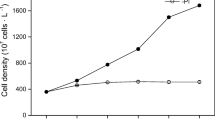
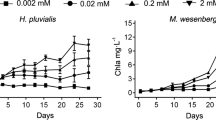
Abstract
Microcystis aeruginosa is one of the most common algae found in eutrophicated water bodies. Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) can be produced by Microcystis aeruginosa to utilize organic phosphates under phosphorus deficiency stress, thereby AKP can be regarded as an important indicator for algal growth. Sulfur compounds are ubiquitous in waters, while investigation on the interactions between sulfur compounds and Microcystis aeruginosa is limited. In this work, we introduced 33 types of sulfur compounds to culture Microcystis aeruginosa, and the results demonstrated that algal growth is positively related to AKP activities. Toxicity of organic sulfur compounds was further evaluated using Toxicity Estimation Software Tool based on quantitative structure-activity relationship prediction. The algal growth results exhibited strong correlation to the toxicity endpoints suggesting the organic sulfur compounds inhibits the algal growth as toxic matters. K-means cluster analyses have been carried out subsequently via Python based on the results of algal growth and AKP activities of each sample and statistically, the sulfur compounds can be adequately clustered into 2 groups. According to clustering results, sulfonic acids exhibit low toxicity while sulfur amino acids can be considered as more toxic compounds.

Varied sulfur compounds (33 types) were investigated to find out the interactions between them and Microcystis aeruginosa, a common alga. K-means cluster and correlation analyses demonstrate that algal growth and alkaline phosphatase activities exhibited strong correlation to the predicted toxicity endpoints.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atekwana EA, Atekwana E, Legall FD, Krishnamurthy RV (2004) Field evidence for geophysical detection of subsurface zones of enhanced microbial activity. Geophys Res Lett:31. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004gl021576
Cai Z, Hao X, Sun X, Du P, Liu W, Fu J (2019) Highly active WO3@anatase-SiO2 aerogel for solar-light-driven phenanthrene degradation: mechanism insight and toxicity assessment. Water Res 162:369–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.017
Caliński T, Harabasz J (1974) A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun Stat 3:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610927408827101
Chauvet C, Menard A, Deng AY (2015) Two candidate genes for two quantitative trait loci epistatically attenuate hypertension in a novel pathway. J Hypertens 33:1791–1801. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000000626
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323:1014–1015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167755
Fu M, Song X, Yu Z, Liu Y (2013) Responses of phosphate transporter gene and alkaline phosphatase in Thalassiosira pseudonana to phosphine. PLoS One 8:e59770. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059770
Fujimoto N, Sudo R, Sugiura N, Inamori Y (1997) Nutrient-limited growth of Microcystis aeruginosa and Phormidium tenue and competition under various N:P supply ratios and temperatures. Limnol Oceanogr 42:250–256
Giordano M, Raven JA (2014) Nitrogen and sulfur assimilation in plants and algae. Aquat Bot 118:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2014.06.012
Guimarães LHS, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Jamur MC, Oliver C (2003) Effect of carbon source on alkaline phosphatase production and excretion in Aspergillus caespitosus. J Basic Microb 43:210–217
Hamelink J (1977) Current bioconcentration test methods and theory. In: Aquatic toxicology and hazard evaluation. vol 634. ASTM International, pp 149–161
Hu H, Mylon SE, Benoit G (2007) Volatile organic sulfur compounds in a stratified lake. Chemosphere 67:911–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.11.012
Huang W, Cao X, Huang DY, Liu WL, Liu X, Zhang JB (2019) Phosphorus characteristics and microbial community in the sediment-water-algal system during algal growth. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:31414–31421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06284-7
Jähnichen S, Long BM, Petzoldt T (2011) Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa: direct regulation by multiple environmental factors. Harmful Algae 12:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.09.002
Jansson M, Olsson H, Pettersson K (1988) Phosphatases: origin, characteristics and function in lakes. Hydrobiologia 170:157–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024903
Kleeberg A (1998) The quantification of sulfate reduction in sulfate-rich freshwater lakes - a means for predicting the eutrophication process of acidic mining lakes? Water Air Soil Poll 108:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005194404417
Li C, Li C, Zhang H, Liao H, Wang X (2017) The purple acid phosphatase GmPAP21 enhances internal phosphorus utilization and possibly plays a role in symbiosis with rhizobia in soybean. Physiol Plantarum 159:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12524
Liu H, Song X, Guan Y, Pan D, Li Y, Xu S, Fang Y (2017) Role of illumination intensity in microcystin development using Microcystis aeruginosa as the model algae. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:23261–23272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9888-2
Long BM (2010) Evidence that sulfur metabolism plays a role in microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 9:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2009.08.003
Mandernack KW, Lynch L, Krouse HR, Morgan MD (2000) Sulfur cycling in wetland peat of the New Jersey Pinelands and its effect on stream water chemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 64:3949–3964. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00491-9
Mitch W, Gosselink J (2000) Wetland (3rd). John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York
Oh H-M, Lee SJ, Jang M-H, Yoon B-D (2000) Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorus-limited chemostat. Appl Environ Microb 66:176–179. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.66.1.176-179.2000
Reynolds CS (1997) Vegetation processes in the pelagic: a model for ecosystem theory vol 9. vol 1
Rodrigues MCA, Guimarães LHS, Liberato JL, de Moraes MLT, dos Santos WF (2006) Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities of a fraction isolated from Parawixia bistriata spider venom. Toxicon 47:854–858
Schindler DW, Carpenter SR, Chapra SC, Hecky RE, Orihel DM (2016) Reducing phosphorus to Curb Lake eutrophication is a success. Environ Sci Technol 50:8923–8929. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02204
Schindler DW, Hecky RE, Findlay DL, Stainton MP, Parker BR, Paterson MJ, Beaty KG, Lyng M, Kasian SE (2008) Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11254–11258. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805108105
Schook LB, Berk RS (1978) Nutritional studies with Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown on inorganic sulfur sources. J Bacteriol 133:1378–1382
Sinha E, Michalak AM, Balaji V (2017) Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 357:405–408. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan2409
Song C, Søndergaard M, Cao X, Zhou Y (2018) Nutrient utilization strategies of algae and bacteria after the termination of nutrient amendment with different phosphorus dosage: a mesocosm case. Geomicrobiol J 35:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2017.1350890
Takahashi H, Kopriva S, Giordano M, Saito K, Hell R (2011) Sulfur assimilation in photosynthetic organisms: molecular functions and regulations of transporters and assimilatory enzymes. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:157–184. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103921
Wang X, Xiang P, Zhang YQ, Wan YH, Lian HL (2018) The inhibition of Microcystis aeruginos by electrochemical oxidation using boron-doped diamond electrode. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:20631–20639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1977-3
Wang Z, Chen Y, Xie P, Shang R, Ma J (2016) Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa by UV-activated persulfate: performance and characteristics. Chem Eng J 300:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.125
Xie C, Lu R, Huang Y, Wang Q, Xu X (2010) Effects of ions and phosphates on alkaline phosphatase activity in aerobic activated sludge system. Bioresour Technol 101:3394–3399
Zhang G, Zhang P, Wang B, Liu H (2006) Ultrasonic frequency effects on the removal of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ultrason Sonochem 13:446–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2005.09.012
Zhao J, Liu X (2013) Organic and inorganic phosphorus uptake by bacteria in a plug-flow microcosm. Front Environ Sci En 7:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0494-3
Zheng L, Ren M, Xie E, Ding A, Liu Y, Deng S, Zhang D (2019a) Roles of phosphorus sources in microbial community assembly for the removal of organic matters and ammonia in activated sludge. Front Microb:10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01023
Zheng M et al (2019b) N2O and NO emission from a biological aerated filter treating coking wastewater: main source and microbial community. J Clean Prod 213:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.182
Funding
This project was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2018YFC1508705-3) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 51509003 and 51909266). Drs. Xiao Zhao and Chaozi Wang are grateful for the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 51809267 and 51909264) and China Agricultural University Startup Fund (grant number: 2018QC169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors En Xie, Fangfang Li, Chaozi Wang, Wei Shi, and Chen Huang aided in preparing/carrying out all the experiments and in drafting the manuscript. En Xie, Xiao Zhao, Keyu Fa, and Dayi Zhang designed and led all the experiments and the construction of the final version of the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vitor Manuel Oliveira Vasconcelos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 145 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, E., Li, F., Wang, C. et al. Roles of sulfur compounds in growth and alkaline phosphatase activities of Microcystis aeruginosa under phosphorus deficiency stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 21533–21541 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08480-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08480-2