected by fibrous filters in different operating conditions. J Aerosol Sci 72:32–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2014.02.004
González LF, Joubert A, Andrès Y, Liard M, Renner C, le Coq L (2016) Filtration performances of HVAC filters for PM10 and microbial aerosols - Influence of management in a lab-scale air handling unit. Aerosol Sci Technol 50:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2016.1167833
Gustavsson J, Ginestet A, Tronville P, Hyttinen M (2010) Air filtration in HVAC systems. REHVA guidebook 11 federation of european heating, ventilation and air-conditioning associations, Brussels
Hamada N, Fujita T (2002) Effect of air-conditioner on fungal contamination. Atmos Environ 36:5443–5448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00661-1
Jung JH, Lee JE, Bae G-N (2013) Use of electrosprayed Sophora flavescens natural-product nanoparticles for antimicrobial air filtration. J Aerosol Sci 57:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2012.09.004
Kemp SJ, Kuehn TH, Pui DYH, Vesley D, Streifel AJ (1995) Growth of Microorganisms on HVAC filters under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. ASHRAE Transactions, (1), 305–316
Klepeis NE, Nelson WC, Ott WR et al (2001) The national human activity pattern survey (NHAPS): a resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 11:231–252. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500165
Kwan SE, Shaughnessy R, Haverinen-Shaughnessy U, Kwan TA, Peccia J (2020) The impact of ventilation rate on the fungal and bacterial ecology of home indoor air. Build Environ 106800:106800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106800
Li A, Xiong J, Yao L, Gou L, Zhang W (2016) Determination of dust and microorganism accumulation in different designs of AHU system in Shaanxi History Museum. Build Environ 104:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.05.014
Li S, Chen D-R, Zhou F, Chen S-C (2020) Effects of relative humidity and particle hygroscopicity on the initial efficiency and aging characteristics of electret HVAC filter media. Build Environ 171:106669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106669
Liu Z, Li A, Hu Z, Sun H (2014) Study on the potential relationships between indoor culturable fungi, particle load and children respiratory health in Xi’an, China. Build Environ 80:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.05.029
Liu Z, Ma S, Cao G, Meng C, He BJ (2018) Distribution characteristics, growth, reproduction and transmission modes and control strategies for microbial contamination in HVAC systems: a literature review. Energy Build 177:77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.07.050
Maus R, Goppelsröder A, Umhauer H (2001) Survival of bacterial and mold spores in air filter media. Atmos Environ 35:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00280-6
Meng J, Barnes CS, Rosenwasser LJ (2012) Identity of the fungal species present in the homes of asthmatic children. Clin Exp Allergy 42:1448–1458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2012.04001.x
Mohamed EF, Awad G (2020) Photodegradation of gaseous toluene and disinfection of airborne microorganisms from polluted air using immobilized TiO2 nanoparticle photocatalyst–based filter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:24507–24517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08779-0
Morisseau K, Joubert A, Coq L, Andres Y (2016) Quantification of the fungal fraction released from various preloaded fibrous filters during a simulated ventilation restart. Indoor Air 27:27–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12330
Nakpan W, Yermakov M, Indugula R, Reponen T, Grinshpun SA Inactivation of bacterial and fungal spores by UV irradiation and gaseous iodine treatment applied to air handling filters. Sci Total Environ 671:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.310
Neas LM, Dockery DW, Burge H, Koutrakis, Speizer FE (1996) Fungus spores, air pollutants, and other determinants of peak expiratory flow rate in children. Am J Epidemiol 143:797–807. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008818
Noris F, Siegel J, Kinney K (2011) Evaluation of HVAC filters as sampling mechanism for indoor microbial communities. Atmos Environ 45:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.10.017
Seppänen O, Fisk WJ (2002) Association of ventilation system type with SBS symptoms in office workers. Indoor Air 12:98–112. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0668.2002.01111.x
Simmons RB, Crow SA (1995) Fungal colonization of air filters for use in heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. J Ind Microbiol 14:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570065
Tronville P, Rivers R (2012) Looking for the minimum efficiency of fibrous air filters during their service life. Proceedings of 11th world filtration congress, Graz - Austria, 16–20
Verdenelli MC, Cecchini C, Orpianesi C, Dadea GM, Cresci A (2003) Efficacy of antimicrobial filter treatments on microbial colonization of air panel filters. J Appl Microbiol 94:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.01820.x
Viegas C, Dias M, Carolino E, Sabino R (2021) Culture media and sampling collection method for Aspergillus spp. Assessment: Tackling the Gap between Recommendations and the Scientific Evidence. Atmosphere 2021(12):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010023
Wargocki P, Sundell J, Bischof W, Brundrett G, Fanger PO, Gyntelberg F, Hanssen SO, Harrison P, Pickering A, Seppänen O, Wouters P (2002) Ventilation and health in non-industrial indoor environments: report from a European Multidisciplinary Scientific Consensus Meeting (EUROVEN). Indoor Air 12:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0668.2002.01145.x
Yoon C, Lee K, Park D (2011) Indoor air quality differences between urban and rural preschools in Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0377-0
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge the Lydall© Company for supplying the filtering media.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
Partial financial support was received from the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Iraq according to the Franco-Iraq convention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Andrès, Joubert; Methodology: Andrès, Joubert; Formal analysis and investigation: Abd Ali, Andrès, Joubert; writing—original draft preparation: Joubert, Abd Ali; writing—review and editing: Frossard; Supervision: Andrès, Joubert.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The article has been prepared in accordance with the Guide for Authors and particularly the Ethics in Publishing Policy.
Consent for publication
All authors adhere to the guidelines for authorship that are mentioned in the Guide for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joubert, A., Abd Ali, S.A.Z., Frossard, M. et al. Dust and microbial filtration performance of regular and antimicrobial HVAC filters in realistic conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 39907–39919 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13330-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13330-w