Abstract
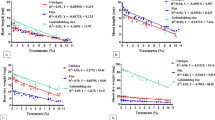
Rice cultivation, particularly prone to weed issues, requires practices able to effectively control them, however reducing the use of herbicides, responsible for damage to human health and ecosystem sustainability. Alternative strategies for weed management can be based on plant-plant interaction phenomena. In this context, a group of organic farmers has developed a pragmatic approach for weed containment using Lolium multiflorum Lam. as a cover crop before rice. The present study aimed to confirm the farmer field observations reporting a preferential inhibitory effect of L. multiflorum on Echinochloa oryzoides (Ard.) Fritsch, one of the most yield-damaging rice weed, compared with Oryza sativa L. The study showed that L. multiflorum was able to significantly reduce the seed germination of E. oryzoides. It was found to be more susceptible than O. sativa both to the effect of the aqueous extract and powder of L. multiflorum leaves (23–79% vs. 3–57% and 26–100% vs. 23–31%, respectively). In addition, the leaf extract was able to affect E. oryzoides growth starting from 20% concentration both in relation to the root and shoot length while O. sativa exhibited differences compared with the control only under the influence of extract 50%. The L. multiflorum leaf characterization by NMR and UPLC-HR-MS analyses led to the identification of 35 compounds including several polyphenols, glycosyl flavonoids and glycosyl terpenoids, as well as different amino acids and organic acids. Some of them (e.g. protocatechuic and gallic acids) are already known as allelochemicals confirming that L. multiflorum is a source of plant growth inhibitors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 July 2020
In the title, it should be Oryza instead of Oriza.
References
Abdul-Baki AA, Anderson JD (1973) Vigour determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Sci 13:630–633. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1973.0011183X001300060013x
Altop EK, Mennan H, Streibig JC, Budak U, Ritz C (2014) Detecting ALS and ACCase herbicide tolerant accession of Echinochloa oryzoides (Ard.) Fritsch. In rice (Oryza sativa L.) fields. Crop Prot 65:202–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2014.07.011
Amigoni L, Stuknytė M, Ciaramelli C, Magoni C, Bruni I, De Noni I, Airoldi C, Regonesi ME, Palmioli A (2017) Green coffee extract enhances oxidative stress resistance and delays aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Funct Foods 33:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.056
Awan TH, Cruz PCS, Chauhan BS (2015) Ecological significance of rice (Oryza sativa) planting density and nitrogen rates in managing the growth and competitive ability of itchgrass (Rottboellia cochinchinensis) in direct-seeded rice systems. J Pest Sci 88(2):427–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0604-4
Bastiaans L, Paolini R, Baumann DT (2008) Focus on ecological weed management. What is hindering adoption? Weed Res 48:481–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.2008.00662.x
Chen L, Yang XG, Wang L, Song NP (2017) Allelopathic effects of Caragana intermedia on monocot and dicot plant species and identification of allelochemicals. Allelopath J 42:251–262. https://doi.org/10.26651/allelo.j/2017-42-2-1121
Cobas C, Seoane F, Domínguez S, Sykora S, Davies (2011) A new approach to improving automated analysis of proton NMR spectra through Global Spectral Deconvolution (GSD). Spectrosc Eur 23:26–30. https://doi.org/10.3247/sl2nmr08.011
Delmotte S, Tittonell P, Mouret JC, Hammond R, Lopez-Ridaura S (2001) On farm assessment of rice yield variability and productivity gaps between organic and conventional cropping systems under Mediterranean climate. Europ J Agr 35:223–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2011.06.006
Directive 79/117/EE (1979) https://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:1979L0117:20040520:EN:PDF.
Directive 91/414/CEE (1991). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A31991L0414.
Ellis RA, Roberts EH (1981) The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds. Seed Sci Technol 9:373–409. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2012.37063
Favaretto A, Scheffer-Basso SM, Perez NB (2018) Allelopathy in Poaceae species present in Brazil. A review Agron Sustain Dev 38:22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-018-0495-5
Fischer AJ, Ateh CM, Bayer DE, Hill JE (2000) Herbicide-resistant Echinochloa oryzoides and E. phyllopogon in California Oryza sativa fields. Weed Sci 48:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1614/0043-1745(2000)048[0225:HREOAE]2.0.CO;2
Gibson KD, Fischer AJ, Foin TC, Hill JE (2002) Implications of delayed Echinochloa spp. germination and duration of competition for integrated weed management in water-seeded rice. Weed Res 42:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3180.2002.00295.x
Hazra KK, Swain DK, Bohra A, Singh SS, Kumar N, Nath CP (2018) Organic rice: potential production strategies, challenges and prospects. Org Agric 8:39–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-016-0172-4
Ispra (2018). https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files2018/pubblicazioni/rapporti/Rapporto_282_2018.pdf
Jang SJ, Kim KR, Yun YB, Kim SS, Kuk YI (2018a) Inhibitory effects of Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Allelopath J 44:219–232. https://doi.org/10.26651/allelo.j/2018-44-2-1165
Jang SJ, Beom YY, Kim YJ, Kuk YI (2018b) Effects of downy brome (Bromus tectorum L.) and Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) on growth inhibition of wheat and weeds. Philipp Agric Sci 101:20–27
Jose CM, Jose, Brandão Torres LM, Torres MAMG, Shirasuna RT, Farias DA, dos Santos Jr. NA, Grombone-Guaratini MT (2016) Phytotoxic effects of phenolic acids from Merostachys riedeliana, a native and overabundant Brazilian bamboo. Chemoecology 26:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04732-4_6
Kadioglu I, Yanar Y (2004) Allelopathic effects of plant extracts against seed germination of some weeds. Asian J Plant Sci 3:472–475. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2004.472.475
Kim KH, Kabir E, Jahan SA (2017) Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci Total Environ 575:525–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.009
Lehoczky E, Nelima MO, Szabó R, Szalai A, Nagy P (2011) Allelopathic effect of Bromus spp. and Lolium spp. shoot extracts on some crops. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 76:537–544
Li G, Zeng RS, Li H, Yang Z, Xin G, Yuan J, Luo Y (2008a) Allelopathic effects of decaying Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum lam.) residues on rice. Allelopath J 22:15–23
Li GX, Li HJ, Yang Z, Xin G, Tang XR, Yuan JG (2008b) The rhizosphere effects in “Italian ryegrass-rice” rotational system V. evidences for the existence of rice stimulators in decaying products of Italian ryegrass residues. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunyatseni 47:88–93
Li ZH, Wang Q, Ruan X, Pan CD, Jiang DA (2010) Phenolics and plant allelopathy. Molecules 15:8933–8952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15128933
Malik MS, Burgos NR, Talbert RE (2010) Confirmation and control of propanil-resistant and quinclorac-resistant barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) in rice. Weed Technol 24:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1614/WT-09-053.1
Lim CJ, Basri M, Ee GCL, Omar D (2017) Phytoinhibitory activities and extraction optimization of potent invasive plants as eco-friendly weed suppressant against Echinochloa colona (L.) link. Ind Crop Prod 100:19–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.01.025
Orlando F, Alali S, Vaglia V, Pagliarino E, Bacenetti J, Network OR, Bocchi S (2020) Participatory approach for developing knowledge on organic rice farming: management strategies and productive performance. Agric Syst 178:102739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102739
Palmioli A, Airoldi C (2019) SMA libraries for metabolite identification and quantification in Lolium multiflorum extracts. Mendeley Data V2. https://doi.org/10.17632/pxyk95g5j6.2
Palmioli A, Bertuzzi S, De Luigi A, Colombo L, La Ferla B, Salmona M, De Noni I, Airoldi C (2019) bioNMR-based identification of natural anti-Aβ compounds in Peucedanum ostruthium. Bioorg Chem 83:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.10.016
Pignatti S (1982) Flora d’Italia. Edagricole, Bologna (Italy)
Ravazi SM (2011) Plant coumarins as allelopathic agents. Int J Biol Chem 5:86–90. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijbc.2011.86.90
Shennan C, Krupnik TJ, Baird G, Cohen H, Forbush K, Lovell RJ, Olimpi EM (2017) Organic and conventional agriculture: a useful framing? Annu Rev Environ Resour 42:317–346. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-110615-085750
Stoop WA, Adam A, Kassam A (2009) Comparing rice production systems: a challenge for agronomic research and for the dissemination of knowledge-intensive farming practices. Agric Water Manag 96:1491–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2009.06.022
Synowiec A, Kalemba D, Drozdek E, Bocianowski J (2017) Phytotoxic potential of essential oils from temperate climate plants against the germination of selected weeds and crops. J Pest Sci 90:407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-016-0759-2
Tabaglio V, Marocco A, Schulz M (2013) Allelopathic cover crop of rye for integrated weed control in sustainable agroecosystems. Ital J Agron 8:e5. https://doi.org/10.4081/ija.2013.e5
Talbert RE, Burgos NR (2007) History and management of herbicide-resistant barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) in Arkansas rice. Weed Technol 21:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1614/WT-06-084.1
Teasdale JR (1996) Contribution of cover crops to weed management in sustainable agricultural system. J Prod Agric 9:475–479. https://doi.org/10.2134/jpa1996.0475
Vitalini S, Orlando F, Vaglia V, Bocchi S, Iriti M (2020) Potential role of Lolium multiflorum Lam. in the management of rice weeds. Plants 9:324. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030324
Wezel A, Casagrande M, Celette F, Vian JF, Ferrer A, Peigné J (2014) Agroecological practices for sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0180-7
Wright AA, Rodriguez-Carres M, Sasidharan R, Koski L, Peterson DG, Nandula VK, Ray JD, Bond JA, Shaw DR (2018) Multiple herbicide–resistant junglerice (Echinochloa colona): identification of genes potentially involved in resistance through differential gene expression analysis. Weed Sci 66:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2018.10
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Dr. Stefano Gomarasca for his help in plant identification and seed treatment; all the members of the multi-actor community “RisoBioVero”, the farmers network “Noi Amici della Terra” and the farm “Terre di Lomellina di Rosalia Caimo Duc” for the efforts in promoting the networking, knowledge exchange and dissemination of best practices; the farm “Una Garlanda” as the early pioneer of the practice.
Funding
This research was supported by “Risobiosystems Project” (Italian Ministry Mipaaf funds, for research and innovation in the organic rice sector) and by EcorNaturaSì s.p.a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Stefano Bocchi, Marcello Iriti, Francesca Orlando and Sara Vitalini contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Cristina Airoldi, Sumer Alali, Ivano De Noni, Francesca Orlando, Alessandro Palmioli, Valentina Vaglia and Sara Vitalini. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Cristina Airoldi, Francesca Orlando, Alessandro Palmioli and Sara Vitalini. All authors commented on later versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Giovanni Benelli
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitalini, S., Orlando, F., Palmioli, A. et al. Different phytotoxic effect of Lolium multiflorum Lam. leaves against Echinochloa oryzoides (Ard.) Fritsch and Oriza sativa L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 33204–33214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09573-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09573-8